jdk1.8-stack 栈源码分析
public
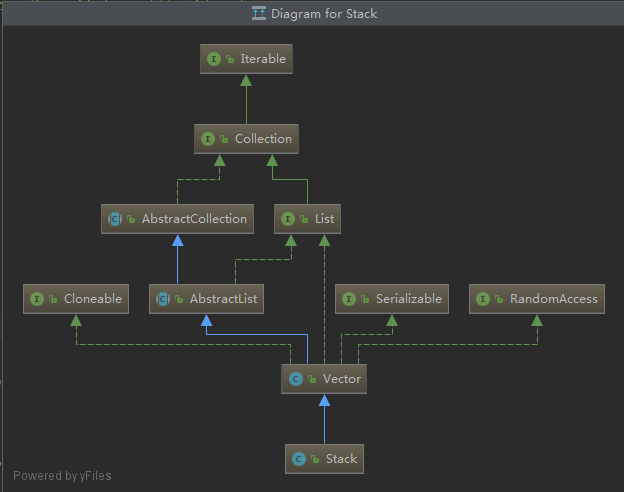
class Stack<E> extends Vector<E>
分析:栈的继承关系很简单,就是继承了Vector,那么我们可以猜测栈操作大部分应该是线程安全的。
/**
* Creates an empty Stack.
*/
public Stack() {
}
/**
* Pushes an item onto the top of this stack. This has exactly
* the same effect as:
* <blockquote><pre>
* addElement(item)</pre></blockquote>
*
* @param item the item to be pushed onto this stack.
* @return the <code>item</code> argument.
* @see java.util.Vector#addElement
*/
public E push(E item) {
//调用父类vector的addElement()方法
addElement(item);
return item;
}
分析:往栈里压入一个元素用push方法,每次往栈的顶部压入元素。addElement()是抽象父类vector方法,我们在vector里已经分析过。从这里我们可以知道,栈的底层数组结构也是数组。
/**
* Removes the object at the top of this stack and returns that
* object as the value of this function.
*
* @return The object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the <tt>Vector</tt> object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
//栈的长度
int len = size();
//栈顶部的元素值(也就是数组最后一个元素值)
obj = peek();
//栈元素减1
removeElementAt(len - 1);
//返回顶部元素
return obj;
}
分析:删除栈顶部的对象,并将该对象作为函数值返回
/**
* Deletes the component at the specified index. Each component in
* this vector with an index greater or equal to the specified
* {@code index} is shifted downward to have an index one
* smaller than the value it had previously. The size of this vector
* is decreased by {@code 1}.
*
* <p>The index must be a value greater than or equal to {@code 0}
* and less than the current size of the vector.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #remove(int)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface). Note that the
* {@code remove} method returns the old value that was stored at the
* specified position.
*
* @param index the index of the object to remove
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
//修改次数加1
modCount++;
//校验是否越界
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
//数组需要移动的个数
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
//从index + 1位置开始,向左移动一个位置,移动的个数为j
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
//数组实际元素减1
elementCount--;
//数组最后一个元素置为null,等待gc回收
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
分析:传进来len -1,栈顶部元素下标,即数组最后一个元素位置。
/**
* Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it
* from the stack.
*
* @return the object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the <tt>Vector</tt> object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
//根据索引从数组里取值,elementAt是调用父类Vector的方法
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
分析:栈的peek()方法,其实就是返回栈顶部的元素值,即数组末尾元素值。
/**
* Returns the component at the specified index.
*
* <p>This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #get(int)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface).
*
* @param index an index into this vector
* @return the component at the specified index
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
分析:这个方法就是根据下标,返回数组的值而已,没啥好分析的。
jdk1.8-stack 栈源码分析的更多相关文章
- Stack的源码分析和应用实例
1.Stack介绍 Stack是栈.它的特性是:先进后出(FILO:First In Last Out). java工具包中的Stack是继承于Vector(矢量队列)的,由于Vector是通过数组实 ...
- Java集合基于JDK1.8的LinkedList源码分析
上篇我们分析了ArrayList的底层实现,知道了ArrayList底层是基于数组实现的,因此具有查找修改快而插入删除慢的特点.本篇介绍的LinkedList是List接口的另一种实现,它的底层是基于 ...
- Java -- 基于JDK1.8的LinkedList源码分析
1,上周末我们一起分析了ArrayList的源码并进行了一些总结,因为最近在看Collection这一块的东西,下面的图也是大致的总结了Collection里面重要的接口和类,如果没有意外的话后面基本 ...
- JDK1.7之 HashMap 源码分析
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/crazy1235/article/details/75451812 类继承关系 构造函数 Entry put put putForNullK ...
- Java -- 基于JDK1.8的ThreadLocal源码分析
1,最近在做一个需求的时候需要对外部暴露一个值得应用 ,一般来说直接写个单例,将这个成员变量的值暴露出去就ok了,但是当时突然灵机一动(现在回想是个多余的想法),想到handle源码里面有使用过Th ...
- Java集合基于JDK1.8的ArrayList源码分析
本篇分析ArrayList的源码,在分析之前先跟大家谈一谈数组.数组可能是我们最早接触到的数据结构之一,它是在内存中划分出一块连续的地址空间用来进行元素的存储,由于它直接操作内存,所以数组的性能要比集 ...
- 基于jdk1.8的ArrayList源码分析
前言ArrayList作为一个常用的集合类,这次我们简单的根据源码来看看AarryList是如何使用的. ArrayList拥有的成员变量 public class ArrayList<E> ...
- Java -- 基于JDK1.8的ArrayList源码分析
1,前言 很久没有写博客了,很想念大家,18年都快过完了,才开始写第一篇,争取后面每周写点,权当是记录,因为最近在看JDK的Collection,而且ArrayList源码这一块也经常被面试官问道,所 ...
- Stack&Vector源码分析 jdk1.6
参照:http://www.cnblogs.com/tstd/p/5104099.html Stack(Fitst In Last Out) 1.定义 public class Stack<E& ...
随机推荐
- unittest 报告——HTMLTestRunner/BSTestRunner+代码覆盖率
1. HTMLTestRunner.py 代码(python3)如下: python2: https://github.com/tungwaiyip/HTMLTestRunner "&qu ...
- AVL树的介绍和实现
一.AVL树 AVL树是一种自平衡二叉查找树,因此在了解AVL树之前先介绍一下平衡二叉树.所谓平衡二叉树即该树中的任一个节点的左子树和右子树高度差不会超过1.如下图左是平衡二叉树,而右图则不是.节点4 ...
- java中创建List<>类型的数组-20171028
遇到了一个问题需要创建List类型的数组,但是在网上查了很多资料,好像发现并不能创建泛型的数组,于是改用Hashmap实现同等的功能. 代码如下: Map<String,List<AddL ...
- Acwing-252-树(点分治)
链接: https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/254/ 题意: 给定一个有N个点(编号0,1,-,N-1)的树,每条边都有一个权值(不超过1000). 树上两个 ...
- 3 触发器报警-->远程执行命令
0.需求 上节课我们讲了,触发器报警,发送邮件,这节课主要讲下远程执行命令 流程图如下 item--> triggers-->action--->Email |——>远 ...
- Ubuntu 保存文件时报E212
命令输入: vim test/conf.conf 出现如下报错: 步骤一: 没有足够的权限!使用如下代码尝试: :w !sudo tee % > /dev/null 如果步骤一没有解决问题,尝 ...
- hdu 5726 GCD GCD+线段树+区间预处理+map
GCD Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submis ...
- Battle ships HDU - 5093二分匹配
Battle shipsHDU - 5093 题目大意:n*m的地图,*代表海洋,#代表冰山,o代表浮冰,海洋上可以放置船舰,但是每一行每一列只能有一个船舰(类似象棋的車),除非同行或者同列的船舰中间 ...
- POJ - 3162 Walking Race 树形dp 单调队列
POJ - 3162Walking Race 题目大意:有n个训练点,第i天就选择第i个训练点为起点跑到最远距离的点,然后连续的几天里如果最远距离的最大值和最小值的差距不超过m就可以作为观测区间,问这 ...
- Ubuntu安裝python3.7版
https://blog.csdn.net/u014775723/article/details/85213793 failed to fetch ppa:https://blog.csdn.net/ ...
