1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)
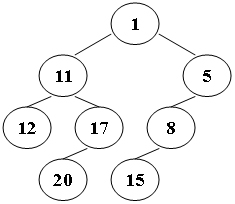
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in "zigzagging order" -- that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
8
12 11 20 17 1 15 8 5
12 20 17 11 15 8 5 1
Sample Output:
1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15题意:中序和后序建树,然后按zigzagging order输出。
分析:层序遍历的时候将节点输出到容器中,最后输出的时候根据奇数还是偶数来输出结点
/**
* Copyright(c)
* All rights reserved.
* Author : Mered1th
* Date : 2019-02-28-14.24.50
* Description : A1127
*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
;
int n,post[maxn],in[maxn];
vector<int> ans[maxn];
struct Node{
int val,layer;
Node* lchild;
Node* rchild;
Node(int _val,int _layer){
val=_val;
lchild=NULL;
rchild=NULL;
layer=_layer;
}
};
;
Node* create(int inL,int inR,int postL,int postR,int layer){
if(inL>inR) return NULL;
if(layer>maxlayer) maxlayer=layer;
int rootVal=post[postR];
Node* root=new Node(rootVal,layer);
int k;
for(int i=inL;i<=inR;i++){
if(post[postR]==in[i]){
k=i;
break;
}
}
int numLeft=k-inL;
root->lchild=create(inL,k-,postL,postL+numLeft-,layer+);
root->rchild=create(k+,inR,postL+numLeft,postR-,layer+);
return root;
}
void BFS(Node* root){
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
Node* now=q.front();
q.pop();
ans[now->layer].push_back(now->val);
if(now->lchild!=NULL) q.push(now->lchild);
if(now->rchild!=NULL) q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
int main(){
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#else
freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
scanf("%d",&n);
;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&in[i]);
}
;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&post[i]);
}
Node* root=create(,n-,,n-,);
BFS(root);
;i<=maxlayer;i++){
){
printf(]);
continue;
}
==){
;j<ans[i].size();j++){
printf(" %d",ans[i][j]);
}
}
else{
;j>=;j--){
printf(" %d",ans[i][j]);
}
}
}
;
}
1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)的更多相关文章
- PAT甲级 1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)
1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- pat 甲级 1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)
1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- PAT Advanced 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30) [中序后序建树,层序遍历]
题目 Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree c ...
- PAT甲题题解-1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)-中序、后序建树
根据中序遍历和前序遍历确定一棵二叉树,然后按“层次遍历”序列输出.输出规则:除根节点外,接下来每层的节点输出顺序是:先从左到右,再从右到左,交替输出 #include <iostream> ...
- PAT 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree[难]
1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分) Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive in ...
- PAT甲级1127. ZigZagging on a Tree
PAT甲级1127. ZigZagging on a Tree 题意: 假设二叉树中的所有键都是不同的正整数.一个唯一的二叉树可以通过给定的一对后序和顺序遍历序列来确定.这是一个简单的标准程序,可以按 ...
- PTA 04-树6 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分)
题目地址 https://pta.patest.cn/pta/test/16/exam/4/question/669 5-7 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分) A ...
- PAT-2019年冬季考试-甲级 7-4 Cartesian Tree (30分)(最小堆的中序遍历求层序遍历,递归建树bfs层序)
7-4 Cartesian Tree (30分) A Cartesian tree is a binary tree constructed from a sequence of distinct ...
- PAT 甲级 1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 分)(不会做,重点复习,模拟中序遍历)
1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 分) A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a bin ...
随机推荐
- hdu3294 Girls' research manacher
One day, sailormoon girls are so delighted that they intend to research about palindromic strings. O ...
- jsp中引入jquery报错:Failed to load resource: the server responded with a status of 404 (Not Found)
问题描述: 今天自己在搭建spring.springMVC.hibernate框架,搭建完成后,在引入jquery时,发现jquery不管用.我的解决顺序是: 1.检查路径,发现路径没错,另外需要注意 ...
- Easyui datagrid 去掉表头的checkbox复选框
$(".datagrid-header-check").html(""); 在onLoadSuccess中加入此行代码即可实现datagrid去除表头的chec ...
- mysql新建用户在本地无法登录
新建了一个mysql用户,但是无法在本地登录,即使已经授权任一ip都可以登录,甚至特地写清楚localhost登录,还是不行,情况如下 [root@localhost zabbix-release-3 ...
- vm centos7中用NAT模式配置上网
第一步:设置虚拟机的NAT相关网络设置: 点击5标致处的“NAT设置”会出现设置6标致处的网关. 第二部:设置操作系统网络设置,右击上图中9标致处的系统,点击设置 第三部:配置操作系统ip ...
- 转载:扒一扒Profiler中这几个“占坑鬼”
https://blog.uwa4d.com/archives/presentandsync.html WaitForTargetFPS.Gfx.WaitForPresent 和 Graphics.P ...
- oracle参数文件与启动过程
oracle随系统启动而启动 cs65-64桌面版orcle-11.2.0.4 启动监听器,后台进程,OEM. 注意: 如果只做一和三,只能启动后台进程,监听器不启动,如果只做二和三,只能启动监听器, ...
- quartz.net实现集群部署的笔记
一..表信息 QRTZ_CALENDARS 以 Blob 类型存储 Quartz 的 Calendar 信息 QRTZ_CRON_TRIGGERS 存储 Cron Trigger,包括Cron表达式和 ...
- C# Monitor的Wait和Pulse方法使用详解
[转载]http://blog.csdn.net/qqsttt/article/details/24777553 Monitor的Wait和Pulse方法在线程的同步锁使用中是比较复杂的,理解稍微困难 ...
- node 学习资料
Node 学习资料: 资料名称 网址 Node.js 中文API文档 http://nodejs.cn/api/ Node 菜鸟教程 http://www.runoob.com/nodejs/node ...
