HDU 1693 Eat the Trees(插头DP,入门题)
So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
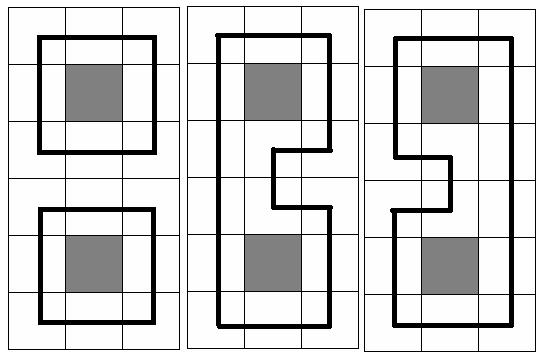
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL; const int MAXN = ; int mat[MAXN][MAXN];
LL dp[MAXN][MAXN][ << MAXN];
int n, m, T; LL solve() {
memset(dp, , sizeof(dp));
dp[][m][] = ;
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
for(int j = ; j < ( << m); ++j) dp[i][][j << ] = dp[i - ][m][j];
for(int k = ; k <= m; ++k) {
for(int state = ; state < ( << (m + )); ++state) {
int y = << k, x = y >> ;
if(mat[i][k]) {
if((state & x) && (state & y)) {
dp[i][k][state] = dp[i][k - ][state - x - y];
} else if((state & x) == && (state & y) == ) {
dp[i][k][state] = dp[i][k - ][state + x + y];
} else dp[i][k][state] = dp[i][k - ][state ^ x ^ y] + dp[i][k - ][state];
} else {
if((state & x) == && (state & y) == ) {
dp[i][k][state] = dp[i][k - ][state];
} else dp[i][k][state] = ;
}
}
}
}
return dp[n][m][];
} int main() {
scanf("%d", &T);
for(int t = ; t <= T; ++t) {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i)
for(int j = ; j <= m; ++j) scanf("%d", &mat[i][j]);
printf("Case %d: There are %I64d ways to eat the trees.\n", t, solve());
}
}
代码(0MS)(hash)(下面代码是lld的……):
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL; const int MAXH = ;
const int SIZEH = ; struct hash_map {
int head[SIZEH];
int next[MAXH], state[MAXH];
LL val[MAXH];
int size; void init() {
memset(head, -, sizeof(head));
size = ;
} void insert(int st, LL sv) {
int h = st % SIZEH;
for(int p = head[h]; ~p; p = next[p]) {
if(state[p] == st) {
val[p] += sv;
return ;
}
}
state[size] = st; val[size] = sv; next[size] = head[h]; head[h] = size++;
}
} hashmap[]; int getB(int state, int i) {
return (state >> i) & ;
} void setB(int &state, int i, int val) {
state = (state & ~( << i)) | (val << i);
} int mat[][];
int n, m, T;
hash_map *cur, *last; void update(int state, LL val, int x, int y) {
int left = getB(state, y);
int up = getB(state, y + );
if(mat[x][y] == ) {
if(left == && up == ) cur->insert(state, val);
return ;
}
if(left == && up == ) {
if(x < n - && y < m - ) {
int newState = state;
setB(newState, y, );
setB(newState, y + , );
cur->insert(newState, val);
}
} else if(left == || up == ) {
if(x < n - ) {
int newState = state;
setB(newState, y, );
setB(newState, y + , );
cur->insert(newState, val);
}
if(y < m - ) {
int newState = state;
setB(newState, y, );
setB(newState, y + , );
cur->insert(newState, val);
}
} else {
int newState = state;
setB(newState, y, );
setB(newState, y + , );
cur->insert(newState, val);
}
} LL solve() {
cur = hashmap, last = hashmap + ;
last->init();
last->insert(, );
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
int sz = last->size;
for(int k = ; k < sz; ++k) last->state[k] <<= ;
for(int j = ; j < m; ++j) {
cur->init();
sz = last->size;
for(int k = ; k < sz; ++k)
update(last->state[k], last->val[k], i, j);
swap(cur, last);
}
}
for(int k = ; k < last->size; ++k)
if(last->state[k] == ) return last->val[k];
return ;
} int main() {
scanf("%d", &T);
for(int t = ; t <= T; ++t) {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = ; i < n; ++i)
for(int j = ; j < m; ++j) scanf("%d", &mat[i][j]);
printf("Case %d: There are %lld ways to eat the trees.\n", t, solve());
}
}
HDU 1693 Eat the Trees(插头DP,入门题)的更多相关文章
- hdu 1693 Eat the Trees——插头DP
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1693 第一道插头 DP ! 直接用二进制数表示状态即可. #include<cstdio> # ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees ——插头DP
[题目分析] 吃树. 直接插头DP,算是一道真正的入门题目. 0/1表示有没有插头 [代码] #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #inc ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees(插头DP)
题目链接 USACO 第6章,第一题是一个插头DP,无奈啊.从头看起,看了好久的陈丹琦的论文,表示木看懂... 大体知道思路之后,还是无法实现代码.. 此题是插头DP最最简单的一个,在一个n*m的棋盘 ...
- hdu1693 Eat the Trees [插头DP经典例题]
想当初,我听见大佬们谈起插头DP时,觉得插头DP是个神仙的东西. 某大佬:"考场见到插头DP,直接弃疗." 现在,我终于懂了他们为什么这么说了. 因为-- 插头DP很毒瘤! 为什么 ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees(插头DP、棋盘哈密顿回路数)+ URAL 1519 Formula 1(插头DP、棋盘哈密顿单回路数)
插头DP基础题的样子...输入N,M<=11,以及N*M的01矩阵,0(1)表示有(无)障碍物.输出哈密顿回路(可以多回路)方案数... 看了个ppt,画了下图...感觉还是挺有效的... 参考 ...
- HDU1693 Eat the Trees 插头dp
原文链接http://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/8433484.html 题目传送门 - HDU1693 题意概括 多回路经过所有格子的方案数. 做法 最基础的插头 ...
- hdu 1693 : Eat the Trees 【插头dp 入门】
题目链接 题意: 给出一个n*m大小的01矩阵,在其中画线连成封闭图形,其中对每一个值为1的方格,线要恰好穿入穿出共两次,对每一个值为0的方格,所画线不能经过. 参考资料: <基于连通性状态压缩 ...
- HDU - 1693 Eat the Trees(多回路插头DP)
题目大意:要求你将全部非障碍格子都走一遍,形成回路(能够多回路),问有多少种方法 解题思路: 參考基于连通性状态压缩的动态规划问题 - 陈丹琦 下面为代码 #include<cstdio> ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees (插头DP)
题意:给一个n*m的矩阵,为1时代表空格子,为0时代表障碍格子,问如果不经过障碍格子,可以画一至多个圆的话,有多少种方案?(n<12,m<12) 思路: 这题不需要用到最小表示法以及括号表 ...
随机推荐
- 使用redux代码文件的组织方式
从架构触发,开始一个新应用的时候,代码文件的组织方式一定要考虑好 如果之前使用过mvc的框架那么对按角色组织方式一定不陌生 角色组织方式 reducer/ todoReducer.js filterR ...
- 关于Echarts的原生js获取DOM元素与动态加载DOM元素的冲突问题
1.前言: 最近在做的看板项目,因为需要循环加载后台数据,并且用Echarts做数据呈现,所以jQuery和angular等库统统靠边站,Echarts用的是原生js获取DOM元素,至于诸多不兼容等深 ...
- ZLG zigbee 虚拟串口配置
一.设置网关工作模式: 在ZNetCom Utility工具中,将设置网关工作模式为 Real COM 模式 启动 ZNetCom Utility 搜索设备 获得设备信息 修改工作模式为:real c ...
- js实现图片点击弹出放大效果
点击图片,显示蒙板,放大图片的简单案例 HTML代码: <div> <img height=" src="https://img-blog.csdn.net/20 ...
- Linux 下文件压缩与解压命令详解
tar 命令 -c 建立压缩档案 -x 解压 -t 查看内容 -r 向压缩归档文件末尾追加文件 -u 更新原压缩包中的文件 这五个是独立的命令,压缩解压都要用到其中一个,可以和别的命令连用但只能用其中 ...
- C#中委托和代理的深刻理解(转载)
在写代码的过程中遇到了一个问题,就是" .net CallbackOnCollectedDelegate 垃圾回收问题. " 使用全局钩子的时候出现: globalKeyboard ...
- phpredis命令
<?php //redis //检查一个扩展是否已经加载.大小写不敏感. if (!function_exists('redis')) { echo '不支持 redis'; return ; ...
- WordPress博客插件程序:搜索下拉框openSug
百度搜索框下拉提示Wordpress组插件. 下载地址:https://www.opensug.org/faq/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/opensug.wordpress ...
- flask 中访问时后台错误 error: [Errno 32] Broken pipe
解决办法:app.run(threaded=True) 个人理解:flask默认单线程,访问一个页面时会访问到很多页面,比如一些图片,加入参数使其为多线程
- narcissus
public class narcissus { public static void main(String args[]) { long u=0,t=0,h=0,y=0,k=0; for(long ...