Spring Boot 启动流程追踪(第一篇)
1、初始化 SpringApplication
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList<>(
getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
在完成初始化工作后,可以看到设置了如下属性:
bootstrapRegistryInitializers:

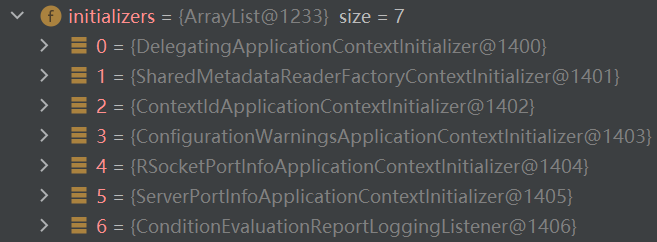
initializers:
listeners:
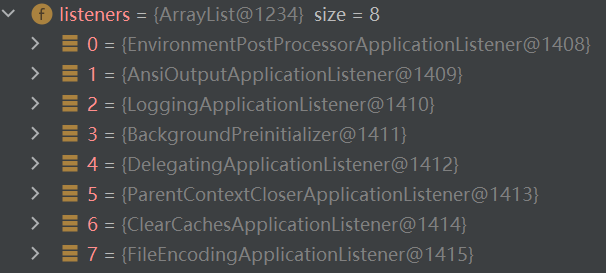
这些属性咋来的上一篇文章中有提到过,会扫描 spring-boot、spring-boot-autoconfigure、spring-beans 包里面 resource 目录下 META-INF/spring.factories 文件进行加载,如果你想添加自己的配置,也可以在自己项目的 resource 目录下添加配置。
2、加载 spring.factories
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)));
cache.put(classLoader, result);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
}
加载结果如下所示:

以后有些地方加载类的时候,就会直接从缓存取了。
3、环境准备前的工作(run 方法代码片段)
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
在 createBootstrapContext 方法里面会调用 bootstrapRegistryInitializers 的 initializer 方法,不过 SpringBoot 该属性没值。
然后会调用 getRunListeners 方法加载 SpringApplicationRunListeners,该值同样也是从 spring.factories 文件进行加载的。
该 listeners(SpringApplicationRunListeners) 下的 SpringApplicationRunListener 只有一个: EventPublishingRunListener
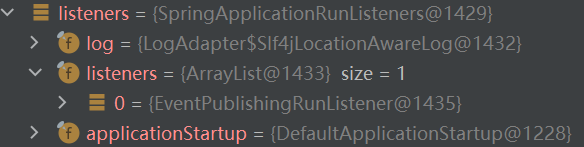
然后会调用该类的 starting 方法,会触发 ApplicationStartingEvent 事件,该事件会被 SpringApplication 下的 listeners 监听。
如果你感兴趣的话,可以看看 8 个 ApplicationListener 干了什么!
4、准备环境(run->prepareEnvironment)
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());
environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
这里是先创建一个默认的 Servlet 环境,然后为该环境配置参数,在 configureEnvironment ->configurePropertySources 方法中可以看到会从命令行参数和 SpringApplication 的 defaultProperties 属性获取可配置参数。环境准备好后,会执行 listeners.environmentPrepared 方法,上文提到过,该方法只有一个实现类,调用该方法会触发 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 事件,同样也会被监听到。该方法目前就看这两个就行了,其他的方法不知道在哪儿用的,看了也说不明白。
5、配置 Banner 和 上下文
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
如果想要知道怎么自定义 Banner,可以看 printBanner,通过创建 banner.txt 文本格式或 banner.png、banner.gif、banner.gif 等图片格式文件,可实现自定义 banner,文件默认放在 resource 目录下就行,如果不嫌麻烦的话也可以自定义 banner 存放目录。
接下来是 context 上下文,这在后面会经常用到,它会使用默认的 contextFactory 来创建 context,并且它是通过 loadSpringFactories 方法来获取的,其实现类在 spring.factories 里配置的是 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。
6、准备上下文(run->prepareContext)
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
((AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) beanFactory).setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context));
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
这里调用了 applyInitializers 方法,之前 SpringApplication 加载了 7 个 ApplicationContextInitializer,这里会调用每个 initializer 的 initialize 方法。接着就调用 listeners 的 contextPrepared 方法,还是之前的 EventPublishingRunListener,该方法会触发 8 个 ApplicationListener 监听 ApplicationContextInitializedEvent 事件。在这之后的 bootstrapContext.close 方法也会 BootstrapContextClosedEvent 事件。然后想 set、add、log 啥的可以直接跳过,beanFactory.registerSingleton 方法可以点进去看看,不过也是 add 啥的,这些其实都是为后面实质性的操作做准备,后面可以再追溯数据来源。
接着看看 load 方法,load 方法的 source 来源一个是 primarySources,另一个是 sources,都是 SpringApplication 的属性,该方法可以加载 Bean,并且该方法细节也是蛮多的,这里先记着,后面再看。最后就是 listeners.contextLoaded 方法了,该方法会触发 ApplicationPreparedEvent 事件。
7、添加上下文销毁线程(refreshcontext...->addRuntimeShutdownHook)
void addRuntimeShutdownHook() {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(this, "SpringApplicationShutdownHook"));
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
Set<ConfigurableApplicationContext> contexts;
Set<ConfigurableApplicationContext> closedContexts;
Set<Runnable> actions;
synchronized (SpringApplicationShutdownHook.class) {
this.inProgress = true;
contexts = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.contexts);
closedContexts = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.closedContexts);
actions = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.handlers.getActions());
}
contexts.forEach(this::closeAndWait);
closedContexts.forEach(this::closeAndWait);
actions.forEach(Runnable::run);
}
这里在线程末尾会执行上下文的 closeAndWait 方法,以及支持自定义的 actions。
8、收尾工作
在刷新完 context 之后,会执行 listeners.started、ready 方法,分别会触发 ApplicationStartedEvent、ApplicationReadyEvent 事件。同样会被 8 个 ApplicationListener 监听到。
另外还有一个 callRunners 方法值得注意,任何实现了 ApplicationRunner、CommandLineRunner 接口的实现类都会得到执行。
9、加载 Bean(load)
前面提到过 load 方法也是一个值得注意的方法,他可以通过好几种方式注册 Bean:
private void load(Object source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
if (source instanceof Class<?>) {
load((Class<?>) source);
return;
}
if (source instanceof Resource) {
load((Resource) source);
return;
}
if (source instanceof Package) {
load((Package) source);
return;
}
if (source instanceof CharSequence) {
load((CharSequence) source);
return;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source type " + source.getClass());
}
首先是 load(Class<?> source) 方法:它会判断本地有没有 groovy 环境,然后 source 对象是 GroovyBeanDefinitionSource 类或其子类的实例时,就实例化它,然后将 loader 对象的 bean 方法返回的 Bean 添加到 groovyReader 中。然后就判断其是否有资格注册为 Bean。
private void load(Class<?> source) {
if (isGroovyPresent() && GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class.isAssignableFrom(source)) {
// Any GroovyLoaders added in beans{} DSL can contribute beans here
GroovyBeanDefinitionSource loader = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(source, GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class);
((GroovyBeanDefinitionReader) this.groovyReader).beans(loader.getBeans());
}
if (isEligible(source)) {
this.annotatedReader.register(source);
}
}
然后是 load(Resource source) 方法:总之它会从 grovvy 文件或者 xml 文件中注册 Bean。
private void load(Resource source) {
if (source.getFilename().endsWith(".groovy")) {
if (this.groovyReader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot load Groovy beans without Groovy on classpath");
}
this.groovyReader.loadBeanDefinitions(source);
}
else {
if (this.xmlReader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Cannot load XML bean definitions when XML support is disabled");
}
this.xmlReader.loadBeanDefinitions(source);
}
}
然后是 load(Package source) 方法:总之它会从 package 里注册 Bean。
private void load(Package source) {
this.scanner.scan(source.getName());
}
最后就是 load(CharSequence source) 方法:它就很有意思了,它会尝试将其作为以上三种方式进行加载。
private void load(CharSequence source) {
String resolvedSource = this.scanner.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(source.toString());
// Attempt as a Class
try {
load(ClassUtils.forName(resolvedSource, null));
return;
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException | ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// swallow exception and continue
}
// Attempt as Resources
if (loadAsResources(resolvedSource)) {
return;
}
// Attempt as package
Package packageResource = findPackage(resolvedSource);
if (packageResource != null) {
load(packageResource);
return;
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid source '" + resolvedSource + "'");
}
10、总结
这篇文章我们了解了自动装配的工作方式,也就是 spring.factories。然后就是 Banner 是如何打印的、context 环境准备完毕后如何执行自定义代码,context 的销毁工作以及最后的两种 runner 怎么使用。本文着重介绍了 load 方法通过几种方式注册 Bean的,包括 Grovvy、xml等文件方式、Package包、Class类、CharSequence字符串等方式进行注册。
最后遗留了一个刷新上下文 refresh 方法没有分析,这也是一个很重要的方法。
Spring Boot 启动流程追踪(第一篇)的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot启动流程分析
引言 早在15年的时候就开始用spring boot进行开发了,然而一直就只是用用,并没有深入去了解spring boot是以什么原理怎样工作的,说来也惭愧.今天让我们从spring boot启动开始 ...
- Spring Boot启动流程详解(一)
环境 本文基于Spring Boot版本1.3.3, 使用了spring-boot-starter-web. 配置完成后,编写了代码如下: @SpringBootApplication public ...
- Spring Boot启动流程详解
注:本文转自http://zhaox.github.io/java/2016/03/22/spring-boot-start-flow 环境 本文基于Spring Boot版本1.3.3, 使用了sp ...
- Spring Boot -- 启动流程分析之ApplicationContext 中
上一节我们已经分析到AbsractApplicationContext类refresh方法中的postProcessBeanFactory方法,在分析registerBeanPostProcessor ...
- Spring Boot(三):Spring Boot中的事件的使用 与Spring Boot启动流程(Event 事件 和 Listeners监听器)
前言:在讲述内容之前 希望大家对设计模式有所了解 即使你学会了本片的内容 也不知道什么时候去使用 或者为什么要这样去用 观察者模式: 观察者模式是一种对象行为模式.它定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系, ...
- Spring Boot启动流程
基础准备 1,BeanPostProcessor:这个接口的作用在于对于新构造的实例可以做一些自定义的修改.比如如何构造.属性值的修改.构造器的选择等等 2,BeanFactoryPostProces ...
- Spring MVC启动流程分析
本文是Spring MVC系列博客的第一篇,后续会汇总成贴子. Spring MVC是Spring系列框架中使用频率最高的部分.不管是Spring Boot还是传统的Spring项目,只要是Web项目 ...
- Spring Boot启动过程(四):Spring Boot内嵌Tomcat启动
之前在Spring Boot启动过程(二)提到过createEmbeddedServletContainer创建了内嵌的Servlet容器,我用的是默认的Tomcat. private void cr ...
- Spring Boot启动过程(七):Connector初始化
Connector实例的创建已经在Spring Boot启动过程(四):Spring Boot内嵌Tomcat启动中提到了: Connector是LifecycleMBeanBase的子类,先是设置L ...
- Spring Boot 启动(四) EnvironmentPostProcessor
Spring Boot 启动(四) EnvironmentPostProcessor Spring 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10198698. ...
随机推荐
- 2021-12-13:字符串解码。给定一个经过编码的字符串,返回它解码后的字符串。 编码规则为: k[encoded_string],表示其中方括号内部的 encoded_string 正好重复 k
2021-12-13:字符串解码.给定一个经过编码的字符串,返回它解码后的字符串. 编码规则为: k[encoded_string],表示其中方括号内部的 encoded_string 正好重复 k ...
- 2021-08-30:给定两个字符串str1和str2,在str1中寻找一个最短子串,能包含str2的所有字符,字符顺序无所谓,str1的这个最短子串也可以包含多余的字符。返回这个最短包含子串。
2021-08-30:给定两个字符串str1和str2,在str1中寻找一个最短子串,能包含str2的所有字符,字符顺序无所谓,str1的这个最短子串也可以包含多余的字符.返回这个最短包含子串. 福大 ...
- Event Tables for Efficient Experience Replay
Abstract 事件表分层抽样(SSET),它将ER缓冲区划分为事件表,每个事件表捕获最优行为的重要子序列. 我们证明了一种优于传统单片缓冲方法的理论优势,并将SSET与现有的优先采样策略相结合,以 ...
- 什么是 Spring?为什么学它?
前言 欢迎来到本篇文章!在这里,我将带领大家快速学习 Spring 的基本概念,并解答两个关键问题:什么是 Spring,以及为什么学习 Spring. 废话少说,下面,我们开始吧! Spring 官 ...
- Linux(redhat)镜像
作为一个合格的程序猿,Linux那就是必须得会玩哟呵,搜集了一些镜像分享大家,望笑纳. 云盘地址https://pan.baidu.com/s/1cB-llYI5RdRm9xJDmjFoWg 提取码 ...
- Doris(五) -- 数据的导入导出
数据导入 使用 Insert 方式同步数据 用户可以通过 MySQL 协议,使用 INSERT 语句进行数据导入 INSERT 语句的使用方式和 MySQL 等数据库中 INSERT 语句的使用方式类 ...
- TVM 源码阅读PASS — VectorizeLoop
本文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanger-sjtu/p/17501119.html VectorizeLoop这个PASS就是对标记为ForKind::kVectoriz ...
- memcached使用中踩的一些坑
背景 线上启用memcached(以下简称mc)作为热点缓存组件已经多年,其稳定性和性能都经历住了考验,这里记录一下踩过的几个坑. 大key存储 某年某月某日,观察mysql的读库CPU占比有些异常偏 ...
- MAC地址、IP地址与子网———计算机网络
计算机具有强大的功能.除了体现与计算机本身具有的计算能力外,其他的功能大多是基于与其他计算机联网提供的. 然而,计算机之间的联网不是一根网线就能解决嘛? 答案当然是否定的.实际上计算机间的交流过程十分 ...
- Mysql基础篇(四)之事务
一. 事务简介 事务是一组操作的集合,它是一个不可分隔的工作单位,事务会把所有的操作作为一个整体一起向系统提交或撤销操作请求,即这些操作要么同时成功,要么同时失败. 就比如:张三给李四转账1000块钱 ...
