Netty源码分析第4章(pipeline)---->第3节: handler的删除
Netty源码分析第四章: pipeline
第三节: handler的删除
上一小节我们学习了添加handler的逻辑操作, 这一小节我们学习删除handler的相关逻辑
如果用户在业务逻辑中进行ctx.pipeline().remove(this)这样的写法, 或者ch.pipeline().remove(new SimpleHandler())这样的写法, 则就是对handler进行删除, 我们学习过添加handler的逻辑, 所以对handler删除操作理解起来也会比较容易
我们首先跟到defaultChannelPipeline的remove(handler)的方法中:
public final ChannelPipeline remove(ChannelHandler handler) {
remove(getContextOrDie(handler));
return this;
}
方法体里有个remove()方法, 传入一个 getContextOrDie(handler) 参数, 这个 getContextOrDie(handler) , 其实就是根据handler拿到其包装类HandlerContext对象
我们跟到getContextPrDie这个方法中:
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext getContextOrDie(ChannelHandler handler) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = (AbstractChannelHandlerContext) context(handler);
//代码省略
}
这里仍然会通过context(handler)方法去寻找, 再跟进去:
public final ChannelHandlerContext context(ChannelHandler handler) {
if (handler == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("handler");
}
//从头遍历节点
AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx = head.next;
for (;;) {
if (ctx == null) {
return null;
}
//找到handler
if (ctx.handler() == handler) {
return ctx;
}
ctx = ctx.next;
}
}
这里我们看到寻找的方法也非常的简单, 就是从头结点开始遍历, 遍历到如果其包装的handler对象是传入的handler对象, 则返回找到的handlerContext
回到remove(handler)方法:
public final ChannelPipeline remove(ChannelHandler handler) {
remove(getContextOrDie(handler));
return this;
}
继续跟到remove方法中:
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext remove(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
//当前删除的节点不能是head, 也不能是tail
assert ctx != head && ctx != tail;
synchronized (this) {
//执行删除操作
remove0(ctx);
if (!registered) {
callHandlerCallbackLater(ctx, false);
return ctx;
}
//回调删除handler事件
EventExecutor executor = ctx.executor();
if (!executor.inEventLoop()) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callHandlerRemoved0(ctx);
}
});
return ctx;
}
}
callHandlerRemoved0(ctx);
return ctx;
}
首先要断言删除的节点不能是tail和head
然后通过remove0(ctx)进行实际的删除操作, 跟到remove0(ctx)中:
private static void remove0(AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
//当前节点的前置节点
AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev = ctx.prev;
//当前节点的后置节点
AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = ctx.next;
//前置节点的下一个节点设置为后置节点
prev.next = next;
//后置节点的上一个节点设置为前置节点
next.prev = prev;
}
这里的操作也非常简单, 做了一个指针移动的操作, 熟悉双向链表的小伙伴应该不会陌生, 删除节点逻辑大概如下图所示:
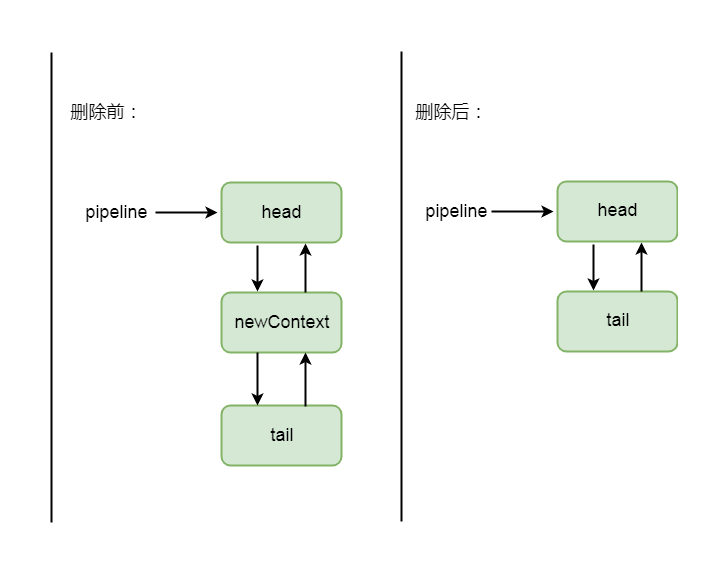
4-3-1
回到remove(ctx)方法:
private AbstractChannelHandlerContext remove(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
//当前删除的节点不能是head, 也不能是tail
assert ctx != head && ctx != tail;
synchronized (this) {
//执行删除操作
remove0(ctx);
if (!registered) {
callHandlerCallbackLater(ctx, false);
return ctx;
}
//回调删除handler事件
EventExecutor executor = ctx.executor();
if (!executor.inEventLoop()) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callHandlerRemoved0(ctx);
}
});
return ctx;
}
}
callHandlerRemoved0(ctx);
return ctx;
}
我们继续往下看, 如果当前线程不是eventLoop线程则将回调删除事件封装成task放在taskQueue中让eventLoop线程进行执行, 否则, 则直接执行回调删除事件
跟到callHandlerRemoved0(ctx)方法中:
private void callHandlerRemoved0(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
try {
try {
//调用handler的handlerRemoved方法
ctx.handler().handlerRemoved(ctx);
} finally {
//将当前节点状态设置为已移除
ctx.setRemoved();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
fireExceptionCaught(new ChannelPipelineException(
ctx.handler().getClass().getName() + ".handlerRemoved() has thrown an exception.", t));
}
}
与添加handler的逻辑一样, 这里会调用当前handler的handlerRemoved方法, 如果用户没有重写该方法, 则会调用其父类的方法, 方法体在ChannelHandlerAdapter类中有定义, 我们跟进去
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
}
同添加handler一样, 也是一个空实现, 这里用户可以通过重写来添加自己需要的逻辑
以上就是删除handler的相关操作
Netty源码分析第4章(pipeline)---->第3节: handler的删除的更多相关文章
- Netty源码分析第4章(pipeline)---->第2节: handler的添加
Netty源码分析第四章: pipeline 第二节: Handler的添加 添加handler, 我们以用户代码为例进行剖析: .childHandler(new ChannelInitialize ...
- Netty源码分析第4章(pipeline)---->第4节: 传播inbound事件
Netty源码分析第四章: pipeline 第四节: 传播inbound事件 有关于inbound事件, 在概述中做过简单的介绍, 就是以自己为基准, 流向自己的事件, 比如最常见的channelR ...
- Netty源码分析第4章(pipeline)---->第5节: 传播outbound事件
Netty源码分析第五章: pipeline 第五节: 传播outBound事件 了解了inbound事件的传播过程, 对于学习outbound事件传输的流程, 也不会太困难 在我们业务代码中, 有可 ...
- Netty源码分析第4章(pipeline)---->第6节: 传播异常事件
Netty源码分析第四章: pipeline 第6节: 传播异常事件 讲完了inbound事件和outbound事件的传输流程, 这一小节剖析异常事件的传输流程 首先我们看一个最最简单的异常处理的场景 ...
- Netty源码分析第4章(pipeline)---->第7节: 前章节内容回顾
Netty源码分析第四章: pipeline 第七节: 前章节内容回顾 我们在第一章和第三章中, 遗留了很多有关事件传输的相关逻辑, 这里带大家一一回顾 首先看两个问题: 1.在客户端接入的时候, N ...
- Netty源码分析第4章(pipeline)---->第1节: pipeline的创建
Netty源码分析第四章: pipeline 概述: pipeline, 顾名思义, 就是管道的意思, 在netty中, 事件在pipeline中传输, 用户可以中断事件, 添加自己的事件处理逻辑, ...
- Netty源码分析第5章(ByteBuf)---->第10节: SocketChannel读取数据过程
Netty源码分析第五章: ByteBuf 第十节: SocketChannel读取数据过程 我们第三章分析过客户端接入的流程, 这一小节带大家剖析客户端发送数据, Server读取数据的流程: 首先 ...
- Netty源码分析第5章(ByteBuf)---->第4节: PooledByteBufAllocator简述
Netty源码分析第五章: ByteBuf 第四节: PooledByteBufAllocator简述 上一小节简单介绍了ByteBufAllocator以及其子类UnPooledByteBufAll ...
- Netty源码分析第5章(ByteBuf)---->第5节: directArena分配缓冲区概述
Netty源码分析第五章: ByteBuf 第五节: directArena分配缓冲区概述 上一小节简单分析了PooledByteBufAllocator中, 线程局部缓存和arean的相关逻辑, 这 ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ4756:[USACO]Promotion Counting(线段树合并)
Description n只奶牛构成了一个树形的公司,每个奶牛有一个能力值pi,1号奶牛为树根. 问对于每个奶牛来说,它的子树中有几个能力值比它大的. Input n,表示有几只奶牛 n<=10 ...
- [SDOI2010]Hide and Seek
题目 非常显然就是求一下距离每一个点曼哈顿距离最近的点和最远的点就好了 最远点非常好算,我们建完\(kd-tree\)之后直接暴力就好了 找最近点的时候会有这样一个问题,就是自己找到了自己 所以我们需 ...
- [USACO19FEB]Moorio Kart
题目 我们的神仙教练在考试里放了这道题,当时我非常惊讶啊 背包是\(O(n^3)\)的吧明明是带根号的好吧,那既然要优化的话 NTT!什么时候我们教练会在考试里放多项式了 模数\(1e9+7\)? 任 ...
- Day5 类和对象
面向对象编程OOP 类:相似对象的集合. 对象 对象:实体.一切可以被描述的事物. 属性:特征. 方法:动作,行为. 类和对象的区别 [1]类时抽象的,对象是具体的. [2]类是一个模板,创建出来的对 ...
- 《Java程序设计》第12周课堂实践总结
<Java程序设计>第12周课堂实践总结 实践一 教材代码检查-p98 要求 修改教材P98 Score2.java, 让执行结果数组填充是自己的学号: 提交在IDEA或命令行中运行结查截 ...
- Python读文件报错:SyntaxError: Non-ASCII character in file
打开city.py文件时报错 问题原因: 程序中的编码错误,python默认是acii模式,没有支持utf8.如果代码中有汉字 ,就会报错 解决方案: 源代码文件(city.py)第一行添加:#cod ...
- ajax和原生ajax、文件的上传
ajax理解: ajax发送的请求是异步处理的.也就是说如下形式: function f1(){ $.ajax( { ....... success:function(){ a= return a } ...
- CommonJS、AMD、CMD、NodeJs、RequireJS到底有什么联系?
JS中的模块规范(CommonJS,AMD,CMD),如果你听过js模块化这个东西,那么你就应该听过或CommonJS或AMD甚至是CMD这些规范,本文包括这三个规范的来源及对应的产物的原理. 一.C ...
- vue组件懒加载(Load On Demand)
在Web应用程序中,系统的瓶颈常在于系统的响应速度.如果系统响应速度过慢,用户就会出现埋怨情绪,系统的价值也因此会大打折扣.因此,提高系统响应速度,是非常重要的. 懒加载(Load On Demand ...
- iOS 用KVC设置结构体
iOS 用KVC设置结构体 在Fundation中KVC提供的键值路径只能访问对象,不能访问结构体.这很不面向对象. 执行下面的语句将会报错: [self setValue:@() forKeyPat ...
