PYTHON3 RE正则表达:
The special characters are:
"." Matches any character except a newline.
"^" Matches the start of the string.
"$" Matches the end of the string or just before the newline at
the end of the string.
"*" Matches 0 or more (greedy) repetitions of the preceding RE.
Greedy means that it will match as many repetitions as possible.
"+" Matches 1 or more (greedy) repetitions of the preceding RE.
"?" Matches 0 or 1 (greedy) of the preceding RE.
*?,+?,?? Non-greedy versions of the previous three special characters.
{m,n} Matches from m to n repetitions of the preceding RE.
{m,n}? Non-greedy version of the above.
"\\" Either escapes special characters or signals a special sequence.
[] Indicates a set of characters.
A "^" as the first character indicates a complementing set.
"|" A|B, creates an RE that will match either A or B.
(...) Matches the RE inside the parentheses.
The contents can be retrieved or matched later in the string.
(?aiLmsux) Set the A, I, L, M, S, U, or X flag for the RE (see below).
(?:...) Non-grouping version of regular parentheses.
(?P<name>...) The substring matched by the group is accessible by name.
(?P=name) Matches the text matched earlier by the group named name.
(?#...) A comment; ignored.
(?=...) Matches if ... matches next, but doesn't consume the string.
(?!...) Matches if ... doesn't match next.
(?<=...) Matches if preceded by ... (must be fixed length).
(?<!...) Matches if not preceded by ... (must be fixed length).
(?(id/name)yes|no) Matches yes pattern if the group with id/name matched,
the (optional) no pattern otherwise.
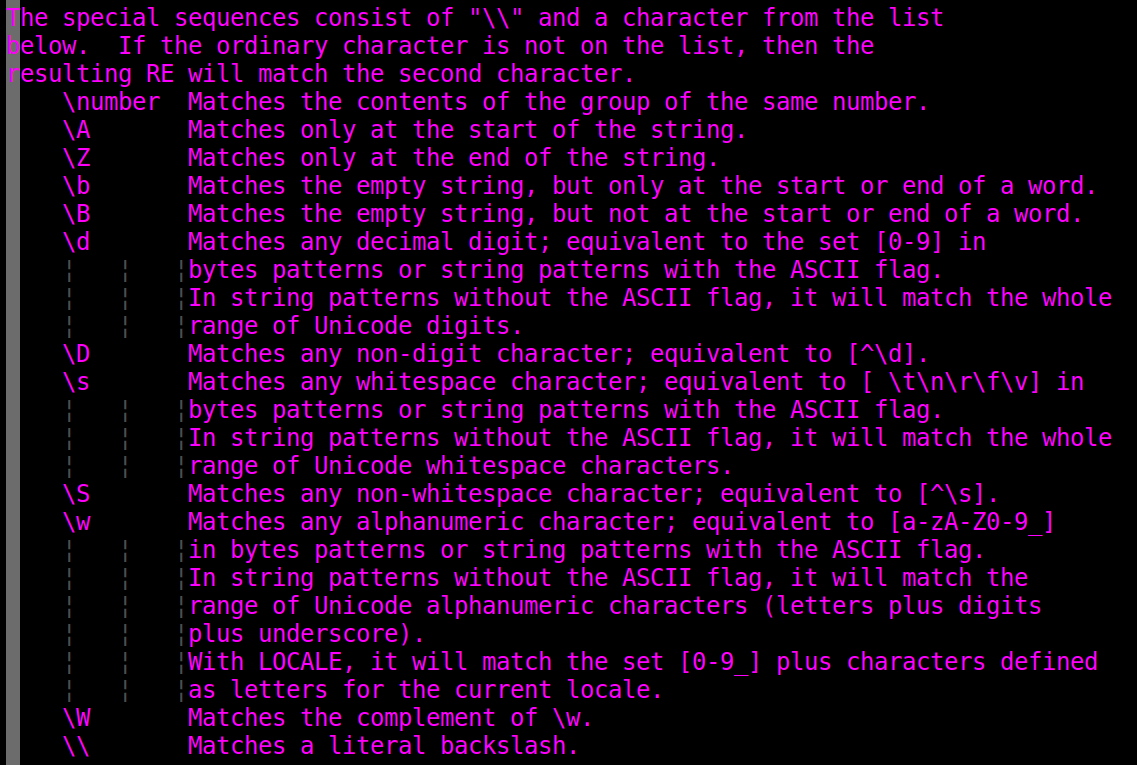
The special sequences consist of "\\" and a character from the list
below. If the ordinary character is not on the list, then the
resulting RE will match the second character.
\number Matches the contents of the group of the same number.
\A Matches only at the start of the string.
\Z Matches only at the end of the string.
\b Matches the empty string, but only at the start or end of a word.
\B Matches the empty string, but not at the start or end of a word.
\d Matches any decimal digit; equivalent to the set [0-9] in
bytes patterns or string patterns with the ASCII flag.
In string patterns without the ASCII flag, it will match the whole
range of Unicode digits.
\D Matches any non-digit character; equivalent to [^\d].
\s Matches any whitespace character; equivalent to [ \t\n\r\f\v] in
bytes patterns or string patterns with the ASCII flag.
In string patterns without the ASCII flag, it will match the whole
range of Unicode whitespace characters.
\S Matches any non-whitespace character; equivalent to [^\s].
\w Matches any alphanumeric character; equivalent to [a-zA-Z0-9_]
in bytes patterns or string patterns with the ASCII flag.
In string patterns without the ASCII flag, it will match the
range of Unicode alphanumeric characters (letters plus digits
plus underscore).
With LOCALE, it will match the set [0-9_] plus characters defined
as letters for the current locale.
\W Matches the complement of \w.
\\ Matches a literal backslash.
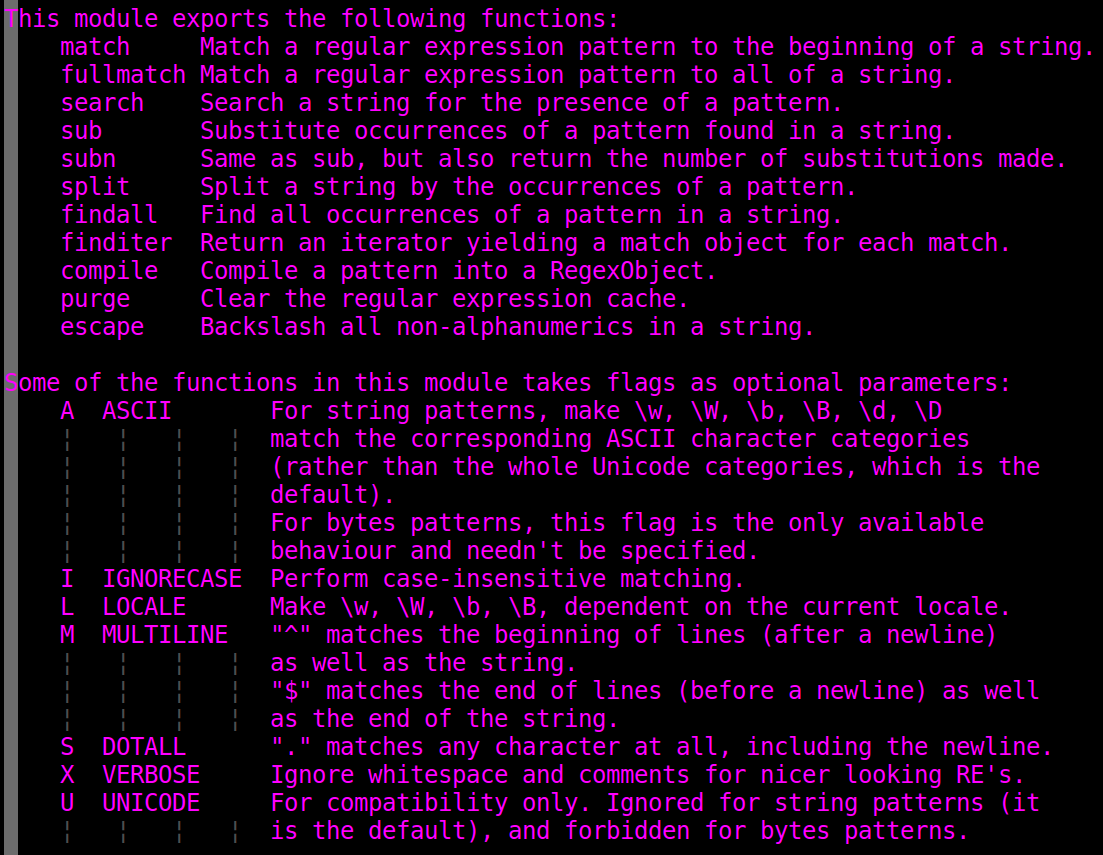
This module exports the following functions:
match Match a regular expression pattern to the beginning of a string.
fullmatch Match a regular expression pattern to all of a string.
search Search a string for the presence of a pattern.
sub Substitute occurrences of a pattern found in a string.
subn Same as sub, but also return the number of substitutions made.
split Split a string by the occurrences of a pattern.
findall Find all occurrences of a pattern in a string.
finditer Return an iterator yielding a match object for each match.
compile Compile a pattern into a RegexObject.
purge Clear the regular expression cache.
escape Backslash all non-alphanumerics in a string.
Some of the functions in this module takes flags as optional parameters:
A ASCII For string patterns, make \w, \W, \b, \B, \d, \D
match the corresponding ASCII character categories
(rather than the whole Unicode categories, which is the
default).
For bytes patterns, this flag is the only available
behaviour and needn't be specified.
I IGNORECASE Perform case-insensitive matching.
L LOCALE Make \w, \W, \b, \B, dependent on the current locale.
M MULTILINE "^" matches the beginning of lines (after a newline)
as well as the string.
"$" matches the end of lines (before a newline) as well
as the end of the string.
S DOTALL "." matches any character at all, including the newline.
X VERBOSE Ignore whitespace and comments for nicer looking RE's.
U UNICODE For compatibility only. Ignored for string patterns (it
is the default), and forbidden for bytes patterns.
# --------------------------------------------------------------------
# public interface
def match(pattern, string, flags=0):
"""Try to apply the pattern at the start of the string, returning
a match object, or None if no match was found."""
return _compile(pattern, flags).match(string)
def fullmatch(pattern, string, flags=0):
"""Try to apply the pattern to all of the string, returning
a match object, or None if no match was found."""
return _compile(pattern, flags).fullmatch(string)
def search(pattern, string, flags=0):
"""Scan through string looking for a match to the pattern, returning
a match object, or None if no match was found."""
return _compile(pattern, flags).search(string)
def sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0):
"""Return the string obtained by replacing the leftmost
non-overlapping occurrences of the pattern in string by the
replacement repl. repl can be either a string or a callable;
if a string, backslash escapes in it are processed. If it is
a callable, it's passed the match object and must return
a replacement string to be used."""
return _compile(pattern, flags).sub(repl, string, count)
def subn(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0):
"""Return a 2-tuple containing (new_string, number).
new_string is the string obtained by replacing the leftmost
non-overlapping occurrences of the pattern in the source
string by the replacement repl. number is the number of
substitutions that were made. repl can be either a string or a
callable; if a string, backslash escapes in it are processed.
If it is a callable, it's passed the match object and must
return a replacement string to be used."""
return _compile(pattern, flags).subn(repl, string, count)
def split(pattern, string, maxsplit=0, flags=0):
"""Split the source string by the occurrences of the pattern,
returning a list containing the resulting substrings. If
capturing parentheses are used in pattern, then the text of all
groups in the pattern are also returned as part of the resulting
list. If maxsplit is nonzero, at most maxsplit splits occur,
and the remainder of the string is returned as the final element
of the list."""
return _compile(pattern, flags).split(string, maxsplit)
def findall(pattern, string, flags=0):
"""Return a list of all non-overlapping matches in the string.
If one or more capturing groups are present in the pattern, return
a list of groups; this will be a list of tuples if the pattern
has more than one group.
Empty matches are included in the result."""
return _compile(pattern, flags).findall(string)
def finditer(pattern, string, flags=0):
"""Return an iterator over all non-overlapping matches in the
string. For each match, the iterator returns a match object.
Empty matches are included in the result."""
return _compile(pattern, flags).finditer(string)
def compile(pattern, flags=0):
"Compile a regular expression pattern, returning a pattern object."
return _compile(pattern, flags)
def purge():
"Clear the regular expression caches"
_cache.clear()
_cache_repl.clear()
def template(pattern, flags=0):
"Compile a template pattern, returning a pattern object"
return _compile(pattern, flags|T)
re.py

PYTHON3 RE正则表达:的更多相关文章
- 正则表达示 for Python3
前情提要 从大量的文字内容中找到自己想要的东西,正则似乎是最好的方法.也是写爬虫不可缺少的技能.所以,别墨迹了赶紧好好学吧! 教程来自http://www.runoob.com/python3/pyt ...
- Javascript正则构造函数与正则表达字面量&&常用正则表达式
本文不讨论正则表达式入门,即如何使用正则匹配.讨论的是两种创建正则表达式的优劣和一些细节,最后给出一些常用正则匹配表达式. Javascript中的正则表达式也是对象,我们可以使用两种方法创建正则表达 ...
- HttpGet协议与正则表达
使用HttpGet协议与正则表达实现桌面版的糗事百科 写在前面 最近在重温asp.net,找了一本相关的书籍.本书在第一章就讲了,在不使用浏览器的情况下生成一个web请求,获取服务器返回的内容.于 ...
- js正则表达test、exec和match的区别
test的用法和exec一致,只不过返回值是 true false. 以前用js很少用到js的正则表达式,即使用到了,也是诸如邮件名称之类的判断,网上代码很多,很少有研究,拿来即用. 最近开发遇到一些 ...
- Python之面向对象和正则表达(代数运算和自动更正)
面向对象 一.概念解释 面对对象编程(OOP:object oriented programming):是一种程序设计范型,同时也是一种程序开发的方法,实现OOP的程序希望能够在程序中包含各种独立而又 ...
- JS写法 数值与字符串的相互转换 取字符中的一部分显示 正则表达规则
http://www.imooc.com/article/15885 正则表达规则 <script type="text/javascript"> </scrip ...
- shell正则表达
shell正则表达 .*和.?的比较: 比如说匹配输入串A: 101000000000100 使用 1.*1 将会匹配到1010000000001,匹配方法:先匹配至输入串A的最后, 然后向前匹配,直 ...
- python 正则表达提取方法 (提取不来的信息print不出来 加个输出type 再print信息即可)
1,正则表达提取 (findall函数提取) import re a= "<div class='content'>你大爷</div>"x=re.finda ...
- grep 正则表达
常见的 grep 正则表达参数 -c # 显示匹配到得行的数目,不显示内容 -h # 不显示文件名 -i # 忽略大小写 -l # 只列出匹配行所在文件的文件名 -n # 在每一行中加上相对行号 -s ...
随机推荐
- spring boot容器启动详解
目录 一.前言 二.容器启动 三.总结 =======正文分割线====== 一.前言 spring cloud大行其道的当下,如果不了解基本原理那么是很纠结的(看见的都是约定大于配置,但是原理呢?为 ...
- 关于layer的坑
真是自己给自己挖坑,坑死人不偿命啊. 在用layui开发时,遇到这种情况,点击按钮出现一个弹出层,然而我不是用button按钮去实现的,而是用a标签做的,本来a标签也是可以实现的,在这里我无形中给自己 ...
- Spark算子--mapPartitions和mapPartitionsWithIndex
mapPartitions--Transformation类算子 代码示例 result mapPartitionsWithIndex--Transformation类算子 代码示例 result ...
- vueThink权限配置
vueThink中的 admin 默认是展示所有权限,其他的权限组用户就要自己去特定进行配置 http://vuedemo.cn:8181 这里我是默认本地配置了apache到 php\public ...
- LAMP和LNMP,你更愿意选择谁,为什么?
https://www.zhihu.com/question/19697826 http://www.simongong.net lamp 的全称是linux + apache + mysql +ph ...
- 利用 HTML5 WebGL 构建的 3D 拓扑图
现在,3D 模型已经用于各种不同的领域.在医疗行业使用它们制作器官的精确模型:电影行业将它们用于活动的人物.物体以及现实电影:视频游戏产业将它们作为计算机与视频游戏中的资源:在科学领域将它们作为化合物 ...
- Angular 4+ HttpClient
个人博客迁移至 http://www.sulishibaobei.com 处: 这篇,算是上一篇Angular 4+ Http的后续: Angular 4.3.0-rc.0 版本已经发布
- JAVA异步加回调的例子
package com.sunchao.callback; /** * callback interface * @author Administrator * */ public interface ...
- python 与rabbitmq
一.rabbitmq简介.安装 简介: MQ全称为Message Queue, 消息队列(MQ)是一种应用程序对应用程序的通信方法.应用程序通过读写出入队列的消息(针对应用程序的数据)来通信,而无需专 ...
- 2017-06-22(locate shutdown half poweroff init0 reboot init 6)
locate locate 文件搜索命令 格式:locate [文件名] locate 在后台数据库中(/var/lib/mlocate/mlocate.db)按文件名搜索,速度快 刚刚新建的文件, ...
