kali 2.0 linux中的Nmap的操作系统扫描功能
不多说,直接上干货!

可以使用-O选项,让Nmap对目标的操作系统进行识别。
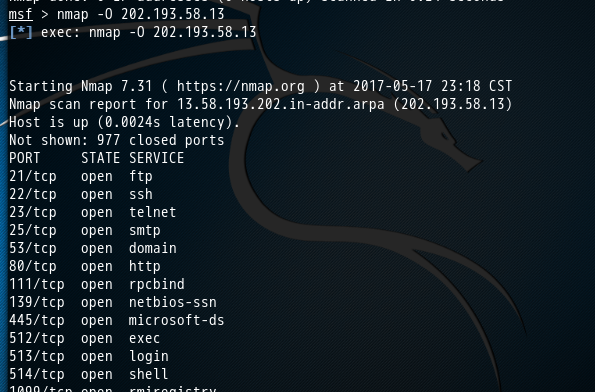
msf > nmap -O 202.193.58.13
[*] exec: nmap -O 202.193.58.13 Starting Nmap 7.31 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2017-05-17 23:18 CST
Nmap scan report for 13.58.193.202.in-addr.arpa (202.193.58.13)
Host is up (.0024s latency).
Not shown: closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
/tcp open ftp
/tcp open ssh
/tcp open telnet
/tcp open smtp
/tcp open domain
/tcp open http
/tcp open rpcbind
/tcp open netbios-ssn
/tcp open microsoft-ds
/tcp open exec
/tcp open login
/tcp open shell
/tcp open rmiregistry
/tcp open ingreslock
/tcp open nfs
/tcp open ccproxy-ftp
/tcp open mysql
/tcp open postgresql
/tcp open vnc
/tcp open X11
/tcp open irc
/tcp open ajp13
/tcp open unknown
MAC Address: :AD::::5C (Unknown)
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 2.6.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:2.6
OS details: Linux 2.6. - 2.6.
Network Distance: hop OS detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: IP address ( host up) scanned in 4.72 seconds
msf >
或者
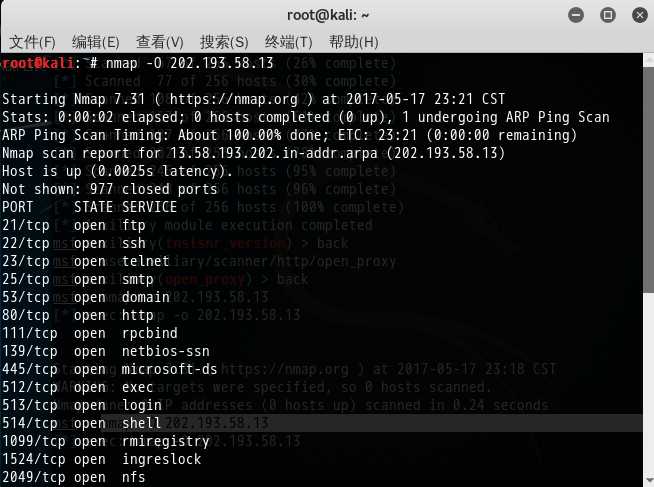
root@kali:~# nmap -O 202.193.58.13 Starting Nmap 7.31 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2017-05-17 23:21 CST
Stats: :: elapsed; hosts completed ( up), undergoing ARP Ping Scan
ARP Ping Scan Timing: About 100.00% done; ETC: : (:: remaining)
Nmap scan report for 13.58.193.202.in-addr.arpa (202.193.58.13)
Host is up (.0025s latency).
Not shown: closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
/tcp open ftp
/tcp open ssh
/tcp open telnet
/tcp open smtp
/tcp open domain
/tcp open http
/tcp open rpcbind
/tcp open netbios-ssn
/tcp open microsoft-ds
/tcp open exec
/tcp open login
/tcp open shell
/tcp open rmiregistry
/tcp open ingreslock
/tcp open nfs
/tcp open ccproxy-ftp
/tcp open mysql
/tcp open postgresql
/tcp open vnc
/tcp open X11
/tcp open irc
/tcp open ajp13
/tcp open unknown
MAC Address: :AD::::5C (Unknown)
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 2.6.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:2.6
OS details: Linux 2.6. - 2.6.
Network Distance: hop OS detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: IP address ( host up) scanned in 5.51 seconds
root@kali:~#
大家,也可以拿下面的主机,来扫描
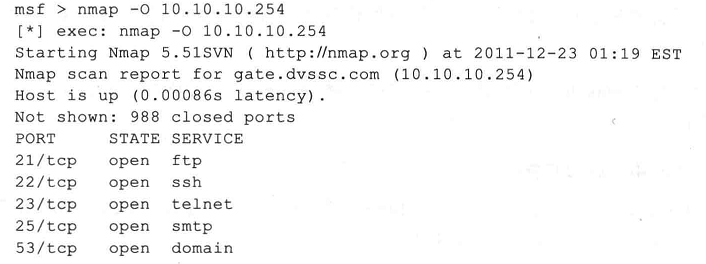


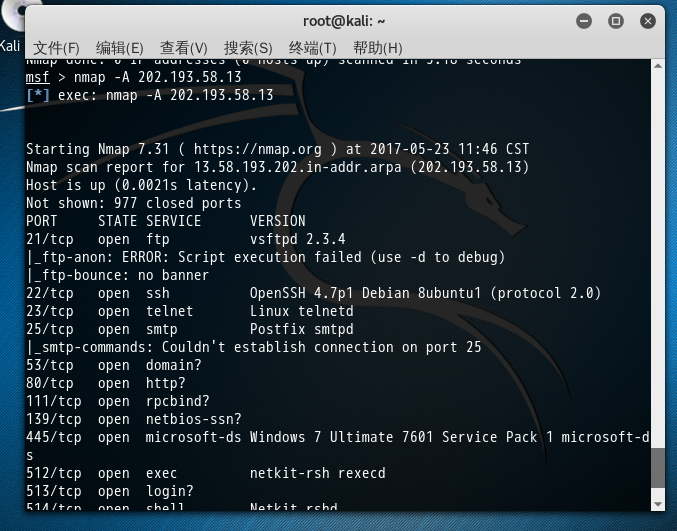
msf > nmap -A 202.193.58.13
[*] exec: nmap -A 202.193.58.13 Starting Nmap 7.31 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2017-05-23 11:46 CST
Nmap scan report for 13.58.193.202.in-addr.arpa (202.193.58.13)
Host is up (.0021s latency).
Not shown: closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
/tcp open ftp vsftpd 2.3.
|_ftp-anon: ERROR: Script execution failed (use -d to debug)
|_ftp-bounce: no banner
/tcp open ssh OpenSSH .7p1 Debian 8ubuntu1 (protocol 2.0)
/tcp open telnet Linux telnetd
/tcp open smtp Postfix smtpd
|_smtp-commands: Couldn't establish connection on port 25
/tcp open domain?
/tcp open http?
/tcp open rpcbind?
/tcp open netbios-ssn?
/tcp open microsoft-ds Windows Ultimate Service Pack microsoft-ds
/tcp open exec netkit-rsh rexecd
/tcp open login?
/tcp open shell Netkit rshd
/tcp open rmiregistry?
/tcp open shell Metasploitable root shell
/tcp open nfs?
/tcp open ccproxy-ftp?
/tcp open mysql MySQL 5.0.51a-3ubuntu5
/tcp open postgresql?
/tcp open vnc VNC (protocol 3.3)
/tcp open X11?
|_x11-access: ERROR: Script execution failed (use -d to debug)
/tcp open irc Unreal ircd
|_irc-info: Unable to open connection
/tcp open ajp13?
/tcp open unknown
MAC Address: :AD::::5C (Unknown)
Device type: firewall
Running (JUST GUESSING): Fortinet embedded (%)
OS CPE: cpe:/h:fortinet:fortigate_100d
Aggressive OS guesses: Fortinet FortiGate 100D firewall (%)
No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal).
Network Distance: hop
Service Info: Hosts: metasploitable.localdomain, irc.Metasploitable.LAN; OSs: Unix, Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: -24s, deviation: 0s, median: -24s
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Windows Ultimate Service Pack (Windows Ultimate 6.1)
| OS CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows_7::sp1
| Computer name: PH-PC
| NetBIOS computer name: PH-PC
| Workgroup: WORKGROUP
|_ System time: --23T11::+:
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: guest
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
|_smbv2-enabled: Server supports SMBv2 protocol TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
2.09 ms 13.58.193.202.in-addr.arpa (202.193.58.13) Post-scan script results:
| clock-skew:
|_ -24s: Majority of systems scanned
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: IP address ( host up) scanned in 72.94 seconds
msf >
更多,其实,
msf > nmap -h
[*] exec: nmap -h Nmap 7.31 ( https://nmap.org )
Usage: nmap [Scan Type(s)] [Options] {target specification}
TARGET SPECIFICATION:
Can pass hostnames, IP addresses, networks, etc.
Ex: scanme.nmap.org, microsoft.com/, 192.168.0.1; 10.0.-255.1-
-iL <inputfilename>: Input from list of hosts/networks
-iR <num hosts>: Choose random targets
--exclude <host1[,host2][,host3],...>: Exclude hosts/networks
--excludefile <exclude_file>: Exclude list from file
HOST DISCOVERY:
-sL: List Scan - simply list targets to scan
-sn: Ping Scan - disable port scan
-Pn: Treat all hosts as online -- skip host discovery
-PS/PA/PU/PY[portlist]: TCP SYN/ACK, UDP or SCTP discovery to given ports
-PE/PP/PM: ICMP echo, timestamp, and netmask request discovery probes
-PO[protocol list]: IP Protocol Ping
-n/-R: Never do DNS resolution/Always resolve [default: sometimes]
--dns-servers <serv1[,serv2],...>: Specify custom DNS servers
--system-dns: Use OS's DNS resolver
--traceroute: Trace hop path to each host
SCAN TECHNIQUES:
-sS/sT/sA/sW/sM: TCP SYN/Connect()/ACK/Window/Maimon scans
-sU: UDP Scan
-sN/sF/sX: TCP Null, FIN, and Xmas scans
--scanflags <flags>: Customize TCP scan flags
-sI <zombie host[:probeport]>: Idle scan
-sY/sZ: SCTP INIT/COOKIE-ECHO scans
-sO: IP protocol scan
-b <FTP relay host>: FTP bounce scan
PORT SPECIFICATION AND SCAN ORDER:
-p <port ranges>: Only scan specified ports
Ex: -p22; -p1-; -p U:,,,T:-,,,,S:
--exclude-ports <port ranges>: Exclude the specified ports from scanning
-F: Fast mode - Scan fewer ports than the default scan
-r: Scan ports consecutively - don't randomize
--top-ports <number>: Scan <number> most common ports
--port-ratio <ratio>: Scan ports more common than <ratio>
SERVICE/VERSION DETECTION:
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
--version-intensity <level>: Set from (light) to (try all probes)
--version-light: Limit to most likely probes (intensity )
--version-all: Try every single probe (intensity )
--version-trace: Show detailed version scan activity (for debugging)
SCRIPT SCAN:
-sC: equivalent to --script=default
--script=<Lua scripts>: <Lua scripts> is a comma separated list of
directories, script-files or script-categories
--script-args=<n1=v1,[n2=v2,...]>: provide arguments to scripts
--script-args-file=filename: provide NSE script args in a file
--script-trace: Show all data sent and received
--script-updatedb: Update the script database.
--script-help=<Lua scripts>: Show help about scripts.
<Lua scripts> is a comma-separated list of script-files or
script-categories.
OS DETECTION:
-O: Enable OS detection
--osscan-limit: Limit OS detection to promising targets
--osscan-guess: Guess OS more aggressively
TIMING AND PERFORMANCE:
Options which take <time> are in seconds, or append 'ms' (milliseconds),
's' (seconds), 'm' (minutes), or 'h' (hours) to the value (e.g. 30m).
-T<->: Set timing template (higher is faster)
--min-hostgroup/max-hostgroup <size>: Parallel host scan group sizes
--min-parallelism/max-parallelism <numprobes>: Probe parallelization
--min-rtt-timeout/max-rtt-timeout/initial-rtt-timeout <time>: Specifies
probe round trip time.
--max-retries <tries>: Caps number of port scan probe retransmissions.
--host-timeout <time>: Give up on target after this long
--scan-delay/--max-scan-delay <time>: Adjust delay between probes
--min-rate <number>: Send packets no slower than <number> per second
--max-rate <number>: Send packets no faster than <number> per second
FIREWALL/IDS EVASION AND SPOOFING:
-f; --mtu <val>: fragment packets (optionally w/given MTU)
-D <decoy1,decoy2[,ME],...>: Cloak a scan with decoys
-S <IP_Address>: Spoof source address
-e <iface>: Use specified interface
-g/--source-port <portnum>: Use given port number
--proxies <url1,[url2],...>: Relay connections through HTTP/SOCKS4 proxies
--data <hex string>: Append a custom payload to sent packets
--data-string <string>: Append a custom ASCII string to sent packets
--data-length <num>: Append random data to sent packets
--ip-options <options>: Send packets with specified ip options
--ttl <val>: Set IP time-to-live field
--spoof-mac <mac address/prefix/vendor name>: Spoof your MAC address
--badsum: Send packets with a bogus TCP/UDP/SCTP checksum
OUTPUT:
-oN/-oX/-oS/-oG <file>: Output scan in normal, XML, s|<rIpt kIddi3,
and Grepable format, respectively, to the given filename.
-oA <basename>: Output in the three major formats at once
-v: Increase verbosity level (use -vv or more for greater effect)
-d: Increase debugging level (use -dd or more for greater effect)
--reason: Display the reason a port is in a particular state
--open: Only show open (or possibly open) ports
--packet-trace: Show all packets sent and received
--iflist: Print host interfaces and routes (for debugging)
--append-output: Append to rather than clobber specified output files
--resume <filename>: Resume an aborted scan
--stylesheet <path/URL>: XSL stylesheet to transform XML output to HTML
--webxml: Reference stylesheet from Nmap.Org for more portable XML
--no-stylesheet: Prevent associating of XSL stylesheet w/XML output
MISC:
-: Enable IPv6 scanning
-A: Enable OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute
--datadir <dirname>: Specify custom Nmap data file location
--send-eth/--send-ip: Send using raw ethernet frames or IP packets
--privileged: Assume that the user is fully privileged
--unprivileged: Assume the user lacks raw socket privileges
-V: Print version number
-h: Print this help summary page.
EXAMPLES:
nmap -v -A scanme.nmap.org
nmap -v -sn 192.168.0.0/ 10.0.0.0/
nmap -v -iR -Pn -p
SEE THE MAN PAGE (https://nmap.org/book/man.html) FOR MORE OPTIONS AND EXAMPLES
msf >
kali 2.0 linux中的Nmap的操作系统扫描功能的更多相关文章
- kali 2.0 linux中的Nmap的主机探测
不多说,直接上干货! 如果是第一次接触Nmap,推荐在MSF终端中输入不加任何参数的Nmap命令,以查看其使用方法. 更多,其实, msf > nmap -h [*] exec: nmap -h ...
- Kali linux 2016.2(Rolling)中的Nmap的端口扫描功能
不多说,直接上干货! 如下,是使用Nmap对主机202.193.58.13进行一次端口扫描的结果,其中使用 root@kali:~# nmap -sS -Pn 202.193.58.13 Starti ...
- 如何在Kali Linux中搭建钓鱼热点
文中提及的部分技术可能带有一定攻击性,仅供安全学习和教学用途,禁止非法使用! 0×00 实验环境 操作系统:Kali 1.0 (VM) FackAP: easy-creds 硬件:NETGEAR wg ...
- Linux中W与Who命令的使用
踢掉一个从某个终端连上的用户pkill -kill -t pts/0 ---------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- linux中vi和vim编辑工具
linux中知名的还有emacs,功能比vim还要强大 vim 如果文件存在vim是打开这个文件,若果不存在,则先新建再打开 命令模式:任何模式都可以通过Esc回到命令模式,命令模式可以通过命令进行选 ...
- linux中shell变量$#,$@,$0,$1,$2的含义解释
linux中shell变量$#,$@,$0,$1,$2的含义解释: 变量说明: $$ Shell本身的PID(ProcessID) $! Shell最后运行的后台Process的PID $? 最后运行 ...
- Kali Linux中MySQL重置root密码
参考:使用mysqladmin命令修改MySQL密码与忘记密码 前言:(在Windows的DOS命令行下和在kali Linux下修改方法是一样的)在kali Linux中默认安装了MySQL的最新版 ...
- linux中shell变量$#,$@,$0,$1,$2的含义解释
linux中shell变量$#,$@,$0,$1,$2的含义解释 linux中shell变量$#,$@,$0,$1,$2的含义解释: 变量说明: $$ Shell本身的PID(ProcessID ...
- kali 2.0中msf连接postgres数据库
装好kali 2.0后直接运行msfconsole msf> db_status postgres selected, no connection 百度到的解决方法多是针对BT和kali 1.0 ...
随机推荐
- 从零開始学android<TabHost标签组件.二十九.>
TabHost主要特点是能够在一个窗体中显示多组标签栏的内容,在Android系统之中每一个标签栏就称为一个Tab.而包括这多个标签栏的容器就将其称为TabHost.TabHost类的继承结构例如以下 ...
- 闲来无事爬了下通讯录 试手 jsdom
curl http://xxx.com/address/addresslist\?search\=%40 --cookie oa_cookie=123 -s| node parss .js js 代码 ...
- IOS7 textkit 的相关
去年基于5.0开发的时候.自己用coreText编写了一个富文本,全部的效果都实现的非常好.可是没有去測试效率.只是在cell重用的时候表现不错.在4s上面也不会卡顿. 唯一一个问题就是,在使用AL的 ...
- 高级程序员与CTO技术总监首席架构师
一.高级程序员 如果你是一个刚刚创业的公司,公司没有专职产品经理和项目经理,你就是公司的产品经理,你如果对你现在的开发员能力不满,那么你只需要的是一个高级程序员. 你定义功能.你做计划推进和管理,他可 ...
- 我的Java历程_maven配置的心路历程
从github上download了个maven管理的开源项目,接下来随笔下安装maven的心路历程: 异常尴尬的是import进ide之后一个红色的感叹号!震惊!google一下知道了,maven没配 ...
- ZBrush实用插件ZAppLink简介
ZAppLink是ZBrush版本推出时被评为最值得期待的插件.事实证明,ZAppLink的出现让工具与工具之间有了交流,搭起软件与软件的沟通桥梁. ZAppLink插件专用于扩展ZBrush®的绘制 ...
- .NET Framework 3.5 无法安装以下功能 安装错误:0x800F0906(客户端加域后出现)
问题:安装错误:0x800F0906 系统安装并加域后,在安装用友软件时提示没有.net 3.5 系统为win10 但是,点击确定后,却出现了这样的错误.如下: 点击下载并安装此功能,出现了这样 ...
- oralce模糊查询之含有通配符
oracle中通配符有 '_'和'%'当like '_ww%'时,会把'_'和'%'当作通配符使用导致查不出含有'_'和'%'的数据.这时用到转译字符 like '\_ww\%' escape '\ ...
- json转换成Map
1.如果转换的是Map.或者是简单的对象 package com.gc.action; import java.util.Map; import net.sf.json.JSONObject; /** ...
- Spring boot配置404、500页面
Spring boot 配置404页面很简单,如果你访问的url没有找到就会出现spring boot 提示的页面,很明显Spring boot不用配置就可以显示404页面了. 在template下创 ...
