用canvas实现一个colorpicker
http://www.cnblogs.com/ufex/p/6382982.html
每个浏览器都有自己的特点,比如今天要做的colorpicker就是,一千个浏览器,一千个哈姆雷特,一千个colorpicker。今天canvas系列就用canvas做一个colorpicker。
**********************************************************************
效果图和demo
突然翻到了之前用js和dom写的一个colorpicker,比较挫,扔张图就好(old)

这个真的很挫,性能很差,因为每一个可选的颜色值都是一个dom,如果要实现256*256,那浏览器就爆了~~~~~
好,回到今天的demo(new)

demo链接: https://win7killer.github.io/can_ps/src/demo/color_picker.html
没错,就是照着PS的颜色选择器的样子仿的。
**********************************************************************
实现
首先我们来看效果图分析怎么做:
1.左侧colorbar
 左侧提供一系列过渡色,不难看出,这个是“红黄绿青蓝紫”这六种颜色,然后加以过渡色处理来的。最后紫色还要过渡回到红色。
左侧提供一系列过渡色,不难看出,这个是“红黄绿青蓝紫”这六种颜色,然后加以过渡色处理来的。最后紫色还要过渡回到红色。
另外换成环状的可能更加好识别,如下图:
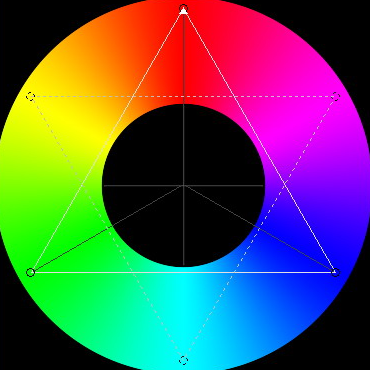
那么,我们就可以用canvas的过渡色来实现左侧这个区域,
代码如下:

1 function colorBar() {
2 var gradientBar = ctx.createLinearGradient(0, 0, 0, width);
3 gradientBar.addColorStop(0, '#f00');
4 gradientBar.addColorStop(1 / 6, '#f0f');
5 gradientBar.addColorStop(2 / 6, '#00f');
6 gradientBar.addColorStop(3 / 6, '#0ff');
7 gradientBar.addColorStop(4 / 6, '#0f0');
8 gradientBar.addColorStop(5 / 6, '#ff0');
9 gradientBar.addColorStop(1, '#f00');
10
11 ctx.fillStyle = gradientBar;
12 ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 20, width);
13 }

这里涉及到canvas的fillStyle或者strokenStyle的填充对象,可以使用过渡色对象(自己瞎叫的名字),了解更多可以去w3cschool。
2.中间颜色区

中间这块乍看很简单,再看有点蒙bi,三看才搞清楚怎么搞。
乍看:其实就是左侧选中的那个颜色(比如A),然后进行过渡处理,不还是过渡么。
再看:恩,颜色,然后黑色,白色,三种颜色三个角怎么过渡~~~~(如果有快捷的过渡实现方式请留言告知我,THX)。
三看:那么,拆借一下,比如红色到白色,然后加一层黑色到透明?是滴,就是这么个方案。(我自己之前弯路到了红色到黑色,白色到透明)
那么就是借助两次过渡色的填充,实现中间色块区域。
代码如下:

1 function colorBox(color) {
2 // 底色填充,也就是(举例红色)到白色
3 var gradientBase = ctx.createLinearGradient(30, 0, width + 30, 0);
4 gradientBase.addColorStop(1, color);
5 gradientBase.addColorStop(0, 'rgba(255,255,255,1)');
6 ctx.fillStyle = gradientBase;
7 ctx.fillRect(30, 0, width, width);
8
9 // 第二次填充,黑色到透明
10 var my_gradient1 = ctx.createLinearGradient(0, 0, 0, width);
11 my_gradient1.addColorStop(0, 'rgba(0,0,0,0)');
12 my_gradient1.addColorStop(1, 'rgba(0,0,0,1)');
13 ctx.fillStyle = my_gradient1;
14 ctx.fillRect(30, 0, width, width);
15 }

需要注意,第一次填充,是从横向填充,这时候中间色块的左边已经不是canvas的原点,所以加了偏移量30px
第二次填充纵向,Y轴还是0。
这个在实际应用中要注意。
到这里,左侧canvas绘制的东西就差不多了。
3. 颜色选择事件处理
首先明确交互事件:
选择左侧colorbar(比如#ff0),中间base颜色要跟着变化,右上角也要是对应颜色(#ff0)【这个时候其实也可以得到选择的颜色,可以结束交互】;
选择中间区域的颜色,左侧不变,可以获取到对应的颜色值,结束交互。
最终就是在右侧的dom区域展示所选到的颜色。
canvas中没有dom对象,所以鼠标点击事件要靠鼠标的位置来确定是否进行相应处理。而且我们绘制的不是path对象,也无法使用inpath之类的方法来判断。
点击事件代码:

1 can.addEventListener('click', function(e) {
2 var ePos = {
3 x: e.offsetX || e.layerX,
4 y: e.offsetY || e.layerY
5 }
6 var rgbaStr = '#000';
7 if (ePos.x >= 0 && ePos.x < 20 && ePos.y >= 0 && ePos.y < width) {
8 // in
9 rgbaStr = getRgbaAtPoint(ePos, 'bar');
10 colorBox('rgba(' + rgbaStr + ')');
11 } else if (ePos.x >= 30 && ePos.x < 30 + width && ePos.y >= 0 && ePos.y < width) {
12 rgbaStr = getRgbaAtPoint(ePos, 'box');
13 } else {
14 return;
15 }
16 outColor(rgbaStr.slice(0, 3).join());
17 cur.style.left = ePos.x + 'px';
18 cur.style.top = ePos.y + 'px';
19 cur.style.outlineColor = (rgbaStr[0] > 256 / 2 || rgbaStr[1] > 256 / 2 || rgbaStr[2] > 256 / 2) ? '#000' : '#fff';
20 });

其中,getRgbaAtPoint是最终的获取颜色值的方法,需要根据不同的鼠标位置传参来决定选取左侧还是右侧图像
获取颜色就比较简单了,就是拿到对应区域的imageData,然后从颜色数组中获取到对应位置的颜色值即可。
做过canvas像素处理的同学会比较明白,不明白的建议先去把getImageData方法看一看,了解一下
获取颜色代码:

1 function getRgbaAtPoint(pos, area) {
2 if (area == 'bar') {
3 var imgData = ctx.getImageData(0, 0, 20, width);
4 } else {
5 var imgData = ctx.getImageData(0, 0, can.width, can.height);
6 }
7
8 var data = imgData.data;
9 var dataIndex = (pos.y * imgData.width + pos.x) * 4;
10 return [
11 data[dataIndex],
12 data[dataIndex + 1],
13 data[dataIndex + 2],
14 (data[dataIndex + 3] / 255).toFixed(2),
15 ];
16 }

这时候拿到的就是rgba颜色对应的值。
需要注意,最后一个数据时alpha通道,canvas的imageData里是0-255【没记错的话】,而不是我们平常用的0-1,所以要做转换。
颜色输出&转换:
拿到颜色后就可以输出到右侧了。
右侧只是用了rgb三通道,所以取数组前三位就好。
至于hex颜色,则用rgb来转换。
转换代码如下:

1 function rgb2hex(rgb) {
2 var aRgb = rgb instanceof Array ? rgb : (rgb.split(',') || [0, 0, 0]);
3 var temp;
4 return [
5 (temp = Number(aRgb[0]).toString(16)).length == 1 ? ('0' + temp) : temp,
6 (temp = Number(aRgb[1]).toString(16)).length == 1 ? ('0' + temp) : temp,
7 (temp = Number(aRgb[2]).toString(16)).length == 1 ? ('0' + temp) : temp,
8 ].join('');
9 }
10
11 function hex2rgb(hex) {
12 if (hex.length == 3) {
13 hex = hex[0] + hex[0] + hex[1] + hex[1] + hex[2] + hex[2];
14 }
15 return [
16 parseInt(hex[0] + hex[1], 16),
17 parseInt(hex[2] + hex[3], 16),
18 parseInt(hex[4] + hex[5], 16),
19 ].join();
20 }

简单来说,就是10进制与16进制的转换。
有个点,就是rgb的三个值,分别对应的是hex的每两个值,比如rgb(255,0,255)对用到hex则分别是 “ff,00,ff”,综合起来就是“#ff00ff”,可以简写“#f0f”。
额外效果:
中间的颜色选择还有个效果,就是鼠标拖拽到哪里,就选中相应的颜色。
鼠标拖拽事件大家都不陌生,直接上代码,不废话

1 can.addEventListener('mousedown', function(e) {
2 var ePos = {
3 x: e.layerX || e.offsetX,
4 y: e.layerY || e.offsetY
5 }
6 if (ePos.x >= 30 && ePos.x < 30 + width && ePos.y >= 0 && ePos.y < width) {
7 document.onmousemove = function(e) {
8 var pos = {
9 x: e.clientX,
10 y: e.clientY
11 }
12
13 pos.x = pos.x < 30 ? 30 : pos.x && (pos.x > (30 + width - 1) ? (30 + width - 1) : pos.x);
14 pos.y = pos.y < 0 ? 0 : pos.y && (pos.y > (width - 1) ? (width - 1) : pos.y);
15
16 rgbaStr = getRgbaAtPoint(pos, 'box');
17 cur.style.left = pos.x + 'px';
18 cur.style.top = pos.y + 'px';
19 cur.style.outlineColor = (rgbaStr[0] > 256 / 2 || rgbaStr[1] > 256 / 2 || rgbaStr[2] > 256 / 2) ? '#000' : '#fff';
20 outColor(rgbaStr.slice(0, 3).join());
21 };
22 document.onmouseup = function() {
23 // outColor(rgbaStr.slice(0, 3).join());
24 document.onmouseup = document.onmousemove = null;
25 }
26 }
27
28 });

这样,每段代码拼凑起来,就是整体的架子了,附上最终代码(比较长,折叠了):
**********************************************************************
写在最后:
最终写完效果在自己玩耍的过程中,发现浏览器对于canvas的过渡色实现有点问题。chrome很明显,FF稍微好一点。

如图: 按道理来说,最下边选到的颜色应该都是rgb(0,0,0)才对,但是图上可见,有些地方并不是~~~
大多数还是000,某些点某个通道有可能会出现1。原因未知。
尝试了email给chrome邮箱,可能我英语比较差人家没看懂,也可能我问题没描述清楚,反正后来没有回复,之后的浏览器更新也没有处理。
相应的,css3的过渡色则没有一丁点问题。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh"> <head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body {
background: #535353;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
} canvas {
cursor: crosshair;
} #cur {
width: 3px;
height: 3px;
outline: 2px solid #535353;
margin-left: -1px;
margin-top: -1px;
position: absolute;
} .wrapper {
position: relative;
} #color_show {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background: #f00;
} .panel {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
position: fixed;
top: 20px;
right: 20px;
background-color: #fff;
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 2em;
}
</style>
</head> <body>
<div class="wrapper">
<canvas id="canvas" width="600" height="600"></canvas>
<em id="cur"></em>
<div class="panel">
<div id="color_show"></div>
<label>
rgb <input type="text" class="color_input" value="" id="rgb_value">
</label><br>
<label>
hex <input type="text" class="color_input" value="" id="hex_value">
</label>
</div>
</div>
<script>
(function() {
var width = 256;
var can = document.getElementById('canvas');
var ctx = can.getContext('2d');
var curColor = 'rgba(255,0,0,1)';
var cur = document.getElementById('cur');
var rgbValue = document.getElementById('rgb_value');
var hexValue = document.getElementById('hex_value');
var colorShow = document.getElementById('color_show'); var aColorInput = document.getElementsByClassName('color_input'); function colorBar() {
var gradientBar = ctx.createLinearGradient(0, 0, 0, width);
gradientBar.addColorStop(0, '#f00');
gradientBar.addColorStop(1 / 6, '#f0f');
gradientBar.addColorStop(2 / 6, '#00f');
gradientBar.addColorStop(3 / 6, '#0ff');
gradientBar.addColorStop(4 / 6, '#0f0');
gradientBar.addColorStop(5 / 6, '#ff0');
gradientBar.addColorStop(1, '#f00'); ctx.fillStyle = gradientBar;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 20, width);
} function rgb2hex(rgb) {
var aRgb = rgb instanceof Array ? rgb : (rgb.split(',') || [0, 0, 0]);
var temp;
return [
(temp = Number(aRgb[0]).toString(16)).length == 1 ? ('0' + temp) : temp,
(temp = Number(aRgb[1]).toString(16)).length == 1 ? ('0' + temp) : temp,
(temp = Number(aRgb[2]).toString(16)).length == 1 ? ('0' + temp) : temp,
].join('');
} function hex2rgb(hex) {
if(hex.length == 3) {
hex = hex[0] + hex[0] + hex[1] + hex[1] + hex[2] + hex[2];
}
return [
parseInt(hex[0] + hex[1], 16),
parseInt(hex[2] + hex[3], 16),
parseInt(hex[4] + hex[5], 16),
].join();
} function putCurDom(color) {
if(/([0-9a-f]{3}|[0-9a-f]{6})/i.test(color)) {
// hex
color = hex2rgb(color);
} else if(color instanceof Array) {
color = color.join(',');
} else if(/\d{1,3}(\,\d{1,3}){2}/i.test(color)) { } else {
return;
}
} function colorBox(color) {
// 底色填充,也就是(举例红色)到白色
var gradientBase = ctx.createLinearGradient(30, 0, width + 30, 0);
gradientBase.addColorStop(1, color);
gradientBase.addColorStop(0, 'rgba(255,255,255,1)');
ctx.fillStyle = gradientBase;
ctx.fillRect(30, 0, width, width);
// 第二次填充,黑色到透明
var my_gradient1 = ctx.createLinearGradient(0, 0, 0, width);
my_gradient1.addColorStop(0, 'rgba(0,0,0,0)');
my_gradient1.addColorStop(1, 'rgba(0,0,0,1)');
ctx.fillStyle = my_gradient1;
ctx.fillRect(30, 0, width, width);
} function init() {
colorBar();
colorBox(curColor);
bind();
} function bind() {
can.addEventListener('click', function(e) {
var ePos = {
x: e.offsetX || e.layerX,
y: e.offsetY || e.layerY
}
var rgbaStr = '#000';
if(ePos.x >= 0 && ePos.x < 20 && ePos.y >= 0 && ePos.y < width) {
// in
rgbaStr = getRgbaAtPoint(ePos, 'bar');
colorBox('rgba(' + rgbaStr + ')');
} else if(ePos.x >= 30 && ePos.x < 30 + width && ePos.y >= 0 && ePos.y < width) {
rgbaStr = getRgbaAtPoint(ePos, 'box');
} else {
return;
}
outColor(rgbaStr.slice(0, 3).join());
cur.style.left = ePos.x + 'px';
cur.style.top = ePos.y + 'px';
cur.style.outlineColor = (rgbaStr[0] > 256 / 2 || rgbaStr[1] > 256 / 2 || rgbaStr[2] > 256 / 2) ? '#000' : '#fff';
}); can.addEventListener('mousedown', function(e) {
var ePos = {
x: e.layerX || e.offsetX,
y: e.layerY || e.offsetY
}
if(ePos.x >= 30 && ePos.x < 30 + width && ePos.y >= 0 && ePos.y < width) {
document.onmousemove = function(e) {
var pos = {
x: e.clientX,
y: e.clientY
} pos.x = pos.x < 30 ? 30 : pos.x && (pos.x > (30 + width - 1) ? (30 + width - 1) : pos.x);
pos.y = pos.y < 0 ? 0 : pos.y && (pos.y > (width - 1) ? (width - 1) : pos.y); rgbaStr = getRgbaAtPoint(pos, 'box');
cur.style.left = pos.x + 'px';
cur.style.top = pos.y + 'px';
cur.style.outlineColor = (rgbaStr[0] > 256 / 2 || rgbaStr[1] > 256 / 2 || rgbaStr[2] > 256 / 2) ? '#000' : '#fff';
outColor(rgbaStr.slice(0, 3).join());
};
document.onmouseup = function() {
// outColor(rgbaStr.slice(0, 3).join());
document.onmouseup = document.onmousemove = null;
}
} });
} function outColor(rgb) {
rgbValue.value = rgb;
hexValue.value = rgb2hex(rgb);
colorShow.style.backgroundColor = 'rgb(' + rgb + ')';
} function getRgbaAtPoint(pos, area) {
if(area == 'bar') {
var imgData = ctx.getImageData(0, 0, 20, width);
} else {
var imgData = ctx.getImageData(0, 0, can.width, can.height);
} var data = imgData.data;
var dataIndex = (pos.y * imgData.width + pos.x) * 4;
return [
data[dataIndex],
data[dataIndex + 1],
data[dataIndex + 2],
(data[dataIndex + 3] / 255).toFixed(2),
];
} init();
})()
</script>
</body> </html>
用canvas实现一个colorpicker的更多相关文章
- 【canvas系列】用canvas实现一个colorpicker
每个浏览器都有自己的特点,比如今天要做的colorpicker就是,一千个浏览器,一千个哈姆雷特,一千个colorpicker.今天canvas系列就用canvas做一个colorpicker. ** ...
- 【canvas系列】用canvas实现一个colorpicker(类似PS的颜色选择器)
每个浏览器都有自己的特点,比如今天要做的colorpicker就是,一千个浏览器,一千个哈姆雷特,一千个colorpicker.今天canvas系列就用canvas做一个colorpicker. ** ...
- 深夜,用canvas画一个时钟
深夜,用canvas画一个时钟 查看demo 这几天准备阿里巴巴的笔试,可以说已经是心力交瘁,自从阿里和蘑菇街的内推被刷掉之后,开始越来越怀疑起自己的能力来,虽然这点打击应该是微不足道的.毕竟校招在刚 ...
- html5 canvas 实现一个简单的叮当猫头部
原文:html5 canvas 实现一个简单的叮当猫头部 html5的canvas是很强大的,今天也是温习了一下之前的基础知识,然后学着做了一个简单的小案例.虽然在这一块几乎空白,但还是乐于尝试... ...
- 使用canvas制作一个移动端画板
概述 使用canvas做一个画板,代码里涵盖了一些canvas绘图的基本思想,各种工具的类也可以分别提出来用 详细 代码下载:http://www.demodashi.com/demo/10503.h ...
- 10分钟,利用canvas画一个小的loading界面
首先利用定义下canvas得样式 <canvas width="1024" height="720" id="canvas" styl ...
- 用Canvas画一个刮刮乐
Canvas 通过 JavaScript 来绘制 2D图形.Canvas 是逐像素进行渲染的.开发者可以通过javascript脚本实现任意绘图.Canvas元素是HTML5的一部分,允许脚本语言动态 ...
- 用HTML5的canvas做一个时钟
对于H5来说,canvas可以说是它最有特色的一个地方了,有了它之后我们可以随意的在网页上画各种各样的图形,做一些小游戏啊什么的.canvas这个标签的用法,在网上也有特别多的教程了,这里就不作介绍了 ...
- 使用 Canvas 实现一个类似 Google 的可视化的页面错误反馈库
使用 Canvas 实现一个类似 Google 的可视化的页面错误反馈库 iframe 嵌套 iframe iframe 包含 复制的 HTML 页面 和支持可以拖拽的工具栏 鼠标经过上面,智能识别 ...
随机推荐
- 对于Nginx+PHP实现大文件上传时候需要修改的参数
post_max_size表示POST表单提交的最大大小upload_max_filesize 表示文件上传的最大大小. 通常post_max_size设置的值必须必upload_max_filesi ...
- Python自动化测试框架——数据驱动(从代码中读取)
今天小编要介绍的是数据驱动最简单和最常用的一种方法,由于只是介绍方法,代码操作后的美观程度略有缺陷,介意者可以自行改动 还是以163邮箱登录为例: 设计一个存放数据的类,这个类的参数是我们需要修改的数 ...
- Spring Cloud Stream在同一通道根据消息内容分发不同的消费逻辑
应用场景 有的时候,我们对于同一通道中的消息处理,会通过判断头信息或者消息内容来做一些差异化处理,比如:可能在消息头信息中带入消息版本号,然后通过if判断来执行不同的处理逻辑,其代码结构可能是这样的: ...
- Solr5.0.0 DIH之增量索引
定时索引相关知识 增量更新需要配置个sql(deltaImportQuery.deltaQuery) deltaImportQuery="select * where id='${dih.d ...
- HDU 4089 && UVa 1498 Activation 带环的概率DP
要在HDU上交的话,要用滚动数组优化一下空间. 这道题想了很久,也算是想明白了,就好好写一下吧. P1:激活游戏失败,再次尝试. P2:连接失服务器败,从队首排到队尾. P3:激活游戏成功,队首的人出 ...
- Head First HTML5 Programming笔记--chapter2 介绍Javascript和DOM
你已经了解了HTML标记(也称为结构),而且知道了CSS样式(也称为表示),剩下的就是Javascript(也称为行为). JavaScript的工作方式 1. 编写 你创建HTML标记和JavaSc ...
- 在后台编辑器Text和Visual切换时,部分代码丢失的解决方法
function fix_tiny_mce_before_init( $in ) { // You can actually debug this without actually needing A ...
- TOJ 2596: Music Notes
2596: Music Notes Time Limit(Common/Java):1000MS/10000MS Memory Limit:65536KByteTotal Submit: 3 ...
- 【drp 12】再识转发和重定向:SpringMVC无法跳转页面
最近再使用SpringMVC进行页面跳转的时候,不知道发生了什么,始终都无法正确跳转.后来问题解决了,发现是对于转发和重定向没有能很好的理解,以此写篇博客,权当做积累了! 声明:本博客的所有代码,均为 ...
- Dialog共通写法(两个button)
package jp.co.hyakujushibank.view import android.app.Dialogimport android.content.Contextimport andr ...
