Spring MVC Hello World Example(转)
In Spring MVC web application, it consist of 3 standard MVC (Model, Views, Controllers) components :
- Models – Domain objects that are processed by service layer (business logic) or persistent layer (database operation).
- Views – Usually JSP page written with Java Standard Tag Library (JSTL).
- Controllers – Interact with service layer for business processing and return a Model.
See following figures 1.1, 1.2 to demonstrate how Spring MVC web application handle a web request.
Figure 1.1 – Image copied from Spring MVC reference with slightly modification.
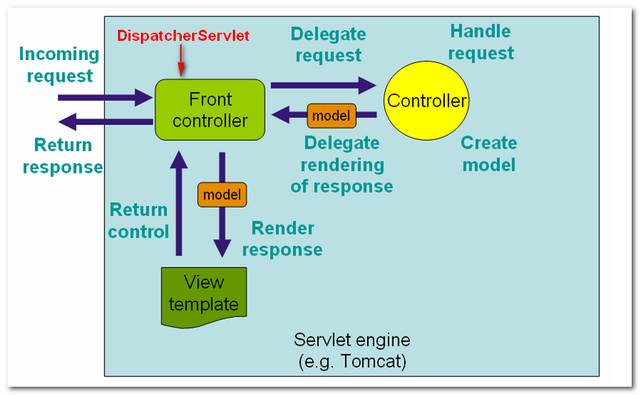
Figure 1.2 – P.S Image copied from book : Spring Recipes
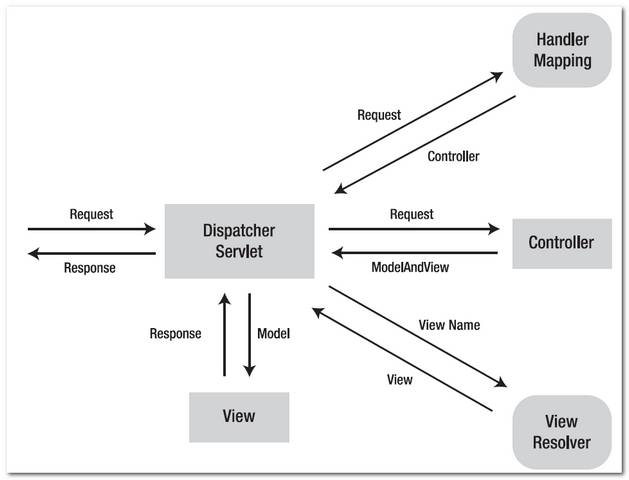
Spring MVC Tutorial
In this tutorial, you will create a simple Spring MVC hello world web application in order to understand the basic concepts and configurations of this framework.
Technologies used in this tutorial.
- Spring 2.5.6
- JDK 1.6
- Eclipse 3.6
- Maven 3
1. Directory Structure
Final directory structure of this tutorial.

2. Dependency library
Spring MVC required two core dependency libraries, spring-version.jar and spring-mvc-version.jar. If you are using JSP page with jstl, include the jstl.jar and standard.jar as well.
File : pom.xml
<!-- Spring framework -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring MVC framework -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>2.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JSTL -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- for compile only, your container should have this -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
3. Spring Controller
Spring comes with many Controllers, normally, you just need to extend the AbstractController, if you do not have other special requirement, and override the handleRequestInternal() method and return a ModelAndView object.
File : HelloWorldController.java
package com.mkyong.common.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.AbstractController;
public class HelloWorldController extends AbstractController{
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleRequestInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView("HelloWorldPage");
model.addObject("msg", "hello world");
return model;
}
}
- ModelAndView(“HelloWorldPage”) – The “HelloWorldPage” will pass to Spring’s viewResolver later, to indentify which view should return back to the user. (see step 6)
- model.addObject(“msg”, “hello world”) – Add a “hello world” string into a model named “msg”, later you can use JSP EL ${msg} to display the “hello world” string.
4. View (JSP page)
In this case, “view” is a jSP page, you can display the value “hello world” that is store in the model “msg” via expression language (EL) ${msg}.
File : HelloWorldPage.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<html>
<body>
<h1>Spring MVC Hello World Example</h1>
<h2>${msg}</h2>
</body>
</html>
5. Spring Configuration
In web.xml, declared a DispatcherServlet servlet, named “mvc-dispatcher“, and act as the front-controller to handle all the entire web request which end with “htm” extension.
File : web.xml
<web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
<display-name>Spring Web MVC Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.htm</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
Alternatively, you can explicitly specify the Spring configuration file in the “contextConfigLocation” servlet parameter, to ask Spring to load your configurations besides the default “mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml“.
File : web.xml
<web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd">
<display-name>Spring Web MVC Application</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.htm</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/SpringMVCBeans.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>
6. Spring Beans Configuration
Declared the Spring Controller and viewResolver.
File : mvc-dispatcher-servlet.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean name="/welcome.htm"
class="com.mkyong.common.controller.HelloWorldController" />
<bean id="viewResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" >
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/pages/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
- Controller – Declared a bean name “/welcome.htm” and map it to HelloWorldController class. It means, if an URL with “/welcome.htm” pattern is requested, it will send to the HelloWorldController controller to handle the request.
- viewResolver – Define how Spring will looking for the view template. In this case, the controller “HelloWorldController” will return a ModelAndView object named “HelloWorldPage”, and the viewResolver will find the file with following mechanism : “prefix + ModelAndView name + suffix“, which is “/WEB-INF/pages/HelloWorldPage.jsp“.
7. Demo
Run it and access via URL : http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/welcome.htm , the “SpringMVC” is your project context name.

How it works?
- http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/welcome.htm is requested.
- URL is end with “.htm” extension, so it will redirect to “DispatcherServlet” and send request to the default BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping.
- BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping return HelloWorldController to the DispatcherServlet.
- DispatcherServlet forward request to the HelloWorldController.
- HelloWorldController process it and return a ModelAndView object named “HelloWorldPage”.
- DispatcherServlet received the ModelAndView and call the viewResolver to process it.
- viewResolver return the “/WEB-INF/pages/HelloWorldPage.jsp” back to the DispatcherServlet.
- DispatcherServlet return the “HelloWorldPage.jsp” back to user.
Download Source Code
Spring MVC Hello World Example(转)的更多相关文章
- 如何用Java类配置Spring MVC(不通过web.xml和XML方式)
DispatcherServlet是Spring MVC的核心,按照传统方式, 需要把它配置到web.xml中. 我个人比较不喜欢XML配置方式, XML看起来太累, 冗长繁琐. 还好借助于Servl ...
- Spring MVC重定向和转发以及异常处理
SpringMVC核心技术---转发和重定向 当处理器对请求处理完毕后,向其他资源进行跳转时,有两种跳转方式:请求转发与重定向.而根据要跳转的资源类型,又可分为两类:跳转到页面与跳转到其他处理器.对于 ...
- Spring MVC入门
1.什么是SpringMvc Spring MVC属于SpringFrameWork的后续产品,已经融合在Spring Web Flow里面.Spring 框架提供了构建 Web 应用程序的全功能 M ...
- Spring7:基于注解的Spring MVC(下篇)
Model 上一篇文章<Spring6:基于注解的Spring MVC(上篇)>,讲了Spring MVC环境搭建.@RequestMapping以及参数绑定,这是Spring MVC中最 ...
- Spring6:基于注解的Spring MVC(上篇)
什么是Spring MVC Spring MVC框架是一个MVC框架,通过实现Model-View-Controller模式来很好地将数据.业务与展现进行分离.从这样一个角度来说,Spring MVC ...
- 高性能的关键:Spring MVC的异步模式
我承认有些标题党了,不过话说这样其实也没错,关于“异步”处理的文章已经不少,代码例子也能找到很多,但我还是打算发表这篇我写了好长一段时间,却一直没发表的文章,以一个更简单的视角,把异步模式讲清楚. 什 ...
- Java Spring mvc 操作 Redis 及 Redis 集群
本文原创,转载请注明:http://www.cnblogs.com/fengzheng/p/5941953.html 关于 Redis 集群搭建可以参考我的另一篇文章 Redis集群搭建与简单使用 R ...
- 深入分析Spring 与 Spring MVC容器
1 Spring MVC WEB配置 Spring Framework本身没有Web功能,Spring MVC使用WebApplicationContext类扩展ApplicationContext, ...
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之前传---FrameworkServlet
做项目时碰到Controller不能使用aop进行拦截,从网上搜索得知:使用spring mvc 启动了两个context:applicationContext 和WebapplicationCont ...
- 我是如何进行Spring MVC文档翻译项目的环境搭建、项目管理及自动化构建工作的
感兴趣的同学可以关注这个翻译项目 . 我的博客原文 和 我的Github 前段时间翻译的Spring MVC官方文档完成了第一稿,相关的文章和仓库可以点击以下链接.这篇文章,主要是总结一下这个翻译项目 ...
随机推荐
- debian网易163更新服务器 源
sudo vi /etc/apt/sources.list 加入如下内容即可: deb http://mirrors.163.com/debian/ jessie main non-free cont ...
- properties 文件的中文转ASCII
在软件开发过程中,经常要涉及到多语言支持问题,常用的解决方案是将各个语言文字放到properties文件中,但中文是需要转为ASCII的 .那么如何将中文进行转换呢,下面就为你列举几种比较方便的方法 ...
- cocos2d-x游戏开发系列教程-坦克大战游戏加载地图的编写
上节课写了关卡选择场景,那么接下来写关卡内容,先写最基本的地图的加载 我们新建一个场景类,如下所示: class CityScene : public cocos2d::CCLayer { publi ...
- 《Head First 设计模式》学习笔记——状态模式
在软件开发过程中.应用程序可能会依据不同的情况作出不同的处理. 最直接的解决方式是将这些全部可能发生的情况全都考虑到.然后使用if... ellse语句来做状态推断来进行不同情况的处理. 可是对复杂状 ...
- N-Queens And N-Queens II [LeetCode] + Generate Parentheses[LeetCode] + 回溯法
回溯法 百度百科:回溯法(探索与回溯法)是一种选优搜索法,按选优条件向前搜索,以达到目标.但当探索到某一步时,发现原先选择并不优或达不到目标,就退回一步又一次选择,这样的走不通就退回再走的技术为回溯法 ...
- Selenium webdriver 常见问题
出现java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/w3c/dom/ElementTraversal 是因为缺少 xml jar ,如果使用的是maven 可以依赖 <d ...
- 查看内存数据的函数(ByteToHex和ByteToBin,最终都变成String)
unit Unit1; interface uses Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Variants, Classes, Graphics, Controls, Forms ...
- frame.bounds和center
CGPoint point=CGPoint(x,y); //表示位置 CGSize size=CGSzieMake(width,height); //表示大小 CGRect rect=CGRect ...
- faith的23堂课:培养良好的工作方法与做事风格
目标:通过每天一点的学习和实践,逐步形成好的做事风格和工作生活习惯. 方式:每天教一点,实践一点. 第一课 计划与总结,工作日志,戴明环 第二课 目的性:搞清楚,你每个行为的目的 第三课 目标管理,调 ...
- Swift - 文本输入框内容改变时响应,并获取最新内容
1,问题描述 有时我们开发的时候需要先把“确认”按钮初始设置为不可用,当文本框中输入文字以后,再将输入按钮变为可用. 2,实现原理 (1)要检测文本框内容的变化,我们需要让新界面的Controller ...
