吴裕雄--天生自然 Tensorflow卷积神经网络:花朵图片识别
import os
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image, ImageChops
from skimage import color,data,transform,io #获取所有数据文件夹名称
fileList = os.listdir("F:\\data\\flowers")
trainDataList = []
trianLabel = []
testDataList = []
testLabel = [] #读取每一种花的文件
for j in range(len(fileList)):
data = os.listdir("F:\\data\\flowers\\"+fileList[j])
#取每一种花四分之一的数据作为测试数据集
testNum = int(len(data)*0.25)
#把每种花的图片进行testNum次乱序处理
while(testNum>0):
np.random.shuffle(data)
testNum -= 1
#把每种花经过乱序后的四分之三当作训练集
trainData = np.array(data[:-(int(len(data)*0.25))])
#把每种花经过乱序后的四分之一当作测试集
testData = np.array(data[-(int(len(data)*0.25)):])
#从上面选出来的训练集中逐张读取出对应的图片
for i in range(len(trainData)):
#其中这些图片都要满足jpg格式的
if(trainData[i][-3:]=="jpg"):
#读取一张jpg图片
image = io.imread("F:\\data\\flowers\\"+fileList[j]+"\\"+trainData[i])
#把这张图片变成64*64大小的图片
image=transform.resize(image,(64,64))
#保存改变大小的图片到trainDataList列表
trainDataList.append(image)
#保存这张图片的标签到trianLabel列表
trianLabel.append(int(j))
#随机生成一个角度,这个角度的范围在顺时针90度和逆时针90度之间
angle = np.random.randint(-90,90)
#然后把上面那张64*64大小的图片随机旋转angle个角度
image =transform.rotate(image, angle)
#把旋转得到的新图片再变成64*64大小的,因为旋转会改变一张图片的大小
image=transform.resize(image,(64,64))
#把旋转后并且大小是64*64的图片保存到trainDataList列表
trainDataList.append(image)
#把旋转后并且大小是64*64的图片对应的标签保存到trianLabel列表
trianLabel.append(int(j))
#逐张读取每种花的测试图片
for i in range(len(testData)):
#选取的图片要满足jpg格式的
if(testData[i][-3:]=="jpg"):
#读取一张图片
image = io.imread("F:\\data\\flowers\\"+fileList[j]+"\\"+testData[i])
#改变这张图片的大小为64*64
image=transform.resize(image,(64,64))
#把改变后的图片保存到testDataList列表中
testDataList.append(image)
#把这张图片对应的标签保存到testLabel列表中
testLabel.append(int(j))
print("图片数据读取完了...")
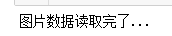
#打印训练集和测试数据集以及它们对应标签的规模
print(np.shape(trainDataList))
print(np.shape(trianLabel))
print(np.shape(testDataList))
print(np.shape(testLabel))
#保存训练集和测试数据集以及它们对应标签到磁盘
np.save("G:\\trainDataList",trainDataList)
np.save("G:\\trianLabel",trianLabel)
np.save("G:\\testDataList",testDataList)
np.save("G:\\testLabel",testLabel)
print("数据处理完了...")

import numpy as np
from keras.utils import to_categorical #将训练数据集和测试数据集对应的标签转变为one-hot编码
trainLabel = np.load("G:\\trianLabel.npy")
testLabel = np.load("G:\\testLabel.npy")
trainLabel_encoded = to_categorical(trainLabel)
testLabel_encoded = to_categorical(testLabel)
np.save("G:\\trianLabel",trainLabel_encoded)
np.save("G:\\testLabel",testLabel_encoded)
print("转码类别写盘完了...")

import random
import numpy as np trainDataList = np.load("G:\\trainDataList.npy")
trianLabel = np.load("G:\\trianLabel.npy")
print("数据加载完了...") trainIndex = [i for i in range(len(trianLabel))]
random.shuffle(trainIndex)
trainData = []
trainClass = []
for i in range(len(trainIndex)):
trainData.append(trainDataList[trainIndex[i]])
trainClass.append(trianLabel[trainIndex[i]])
print("训练数据shuffle完了...") np.save("G:\\trainDataList",trainData)
np.save("G:\\trianLabel",trainClass)
print("训练数据写盘完毕...")

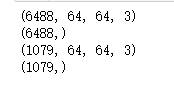
X = np.load("G:\\trainDataList.npy")
Y = np.load("G:\\trianLabel.npy")
print(np.shape(X))
print(np.shape(Y))

import random
import numpy as np testDataList = np.load("G:\\testDataList.npy")
testLabel = np.load("G:\\testLabel.npy") testIndex = [i for i in range(len(testLabel))]
random.shuffle(testIndex)
testData = []
testClass = []
for i in range(len(testIndex)):
testData.append(testDataList[testIndex[i]])
testClass.append(testLabel[testIndex[i]])
print("测试数据shuffle完了...") np.save("G:\\testDataList",testData)
np.save("G:\\testLabel",testClass)
print("测试数据写盘完毕...")

X = np.load("G:\\testDataList.npy")
Y = np.load("G:\\testLabel.npy")
print(np.shape(X))
print(np.shape(Y))
print(np.shape(testData))
print(np.shape(testLabel))
import tensorflow as tf
from random import shuffle INPUT_NODE = 64*64
OUT_NODE = 5
IMAGE_SIZE = 64
NUM_CHANNELS = 3
NUM_LABELS = 5 #第一层卷积层的尺寸和深度
CONV1_DEEP = 16
CONV1_SIZE = 5
#第二层卷积层的尺寸和深度
CONV2_DEEP = 32
CONV2_SIZE = 5
#全连接层的节点数
FC_SIZE = 512 def inference(input_tensor, train, regularizer):
#卷积
with tf.variable_scope('layer1-conv1'):
conv1_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([CONV1_SIZE,CONV1_SIZE,NUM_CHANNELS,CONV1_DEEP],stddev=0.1),name='weight')
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer1/weights1', conv1_weights)
conv1_biases = tf.Variable(tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([CONV1_DEEP])),name="bias")
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer1/bias1', conv1_biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(input_tensor,conv1_weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer1/conv1', conv1)
relu1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv1,conv1_biases))
tf.summary.histogram('ConvLayer1/relu1', relu1)
#池化
with tf.variable_scope('layer2-pool1'):
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu1,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
tf.summary.histogram('ConvLayer1/pool1', pool1)
#卷积
with tf.variable_scope('layer3-conv2'):
conv2_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([CONV2_SIZE,CONV2_SIZE,CONV1_DEEP,CONV2_DEEP],stddev=0.1),name='weight')
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer2/weights2', conv2_weights)
conv2_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([CONV2_DEEP]),name="bias")
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer2/bias2', conv2_biases)
#卷积向前学习
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1,conv2_weights,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
tf.summary.histogram('convLayer2/conv2', conv2)
relu2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv2,conv2_biases))
tf.summary.histogram('ConvLayer2/relu2', relu2)
#池化
with tf.variable_scope('layer4-pool2'):
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu2,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
tf.summary.histogram('ConvLayer2/pool2', pool2)
#变型
pool_shape = pool2.get_shape().as_list()
#计算最后一次池化后对象的体积(数据个数\节点数\像素个数)
nodes = pool_shape[1]*pool_shape[2]*pool_shape[3]
#根据上面的nodes再次把最后池化的结果pool2变为batch行nodes列的数据
reshaped = tf.reshape(pool2,[-1,nodes]) #全连接层
with tf.variable_scope('layer5-fc1'):
fc1_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([nodes,FC_SIZE],stddev=0.1),name='weight')
if(regularizer != None):
tf.add_to_collection('losses',tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.03)(fc1_weights))
fc1_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([FC_SIZE]),name="bias")
#预测
fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshaped,fc1_weights)+fc1_biases)
if(train):
fc1 = tf.nn.dropout(fc1,0.5)
#全连接层
with tf.variable_scope('layer6-fc2'):
fc2_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([FC_SIZE,64],stddev=0.1),name="weight")
if(regularizer != None):
tf.add_to_collection('losses',tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.03)(fc2_weights))
fc2_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64]),name="bias")
#预测
fc2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(fc1,fc2_weights)+fc2_biases)
if(train):
fc2 = tf.nn.dropout(fc2,0.5)
#全连接层
with tf.variable_scope('layer7-fc3'):
fc3_weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64,NUM_LABELS],stddev=0.1),name="weight")
if(regularizer != None):
tf.add_to_collection('losses',tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(0.03)(fc3_weights))
fc3_biases = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([NUM_LABELS]),name="bias")
#预测
logit = tf.matmul(fc2,fc3_weights)+fc3_biases
return logit
import time
import keras
import numpy as np
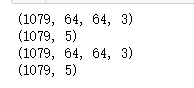
from keras.utils import np_utils X = np.load("G:\\trainDataList.npy")
Y = np.load("G:\\trianLabel.npy")
print(np.shape(X))
print(np.shape(Y))
print(np.shape(testData))
print(np.shape(testLabel)) batch_size = 10
n_classes=5
epochs=16#循环次数
learning_rate=1e-4
batch_num=int(np.shape(X)[0]/batch_size)
dropout=0.75 x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,64,64,3])
y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,n_classes])
# keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
#加载测试数据集
test_X = np.load("G:\\testDataList.npy")
test_Y = np.load("G:\\testLabel.npy")
back = 64
ro = int(len(test_X)/back) #调用神经网络方法
pred=inference(x,1,"regularizer")
cost=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred,labels=y)) # 三种优化方法选择一个就可以
optimizer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cost)
# train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cost)
# train_step = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(0.001,0.9).minimize(cost) #将预测label与真实比较
correct_pred=tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1),tf.argmax(y,1))
#计算准确率
accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred,tf.float32))
merged=tf.summary.merge_all()
#将tensorflow变量实例化
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
start_time = time.time() with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
#保存tensorflow参数可视化文件
writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('F:/Flower_graph', sess.graph)
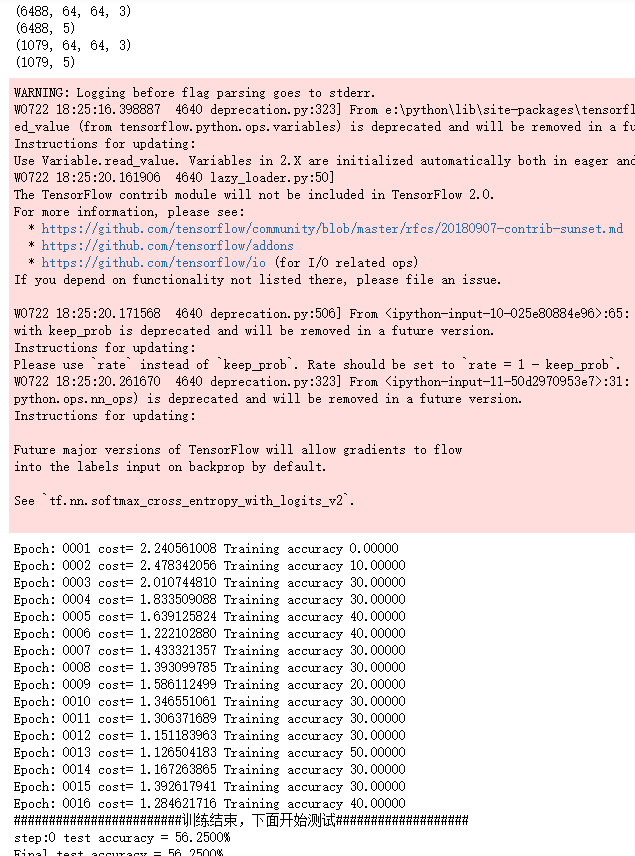
for i in range(epochs):
for j in range(batch_num):
offset = (j * batch_size) % (Y.shape[0] - batch_size)
# 准备数据
batch_data = X[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
batch_labels = Y[offset:(offset + batch_size), :]
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x:batch_data,y:batch_labels})
result=sess.run(merged, feed_dict={x:batch_data,y:batch_labels})
writer.add_summary(result, i)
loss,acc = sess.run([cost,accuracy],feed_dict={x:batch_data,y:batch_labels})
print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (i+1),"cost=", "{:.9f}".format(loss),"Training accuracy","{:.5f}".format(acc*100))
writer.close()
print("########################训练结束,下面开始测试###################")
for i in range(ro):
s = i*back
e = s+back
test_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:test_X[s:e],y:test_Y[s:e]})
print("step:%d test accuracy = %.4f%%" % (i,test_accuracy*100))
print("Final test accuracy = %.4f%%" % (test_accuracy*100)) end_time = time.time()
print('Times:',(end_time-start_time))
print('Optimization Completed')

吴裕雄--天生自然 Tensorflow卷积神经网络:花朵图片识别的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:使用TFLearn处理MNIST数据集实现LeNet-5模型
# 1. 通过TFLearn的API定义卷机神经网络. import tflearn import tflearn.datasets.mnist as mnist from tflearn.layer ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:使用TensorFlow-Slim处理MNIST数据集实现LeNet-5模型
# 1. 通过TensorFlow-Slim定义卷机神经网络 import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow.contrib. ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Estimator-自定义模型
# 1. 自定义模型并训练. import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist i ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Estimator-DNNClassifier
# 1. 模型定义. import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist impor ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Keras-TensorFlow API
# 1. 模型定义. import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist_ ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Keras-RNN
# 1. 数据预处理. from keras.layers import LSTM from keras.datasets import imdb from keras.models import S ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Keras-CNN
# 1. 数据预处理 import keras from keras import backend as K from keras.datasets import mnist from keras.m ...
- 吴裕雄 python 神经网络——TensorFlow 卷积神经网络水果图片识别
#-*- coding:utf- -*- import time import keras import skimage import numpy as np import tensorflow as ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然TensorFlow高层封装:Keras-多输入输出
# 1. 数据预处理. import keras from keras.models import Model from keras.datasets import mnist from keras. ...
随机推荐
- RegressionTree(回归树)
1.概述 回归树就是用树模型做回归问题,每一片叶子都输出一个预测值.预测值一般是该片叶子所含训练集元素输出的均值, 即
- Methyl-SeqDNA的甲基化图谱|DNase I-Seq|ChIP-Seq|3C-Seq|
生物医学大数据 Methyl-SeqDNA的甲基化图谱 DNase I-Seq全基因组染色质DNA的开放程度.非基因编码区的调控元件的分布 DNase I高敏感位点:基因处于转录活性状态时,其染色质结 ...
- python-day4爬虫基础之正则表达式
正则表达式:(字符串匹配) 使用单个字符串来描述匹配一系列符合某个句法规则的字符串 是对字符串操作的一种逻辑公式 应用场景:处理文本和数据 正则表达式过程:依次拿出表达式和文本中的字符比较,如果每一个 ...
- Python3.7离线安装Requests无法正常使用问题
继续搬砖...... 春节前,克服了网络受限的情况下离线安装Python库文件问题,传送门如下: https://www.cnblogs.com/mrgavin/p/12202214.html htt ...
- python获取当前的日期和时间
import datetime import time print ("格式参数:") print (" %a 星期几的简写") print (" % ...
- 2019ICPC 上海网络赛 L. Digit sum(二维树状数组+区间求和)
https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/41422 题目大意: 给出n和b,求1到n,各数在b进制下各位数之和的总和. 直接暴力模拟,TLE.. 没想到是要打表...还是太菜了. # ...
- shell的集合运算
用cat,sort,uniq命令实现文件行的交集 .并集.补集 交集 $F_1 \cap F_2 $ cat f1 f2 | sort | uniq -d 并集 $F_1 \cup F_2 $ cat ...
- TPO5-2 The Origin of Pacific Island People
Contrary to the arguments of some (that much of the pacific was settled by Polynesians accidentally ...
- 达梦、oracel、mysql数据库兼容
联合表更新sql语句: 只支持mysql.oracle,不支持达梦 update to_pub_report a, to_pub_rec_process b set a.Satisfy_ID , a. ...
- F. Maximum Weight Subset(贪心or树形dp解法)
题:https://codeforces.com/contest/1249/problem/F 题意:给一颗树,边权为1,节点有点权,问取到一个点集,俩俩之间路径超过k,是点权和最大 思路:贪心地取点 ...
