Look into Bitmap images
What's a Bitmap image?
I'm not going to explain the differences between raster and vector images, nor the difference between bitmap image with extension .bmp and jpg/png images. Herein, the bitmap refers to raster images with .bmp extension only.
Bitmap is uncompressed, and the image is represented with arrays, namely, RGB arrays.
What's the storage of a bitmap
File structure of a bitmap
- The bitmaps stored on the physical devices contains serval parts:
- BITMAPINFO
1. BITMAPINFOHEADER
2. RGBQUAD
2. The stored data in array
A bitmap file is composed with
- BITMAPFILEHEADER
- BITMAPINFOHEADER
- Data array
The definition are
typedef struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER {
WORD bfType; // 2 bytes
DWORD bfSize; // 4 bytes
WORD bfReserved1; // 2 bytes
WORD bfReserved2; // 2 bytes
DWORD bfOffBits; // 4 bytes
} BITMAPFILEHEADER, *LPBITMAPFILEHEADER, *PBITMAPFILEHEADER;
typedef struct tagBITMAPINFO {
BITMAPINFOHEADER bmiHeader;
RGBQUAD bmiColors[1]; // the '1' here is pretty tricky
} BITMAPINFO, *LPBITMAPINFO, *PBITMAPINFO;
typedef struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER {
DWORD biSize; // 8 bytes
LONG biWidth; // 4 bytes
LONG biHeight; // 4 bytes
WORD biPlanes; //
WORD biBitCount;
DWORD biCompression;
DWORD biSizeImage;
LONG biXPelsPerMeter;
LONG biYPelsPerMeter;
DWORD biClrUsed;
DWORD biClrImportant;
} BITMAPINFOHEADER, *PBITMAPINFOHEADER;
typedef struct tagRGBQUAD {
BYTE rgbBlue;
BYTE rgbGreen;
BYTE rgbRed;
BYTE rgbReserved;
} RGBQUAD;
Let's use Lena.bmp as an illustration:

(Well, this blog doesn;t support BMP image, please see the attach file)
Open it with a hex editor, such as WinHex, and it shows
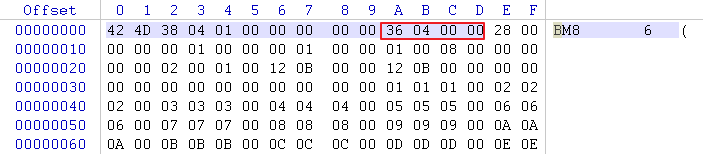
The highlighted 14 bytes are BITMAPFILEHEADER,
WORD bfType -> 0x4D42
DWORD bfSize -> 0x00010438 = 66616
WORD bfReserved1 -> 0x0000 = 0
WORD bfReserved2 -> 0x0000 = 0
DWORD bfOffBits -> 0x00000436 = 1078
bfTypeshows that this file is a bitmap file;bfSizeis the file size, as we can see below, the file sis 66,614 bytes;bfReserved1andbfReserved2must be zerosbfOffBitsis the offset, in bytes, from the beginning of the BITMAPFILEHEADER structure to the bitmap bits.
e:\temp\code\MFC_PICTURE_TEST\Look into Bitmap images.assets\1566902617332.png
And this is the start of array data,

seen what I mean?
The next is BITMAPINFOHEADER, and the data are highlighted in different colors,

and these values can be calculated as
DWORD biSize = 0x00000028 = 40
LONG biWidth = 0x00000100 = 256
LONG biHeight = 0x00000100 = 256
WORD biPlanes = 0x0001 = 1
WORD biBitCount = 0x0008 = 8
DWORD biCompression = 0x00000000 = 0
DWORD biSizeImage = 0x00010002 = 65,538
LONG biXPelsPerMeter = 0x00000B12 = 2,834
LONG biYPelsPerMeter = 0x00000B12 = 2,834
DWORD biClrUsed = 0x000000 = 0
DWORD biClrImportant = 0x000000 = 0
And we can see,
0x0436 + 0x00010002 = 0x00010438
1,078 + 65,538 = 66,616
i.e.
data_start_offset + data_length = file_end
It's the start of data, however, since Lena.bmp is a gray image, all the three channels are same, you can find a pure red/blue image, you will find that, the bitmap is stored in [B, G, R, reserved] order, therefore, if you want to interpret in RGB mode, you should be careful with it.

[C++]Read Bitmap File
The following code are mainly from this website, slightly modified.
typedef unsigned int Uint8;
Uint8* datBuff[2] = { nullptr, nullptr }; // Header buffers
Uint8* pixels = nullptr; // Pixels
BITMAPFILEHEADER* bmpHeader = nullptr; // Header
BITMAPINFOHEADER* bmpInfo = nullptr; // Info
// The file... We open it with it's constructor
std::ifstream file(_T("Lena.bmp"), std::ios::binary);
if (!file){
std::cout << "Failure to open bitmap file.\n";
return 1;
}
// Allocate byte memory that will hold the two headers
datBuff[0] = new Uint8[sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER)];
datBuff[1] = new Uint8[sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER)];
file.read((char*)datBuff[0], sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER));
file.read((char*)datBuff[1], sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER));
// Construct the values from the buffers
bmpHeader = (BITMAPFILEHEADER*)datBuff[0];
bmpInfo = (BITMAPINFOHEADER*)datBuff[1];
// Check if the file is an actual BMP file
if (bmpHeader->bfType != 0x4D42){
std::cout << "File isn't a bitmap file\n";
return 2;
}
// First allocate pixel memory
pixels = new Uint8[bmpInfo->biSizeImage];
// Go to where image data starts, then read in image data
file.seekg(bmpHeader->bfOffBits);
file.read((char*)pixels, bmpInfo->biSizeImage);
// First allocate pixel memory
pixels = new Uint8[bmpInfo->biSizeImage];
// Go to where image data starts, then read in image data
file.seekg(bmpHeader->bfOffBits);
file.read((char*)pixels, bmpInfo->biSizeImage);
// Set width and height to the values loaded from the file
int w = bmpInfo->biWidth;
int h = bmpInfo->biHeight;
// We're almost done. We have our image loaded, however it's not in the right format.
// .bmp files store image data in the BGR format, and we have to convert it to RGB.
// Since we have the value in bytes, this shouldn't be to hard to accomplish
Uint8 tmpRGB = 0; // Swap buffer
for (unsigned long i = 0; i < bmpInfo->biSizeImage; i += 3){
tmpRGB = pixels[i];
pixels[i] = pixels[i + 2];
pixels[i + 2] = tmpRGB;
}
delete[] datBuff[0];
delete[] datBuff[1];
delete[] pixels;
Create Bitmap Image in memory, and draw on screen
The code is mainly from this webpage, slightly modified.
Again, the reference are given:
void CChildView::OnPaint()
{
CPaintDC dc(this); // device context for painting
HDC hdc = dc.m_hDC;
int nWidth = 100;
int nHeight = 100;
int nChannels = 3;
int nImages = 3; // three images in a row, presented in a column
auto nSize = nWidth * nHeight * nChannels * nImages;
unsigned char* data = new unsigned char[nSize] {0};
//memset(data, 0xFF, nSize);
long split = nWidth * nHeight / 4,
nPixel = nWidth * nHeight; // Pixels in an image
// Fill the different images for differnt channels
unsigned char* dat = data;
for (int i = 0; i < nPixel; ++i, dat += 3) // Image 0
dat[0] = (i / nWidth) * (255.0 / nHeight);
for (int i = 0; i < nPixel; ++i, dat += 3) // Image 1
dat[1] = (i / nWidth) * (255.0 / nHeight);
for (int i = 0; i < nPixel; ++i, dat += 3) // Image 2
dat[2] = (i / nWidth) * (255.0 / nHeight);
// Allocate enough memory for the BITMAPINFOHEADER and 256 RGBQUAD palette entries
// NOTE: the pallet bytes are ONLY NEEDED for color LUT images ...
// not needed here
int nColors = 0; // In BI_RGB image, the look-up-table isn't used, so the size can be zero
LPBITMAPINFO lpbi = (LPBITMAPINFO) new BYTE[sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER)+ (nColors * sizeof(RGBQUAD))];
// These are all the members of the bitmap header struct
lpbi->bmiHeader.biSize = sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER); // bytes
lpbi->bmiHeader.biWidth = nWidth; // pixels units
lpbi->bmiHeader.biHeight = -nHeight * 3; // negative = = top down; pos =
// origin LLeft
lpbi->bmiHeader.biPlanes = 1; // must be 1
lpbi->bmiHeader.biBitCount = 24; // can be 32 for 4-byte pixels
// (Upper byte ignored)
lpbi->bmiHeader.biCompression = BI_RGB; // BI_RGB means uncompressed
lpbi->bmiHeader.biSizeImage = 0; // size of img in bytes; 0 okay
// for BI_RGB
lpbi->bmiHeader.biXPelsPerMeter = 0; // physical device information unavailable
lpbi->bmiHeader.biYPelsPerMeter = 0; // physical device information unavailable
lpbi->bmiHeader.biClrUsed = 0; // Look-Up-Tables (LUT) only
lpbi->bmiHeader.biClrImportant = 0; // LUTs only
// Draw the image into the CRT device
::SetDIBitsToDevice(
hdc, // handle to DC
0, 0, // x-y-coord of destination upper-left corner
nWidth, nHeight * 3, // width-height of source rectangle
// three images present in one column
0, 0, // x-y-coord of source upper-left corner
0, // uStartScan, // first scan line in array
nHeight * 3, // number of scan lines ...
data, // array of DIB bits
lpbi, // bitmap information
DIB_RGB_COLORS); // RGB vs. palette indexes ... RGB means raw
delete[] data;
delete[] lpbi;
}

As we can see from the result, the array is stored in [B, G, R] sequence, and no more reserved byte is need.
Besides, if you uncomment the memset(data, 0xFF, nSize); at the 12th line, which means you set all the other values to be 255, you'll get a more beautiful image as

If you are a Chinese, this blog may help you.
The source code can be found in: 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/12NCP1tQjtLOdDccODOwpEg 提取码: 4uka 复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操作更方便哦
Look into Bitmap images的更多相关文章
- [翻译]开发文档:android Bitmap的高效使用
内容概述 本文内容来自开发文档"Traning > Displaying Bitmaps Efficiently",包括大尺寸Bitmap的高效加载,图片的异步加载和数据缓存 ...
- 【开源毕设】一款精美的家校互动APP分享——爱吖校推 [你关注的,我们才推](持续开源更新3)附高效动态压缩Bitmap
一.写在前面 爱吖校推如同它的名字一样,是一款校园类信息推送交流平台,这么多的家校互动类软件,你选择了我,这是我的幸运.从第一次在博客园上写博客到现在,我一次一次地提高博文的质量和代码的可读性,都是为 ...
- Android Bitmap 和 ByteArray的互相转换
Android Bitmap 和 ByteArray的互相转换 移动平台图像处理,需要将图像传给native处理,如何传递?将bitmap转换成一个 byte[] 方便传递也方便cpp代码直接处理图像 ...
- Android-Drawable、Bitmap、byte[]、资源文件相互转换
我们在Android的开发中,经常可以遇到图片的处理,当中,有很多是 Bitmap.Drawable.byte[]和资源文件它们直接相互转换. 今天就此总结一下: 1.资源文件转为Drawable 2 ...
- bitmap对海量无重复的整数排序--转
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u013074465/article/details/46956295 现在有n个无重复的正整数(n 小于10的7次方),如果内存限制在1.5M以内 ...
- 基于位图(Bitmap、BitmapData)的图片处理方法(C#)
目前操作位图的主流方法有三种: 1.基于Bitmap像素的处理方法,以GetPixel()和SetPixel()方法为主.方法调用简单,但是效率偏低. 2.基于内存的像素操作方法,以System.Ru ...
- android:布局、绘制、内存泄露、响应速度、listview和bitmap、线程优化以及一些优化的建议!
1.布局优化 首先删除布局中无用的控件和层级,其次有选择地使用性能较低的viewgroup,比如布局中既可以使用RelativeLayout和LinearLayout,那我们就采用LinearLayo ...
- 获取View的截图-将View转换为Bitmap对象
开发中,有时候需要获取View的截图来做动画来达到动画流程的目的 原理:将View的内容画到一个Bitmap画布上,然后取出 下面封装了一个从View生成Bitmap的工具类 /** * 将View转 ...
- bitmap解码
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #define BYTE unsigned c ...
- Bitmap转换成BitmapImage
public BitmapImage BitmapToBitmapImage(System.Drawing.Bitmap bitmap) { MemoryStream ms = new MemoryS ...
随机推荐
- Python_函数做字典的值
当需要用到3个及以上的if...elif...else时就要考虑该方法进行简化 通过将函数名称当做字典的值,利用字典的关键字查询,可以快速定位函数,进行执行 [场景]用户查询信息,输入fn查询,执行对 ...
- 致远OA_0day批量植Cknife马一步到位
最近各位师傅都在刷这个嘛,原本的exp是上传一个test123456.jsp的命令执行的马子,不过我在试的时候发现替换成C刀一句话出错,原因未知,并且test123456.jsp如果存在的话用原来ex ...
- nginx::certbot制作免费证书
环境 Ubuntu8.04apt-get update apt-get install software-properties-common add-apt-repository ppa:certbo ...
- windows下Python开发错误记录以及解决方法
windows下使用pip提示ImportError: cannot import name 'main' 原因:将pip更新为10.0.0后库里面的函数有所变动造成这个问题 解决方法:先卸载现在的p ...
- volatile关键字使用
1.volatile 使用场景(多线程情况下): 适合使用在 一写多读 的情况下: 2.volatile 理解分析: 使用 volatile 关键字修饰的变量,值在改变时会直接刷新到 主内存 中,而不 ...
- Java基础(十六)断言(Assertions)
1.断言的概念 假设确信某个属性符合要求,并且代码的执行依赖于这个属性. 断言机制允许在测试期间向代码插入一些检查语句,当代码发布时,这些插入的检查语句将会被自动地移走. 断言失败是致命的,不可恢复的 ...
- MongoDB一次节点宕机引发的思考(源码剖析)
目录 简介 日志分析 副本集 如何实现 Failover 心跳的实现 electionTimeout 定时器 业务影响评估 参考链接 声明:本文同步发表于 MongoDB 中文社区,传送门: http ...
- ios发送短信验证码计时器的swift实现
转载自:http://www.jianshu.com/p/024dd2d6e6e6# Update: Xcode 8.2.1 Swift 3 先介绍一下 属性观测器(Property Observer ...
- 数竞大佬jhc的三角函数复习题
班主任让数竞大佬jhc整理的三角函数复习题,我参与编辑完成.个别题目来自参考书.度盘pdf格式下载:复习题提取码419d,答案提取码5a12 "单纯"的运算 本文由蒋浩川原创,由\ ...
- 洛谷P5520 【[yLOI2019] 青原樱】
这题是小学奥数啊. 题意:求\(m\)个不同物品两两不相邻的方案数. 直接排列组合. 我们可以减掉他们之间最少需要空出来的位数--\(m-1\)个空位 像这样,我们只用留\(m-1\)个空位放在每两个 ...
