004 Android XML文件常用五大页面布局方式
1.线性布局(LinearLayout)最常用
<1>使用线性布局,首先在xml文件中修改布局为LinearLayout

修改完成后,可在Component Tree中看见如下内容:
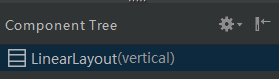
<2>点击LinearLayout,可在右侧的Attributes(属性)中进一步设置是水平放置或者垂直放置
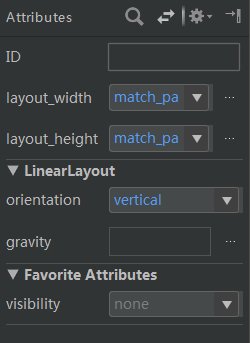
注意:每个控件的大小其实还是需要设置的,即需要设置布局高度(layout_width)和布局宽度(layout_height),默认采用match_parent
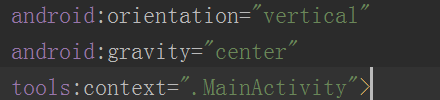
<3>对齐方式设置:即可以在xml文件中输入
android:gravity="center" 设置该线性布局内的组件居中放置
<4> 控件属性设置(attribute)
Plain Test控件设置提示字符
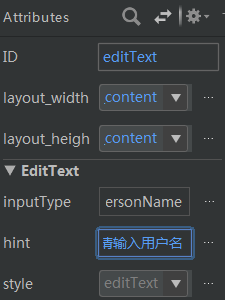
方法:在Attributes中的hint中设置提示字符
<5>设置组件的大小为自适应大小
必须删除xml文件中组件属性里的 android:layout_weight="1"
<6>设置控件的对齐方式、边距
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"> <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_marginLeft="80dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView" />
</LinearLayout>
(1)在父容器的线性布局中设置属性
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
使得,该线性布局内的所有组件全都水平居中。
(2)在子容器TextView中设置属性
android:layout_marginLeft="80dp"
使得,这个TextView组件在水平居中的基础上,向右移动的80dp(即左边距为80dp)
<7>设置字体的大小、颜色
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_login"
android:layout_marginLeft="80dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#044BA3"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:text="TextView" />
(1)在组件中添加
android:textColor="#044BA3"
设置字体的颜色。
(2)在组件中添加
android:textSize="20dp"
设置字体的大小。
<8>设置控件的id
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_login"
android:layout_marginLeft="80dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView" />
注意:设置组件的id的命名方法为提取组件的两个驼峰+组件实际功能(例如:TextView---> 变为tv_login)
2.表格布局(TableLayout)
注意:表格布局不推荐使用。
<1>使用表格布局,首先在xml文件中修改布局为TableLayout
<2>外部图片导入工程后的存放位置
任选project 工程名-->app-->src-->main下的一个文件夹
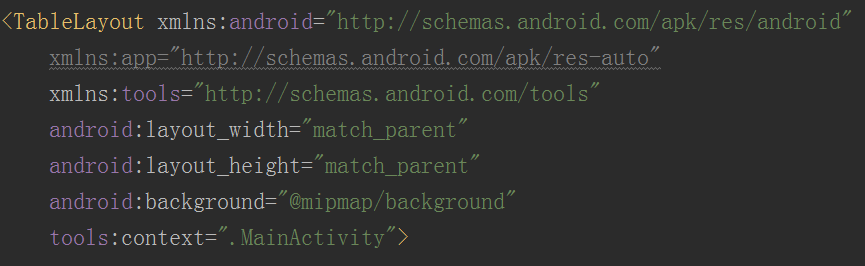
<3>app设置背景图片
在xml文件中输入 android:background="@mipmap/background"
<4>图片组件
palatte-->widgets--->imageview
多个图片设置对齐方式
选择父容器,选择对齐方式(orientation、gratity)
TableLayout布局使用案例(test02):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/background"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> <TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="0.5"> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@mipmap/blockbg_big"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="2019/3/2" />
</LinearLayout> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@mipmap/blockbg_big"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="horizontal"> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView4"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/img01" /> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView6"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/img07" /> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView5"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/img06" /> </LinearLayout>
</TableRow> <TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="@mipmap/blockbg_big"
android:orientation="horizontal"> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView9"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/img05" /> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView8"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/img03a" /> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView7"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/img02" />
</LinearLayout> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="@mipmap/blockbg_big"
android:orientation="horizontal"> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView12"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/img07" /> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView11"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/ic_launcher" /> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView10"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/img03a" />
</LinearLayout>
</TableRow> <TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="@mipmap/blockbg_big"
android:orientation="horizontal"> <ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView13"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/email" />
</LinearLayout>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
效果图为:
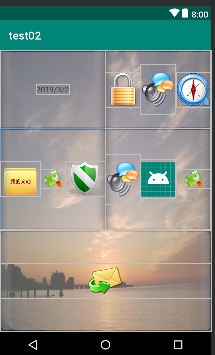
3 约束布局(ConstraintLayout)
<1>图片组件(imageview)分别与约束布局的父容器的上下左右对齐
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
<2>imageview 组件与imageview 组件可以在design中采用拖拽的方式使其对齐(注意:下图的连线方式)
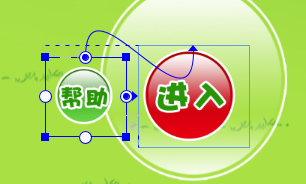
注意:约束布局(ConstraintLayout)最大的特点是可以以拖拽的方式固定组件的位置
案例:test03
4 相对布局(RelativeLayout) 常用
下面是RelativeLayout各个属性 android:layout_above="@id/xxx" --将控件置于给定ID控件之上 android:layout_below="@id/xxx" --将控件置于给定ID控件之下 android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/xxx" --将控件的右边缘和给定ID控件的左边缘对齐 android:layout_toRightOf="@id/xxx" --将控件的左边缘和给定ID控件的右边缘对齐 android:layout_alignLeft="@id/xxx" --将控件的左边缘和给定ID控件的左边缘对齐 android:layout_alignTop="@id/xxx" --将控件的上边缘和给定ID控件的上边缘对齐 android:layout_alignRight="@id/xxx" --将控件的右边缘和给定ID控件的右边缘对齐 android:layout_alignBottom="@id/xxx" --将控件的底边缘和给定ID控件的底边缘对齐 android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" --将控件的左边缘和父控件的左边缘对齐 android:layout_alignParentTop="true" --将控件的上边缘和父控件的上边缘对齐 android:layout_alignParentRight="true" --将控件的右边缘和父控件的右边缘对齐 android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" --将控件的底边缘和父控件的底边缘对齐 android:layout_centerInParent="true" --将控件置于父控件的中心位置 android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" --将控件置于水平方向的中心位置 android:layout_centerVertical="true" --将控件置于垂直方向的中心位置
(1)使用小案例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".UserGuideActivity"> <Button
android:id="@+id/bt_userguide_start"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="60dp"
android:text="开始体验"/>
</RelativeLayout>
(2)效果图

(3)代码分析
<1>设置按钮距离底部60dp
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="60dp"
<2>水平方向居中
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
5、网格布局(GridLayout)
典型应用:计算器的布局
源码案例:test16
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:columnCount="4"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:rowCount="5"
android:useDefaultMargins="true"
tools:context=".MainActivity"> <Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="0"
android:text="1" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="1"
android:text="2" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="2"
android:text="3" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="3"
android:text="+" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_column="0"
android:text="4" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_column="1"
android:text="5" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button7"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_column="2"
android:text="6" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button8"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_column="3"
android:text="-" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button9"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_column="0"
android:text="7" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button10"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_column="1"
android:text="8" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button11"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_column="2"
android:text="9" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button12"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_column="3"
android:text="*" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button13"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="3"
android:layout_column="0"
android:text="0" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button14"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="3"
android:layout_column="1"
android:layout_columnSpan="2"
android:layout_gravity="fill_horizontal"
android:text="删除" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button15"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="3"
android:layout_column="3"
android:text="/" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button18"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="4" android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_columnSpan="2"
android:layout_gravity="fill_horizontal"
android:text="clear" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/button20"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_row="4"
android:layout_column="2"
android:layout_columnSpan="2"
android:layout_gravity="fill_horizontal"
android:text="Button" /> </GridLayout>
004 Android XML文件常用五大页面布局方式的更多相关文章
- maven(4)------maven核心pom.xml文件常用元素分析
在maven项目中,pom文件是核心文件 pom.xml: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <p ...
- 《!--suppress ALL --> 在Android XML 文件中的用途是什么?
<!--suppress ALL --> 在Android XML 文件中的用途是什么? 警告一次又一次地出现在谷歌地图的 XML 文件中,但是当我使用时,所有警告都被禁用.那么压制所有评 ...
- 006 Android XML 文件布局及组件属性设置技巧汇总
1.textview 组件文本实现替换(快速实现字符资源的调用) android 应用资源位置在 project(工程名)--->app--->res--->values 在stri ...
- 【Android】纯代码创建页面布局(含异步加载图片)
开发环境:macOS 10.12 + Android Studio 2.2,MinSDK Android 5.1 先看看总体效果 本示例是基于Fragment进行的,直接上代码: [界面结构] 在 F ...
- android xml文件
一.布局文件:在layout目录下,使用比较广泛: 我们可以为应用定义两套或多套布局,例如:可以新建目录layout_land(代表手机横屏布局),layout_port(代表手机竖屏布局),系统会根 ...
- Android XML文件解析
在Android平台上可以使用Simple API for XML(SAX) . Document Object Model(DOM)和Android附带的pull解析器解析XML文件. 下面是本例子 ...
- [android] xml文件的序列化
生成xml文件,模拟备份短信,创建短信的业务bean,创建一个domain的包放业务bean,这个业务bean里面,定义成员属性,生成get set方法,生成有参和无参的构造方法. 生成随机数,实例化 ...
- Android--->LinearLayout页面布局方式
main.xml布局方式 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns ...
- Web页面布局方式小结
Web页面是由块元素组成的,正常情况下块元素一个个按垂直方向排布,构成了页面.可是这样的主要的布局方式绝大多时候不能满足我们的需求,所以各种布局方式应运而生,本文就对这些布局方式做个小结. 1.元素漂 ...
随机推荐
- Python3.7安装PyQt5的方法
一.系统环境 操作系统:Win7 64位 Python Version:3.7 二.安装参考 方法1:pip install PyQt5 方法2:下载whl安装包安装 a.下载网址:https://p ...
- Python 安装selenium
一.报错信息 No module named 'selenium' 二.系统环境 操作系统:Win10 64位 Python版本:Python 3.7.0 三.安装参考 1.使用pip安装seleni ...
- rpmbuild spec 打包jar变小了、设置禁止压缩二进制文件Disable Binary stripping in rpmbuild
Disable Binary stripping in rpmbuild 摘自:http://livecipher.blogspot.com/2012/06/disable-binary-stripp ...
- Part10-C语言环境初始化-C与汇编混合编程lesson4
1.为什么要混合编程 汇编语言:执行效率高:编写繁琐: 执行效率高:能够更直接地控制处理器. c语言:可读性强,移植性好,调试方便. 1.汇编调用c函数 2.c调用汇编函数 汇编语言定义的函数(标号) ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(40):Validate Entity
Validate Entity You can write custom server side validation for any entity. To accomplish this, over ...
- hdu 4279 Number(G++提交)
打表找规律: #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> #define N 250 bool judge(int i,int j) { ;k< ...
- Visual Studio 2010调试本地 IIS 站点
点击vs的Debug-Attach to Process选中 w3wp.exe,然后点击Attach, vs便进入debug模式.
- Regist&Login
关于注册页面和登录页面的业务流程 form表单中确定action提交地址 method 确定提交的方法--->写出相对应的Servlet,假如接受的数据不多 ,那么用 String userna ...
- jQuery 隐藏和显示
jQuery 隐藏和显示 通过 hide() 和 show() 两个函数,jQuery 支持对 HTML 元素的隐藏和显示: 实例 $("#hide").click(functio ...
- iOS play video
iOS: How to use MPMoviePlayerController up vote6down votefavorite 3 I've created a blank project (iO ...
