Codeforces Round #442 (Div. 2)A,B,C,D,E(STL,dp,贪心,bfs,dfs序+线段树)
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
One day Alex was creating a contest about his friends, but accidentally deleted it. Fortunately, all the problems were saved, but now he needs to find them among other problems.
But there are too many problems, to do it manually. Alex asks you to write a program, which will determine if a problem is from this contest by its name.
It is known, that problem is from this contest if and only if its name contains one of Alex's friends' name exactly once. His friends' names are "Danil", "Olya", "Slava", "Ann" and "Nikita".
Names are case sensitive.
The only line contains string from lowercase and uppercase letters and "_" symbols of length, not more than 100 — the name of the problem.
Print "YES", if problem is from this contest, and "NO" otherwise.
Alex_and_broken_contest
NO
NikitaAndString
YES
Danil_and_Olya
NO
思路:
直接用string带的find函数查就行了
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; int main()
{
string s;
cin>>s;
int flag = ;
int len = s.size();
if(s.find("Danil")!=s.npos){
if(s.find("Danil",s.find("Danil")+)==s.npos)
flag ++;
else flag += ;
}
if(s.find("Olya")!=s.npos){
if(s.find("Olya",s.find("Olya")+)==s.npos)
flag ++;
else flag += ;
}
if(s.find("Slava")!=s.npos){
if(s.find("Slava",s.find("Slava")+)==s.npos)
flag ++;
else flag += ;
}
if(s.find("Ann")!=s.npos){
if(s.find("Ann",s.find("Ann")+)==s.npos)
flag ++;
else
flag += ;
}
if(s.find("Nikita")!=s.npos){
if(s.find("Nikita",s.find("Nikita")+)==s.npos)
flag ++;
else
flag += ;
}
if(flag == )
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
else
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
One day Nikita found the string containing letters "a" and "b" only.
Nikita thinks that string is beautiful if it can be cut into 3 strings (possibly empty) without changing the order of the letters, where the 1-st and the 3-rd one contain only letters "a" and the 2-nd contains only letters "b".
Nikita wants to make the string beautiful by removing some (possibly none) of its characters, but without changing their order. What is the maximum length of the string he can get?
The first line contains a non-empty string of length not greater than 5 000 containing only lowercase English letters "a" and "b".
Print a single integer — the maximum possible size of beautiful string Nikita can get.
abba
4
bab
2
It the first sample the string is already beautiful.
In the second sample he needs to delete one of "b" to make it beautiful.
思路:
dp,
dp[0][i] 代表为当前字符串类型为a的情况,dp[1][i]代表当前字符串类型为ab的情况,dp2[[i]代表当前字符串类型为aba的情况
状态转移方程可以表示为:
dp[0][i+1] = dp[0][i] + (s[i] == 'a'); a状态只能由a+a得到的,当si = a时,dp[0][i]++即可;
dp[1][i+1] = max(dp[1][i],dp[0][i]) + (s[i] == 'b'); ab状态可由a+b或ab+b得到当si = b时2取两种情况下最大的即可,
dp[2][i+1] = max(max(dp[1][i],dp[0][i]),dp[2][i]) + (s[i] == 'a'); aba情况包括了前两中状态同时也可以由自身aba+a得到,所有当s==a时取三种状态中最大的 最后取三种情况下最大的即可 实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dp[][];
int main()
{
string s;
cin>>s;
int len = s.size();
dp[][] = ; //代表情况a
dp[][] = ; //代表情况ab
dp[][] = ; //代表情况aba
for(int i = ;i < len;i ++){
dp[][i+] = dp[][i] + (s[i] == 'a');
dp[][i+] = max(dp[][i],dp[][i]) + (s[i] == 'b');
dp[][i+] = max(max(dp[][i],dp[][i]),dp[][i]) + (s[i] == 'a');
}
cout<<max(max(dp[][len],dp[][len]),dp[][len])<<endl;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Slava plays his favorite game "Peace Lightning". Now he is flying a bomber on a very specific map.
Formally, map is a checkered field of size 1 × n, the cells of which are numbered from 1 to n, in each cell there can be one or several tanks. Slava doesn't know the number of tanks and their positions, because he flies very high, but he can drop a bomb in any cell. All tanks in this cell will be damaged.
If a tank takes damage for the first time, it instantly moves to one of the neighboring cells (a tank in the cell n can only move to the cell n - 1, a tank in the cell 1 can only move to the cell 2). If a tank takes damage for the second time, it's counted as destroyed and never moves again. The tanks move only when they are damaged for the first time, they do not move by themselves.
Help Slava to destroy all tanks using as few bombs as possible.
The first line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the size of the map.
In the first line print m — the minimum number of bombs Slava needs to destroy all tanks.
In the second line print m integers k1, k2, ..., km. The number ki means that the i-th bomb should be dropped at the cell ki.
If there are multiple answers, you can print any of them.
2
3
2 1 2
3
4
2 1 3 2
思路:
之前直接扔翻译看中文结果看成是轰炸n,会移到n-1,漏了n+1,搞得wa到怀疑人生,轰炸n会移到n-1和n+1,那么只要先炸一遍偶数区域再炸一遍奇数,再炸一遍偶数那么就可以保证最少的情况全部炸毁
为什么不先炸奇数,,因为当n为奇数的时候,先炸奇数会多出一步操作
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dp[][];
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
cout<<n+n/<<endl;
for(int i = ;i <= n;i +=)
cout<<i<<" ";
for(int i = ;i <= n;i +=)
cout<<i<<" ";
for(int i = ;i <= n;i +=)
cout<<i<<" ";
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Olya loves energy drinks. She loves them so much that her room is full of empty cans from energy drinks.
Formally, her room can be represented as a field of n × m cells, each cell of which is empty or littered with cans.
Olya drank a lot of energy drink, so now she can run k meters per second. Each second she chooses one of the four directions (up, down, left or right) and runs from 1 to k meters in this direction. Of course, she can only run through empty cells.
Now Olya needs to get from cell (x1, y1) to cell (x2, y2). How many seconds will it take her if she moves optimally?
It's guaranteed that cells (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are empty. These cells can coincide.
The first line contains three integers n, m and k (1 ≤ n, m, k ≤ 1000) — the sizes of the room and Olya's speed.
Then n lines follow containing m characters each, the i-th of them contains on j-th position "#", if the cell (i, j) is littered with cans, and "." otherwise.
The last line contains four integers x1, y1, x2, y2 (1 ≤ x1, x2 ≤ n, 1 ≤ y1, y2 ≤ m) — the coordinates of the first and the last cells.
Print a single integer — the minimum time it will take Olya to get from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2).
If it's impossible to get from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2), print -1.
3 4 4
....
###.
....
1 1 3 1
3
3 4 1
....
###.
....
1 1 3 1
8
2 2 1
.#
#.
1 1 2 2
-1
In the first sample Olya should run 3 meters to the right in the first second, 2 meters down in the second second and 3 meters to the left in the third second.
In second sample Olya should run to the right for 3 seconds, then down for 2 seconds and then to the left for 3 seconds.
Olya does not recommend drinking energy drinks and generally believes that this is bad.
思路:
一开始想简单了以为是直接找最短的路径长度,题目说的是1s朝某个方向跑k米,那么我们就直接枚举每个方向每秒跑的1-k米之间的所有情况,直接用bfs
暴力搜就行了。因为bfs是分层次访问的,那么最先到达终点的肯定就是耗时最短的。
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int M = ;
struct node{
int x,y,time;
};
int dx[] = {,,,-};
int dy[] = {,-,,};
int vis[M][M][];
char mp[M][M];
int ex,ey,sx,sy,n,m,k;
int bfs(){
node t,t1;
queue<node>q;
t.x = sx;t.y = sy;t.time = ;
vis[sx][sy][] = ;vis[sx][sy][] = ;
vis[sx][sy][] = ;vis[sx][sy][] = ;
q.push(t);
while(!q.empty()){
t = q.front(); q.pop();
if(t.x == ex&&t.y == ey) return t.time;
for(int i = ;i < ;i ++){
for(int j = ;j <= k;j ++){
int nx = t.x + j*dx[i];
int ny = t.y + j*dy[i];
if(mp[nx][ny] == '.'&&nx >= &&nx <= n&&ny >= &&ny <= m&&!vis[nx][ny][i]){
vis[nx][ny][i] = ;
t1.x = nx; t1.y = ny; t1.time = t.time+;
q.push(t1);
}
else break;
}
}
}
return -;
} int main()
{
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i = ;i <= n;i ++)
for(int j = ;j <= m;j ++)
cin>>mp[i][j];
cin>>sx>>sy>>ex>>ey;
cout<<bfs()<<endl;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Danil decided to earn some money, so he had found a part-time job. The interview have went well, so now he is a light switcher.
Danil works in a rooted tree (undirected connected acyclic graph) with n vertices, vertex 1 is the root of the tree. There is a room in each vertex, light can be switched on or off in each room. Danil's duties include switching light in all rooms of the subtree of the vertex. It means that if light is switched on in some room of the subtree, he should switch it off. Otherwise, he should switch it on.
Unfortunately (or fortunately), Danil is very lazy. He knows that his boss is not going to personally check the work. Instead, he will send Danil tasks using Workforces personal messages.
There are two types of tasks:
- pow v describes a task to switch lights in the subtree of vertex v.
- get v describes a task to count the number of rooms in the subtree of v, in which the light is turned on. Danil should send the answer to his boss using Workforces messages.
A subtree of vertex v is a set of vertices for which the shortest path from them to the root passes through v. In particular, the vertex v is in the subtree of v.
Danil is not going to perform his duties. He asks you to write a program, which answers the boss instead of him.
The first line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The second line contains n - 1 space-separated integers p2, p3, ..., pn (1 ≤ pi < i), where pi is the ancestor of vertex i.
The third line contains n space-separated integers t1, t2, ..., tn (0 ≤ ti ≤ 1), where ti is 1, if the light is turned on in vertex i and 0 otherwise.
The fourth line contains a single integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 200 000) — the number of tasks.
The next q lines are get v or pow v (1 ≤ v ≤ n) — the tasks described above.
For each task get v print the number of rooms in the subtree of v, in which the light is turned on.
4
1 1 1
1 0 0 1
9
get 1
get 2
get 3
get 4
pow 1
get 1
get 2
get 3
get 4
2
0
0
1
2
1
1
0
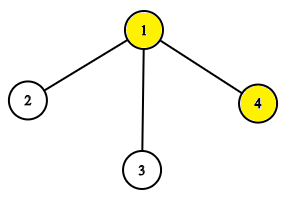 The tree before the task pow 1.
The tree before the task pow 1.
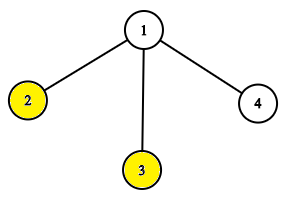 The tree after the task pow 1.
The tree after the task pow 1.
思路:
题意就是在一棵树上修改点然后查询子树,很裸的dfs序+线段树了,dfs序把树结构转化成线性结构,然后直接用线段树区间修改和查询就可以了。注意下dfs序转化的结点编号和之前的编号是不同的。
其中l[x]代表x结点转化后的编号,r[x]代表转化后x结点的子树中l[x]最大的那个,且由于dfs转化的规则,x结点的子树转换后必定为一段连续的区间,那么lx就是这段区间的左端点,rx是这段区间的右端点
所以 rx - lx + 1 等于x结点的子树所含的结点数(包括自己),这个自己看下dfs序应该就知道了。
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define lson l,m,rt<<1
#define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1
const int M = 2e5+;
vector<int>g[M];
int lazy[M<<],sum[M<<],a[M],id[M],l[M],r[M],tot;
void dfs(int x){
l[x] = tot;
for(int i = ;i < g[x].size();i ++)
tot++,dfs(g[x][i]);
r[x] = tot;
} void pushup(int rt){
sum[rt] = sum[rt<<] + sum[rt<<|];
} void pushdown(int rt,int m){
if(lazy[rt]){
sum[rt<<] = (m-(m>>)) - sum[rt<<];
sum[rt<<|] = (m>>) - sum[rt<<|];
lazy[rt<<] ^= ;
lazy[rt<<|] ^= ;
lazy[rt] = ;
}
} void build(int l,int r,int rt){
if(l == r){
sum[rt] = a[id[l]];
return ;
}
int m = (l + r) >> ;
build(lson);
build(rson);
pushup(rt);
} void update(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt){
if(L <= l&&R >= r){
sum[rt] = r - l + - sum[rt];
lazy[rt] ^= ;
return ;
}
pushdown(rt,r-l+);
int m = (l + r) >> ;
if(L <= m) update(L,R,lson);
if(R > m) update(L,R,rson);
pushup(rt);
} int query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt){
if(L <= l&&R >= r){
return sum[rt];
}
pushdown(rt,r-l+);
int ret = ;
int m = (l + r) >> ;
if(L <= m) ret += query(L,R,lson);
if(R > m) ret += query(L,R,rson);
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int x,n,m,k;
string s;
ios::sync_with_stdio();
cin.tie();
cout.tie();
cin>>n;
for(int i = ;i <= n;i ++){
cin>>x;
g[x].push_back(i);
}
for(int i = ;i <= n;i ++)
cin>>a[i];
tot = ;
dfs();
for(int i = ;i <= n;i ++)
id[l[i]] = i;
build(,n,);
cin>>m;
while(m--){
cin>>s>>k;
if(s=="get")
cout<<query(l[k],r[k],,n,)<<endl;
else{
update(l[k],r[k],,n,);
}
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #442 (Div. 2)A,B,C,D,E(STL,dp,贪心,bfs,dfs序+线段树)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #442 Div.2 A B C D E
A. Alex and broken contest 题意 判断一个字符串内出现五个给定的子串多少次. Code #include <bits/stdc++.h> char s[110]; ...
- CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树
CodeForces 877E DFS序+线段树 题意 就是树上有n个点,然后每个点都有一盏灯,给出初始的状态,1表示亮,0表示不亮,然后有两种操作,第一种是get x,表示你需要输出x的子树和x本身 ...
- Codeforces Round #442 (Div. 2) Danil and a Part-time Job
http://codeforces.com/contest/877/problem/E 真的菜的不行,自己敲一个模板,到处都是问题.哎 #include <bits/stdc++.h> u ...
- Codeforces Round #396 (Div. 2) A B C D 水 trick dp 并查集
A. Mahmoud and Longest Uncommon Subsequence time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 ...
- Codeforces Round #587 (Div. 3) F. Wi-Fi(单调队列优化DP)
题目:https://codeforces.com/contest/1216/problem/F 题意:一排有n个位置,我要让所有点都能联网,我有两种方式联网,第一种,我直接让当前点联网,花费为i,第 ...
- Codeforces 838B - Diverging Directions - [DFS序+线段树]
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/838/B You are given a directed weighted graph with n n ...
- Codeforces Round #442 (Div. 2)
A. Alex and broken contest time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input s ...
- Codeforces Round #442 (Div. 2) E Danil and a Part-time Job (dfs序加上一个线段树区间修改查询)
题意: 给出一个具有N个点的树,现在给出两种操作: 1.get x,表示询问以x作为根的子树中,1的个数. 2.pow x,表示将以x作为根的子树全部翻转(0变1,1变0). 思路:dfs序加上一个线 ...
- 【Codeforces Round #442 (Div. 2) D】Olya and Energy Drinks
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 给一张二维点格图,其中有一些点可以走,一些不可以走,你每次可以走1..k步,问你起点到终点的最短路. [题解] 不能之前访问过那个点就不访问了.->即k ...
随机推荐
- jqgrid 将列头设置为超链接或按钮
有时,需要将某个列头设置为超链接或按钮,点击超链接或按钮能够跳转至其他页面(或执行一个事件操作). 可以把 label 值设置成一个a标签或button 代码如下: colModel: [{ labe ...
- php删除文件夹和其下的内容
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaochaohuashengmi/archive/2011/05/13/2045158.html <?php function del ...
- DOTNET Core 命令
dotnet 命令目录: 1.dotnet-new 2.dotnet-restore 3.dotnet-build 4.dotnet-run 5.dotnet-test 6.dotnet-pack 7 ...
- odoo 打印单
<td style="word-wrap:break-word;width:20%;font-size:16"> <t t-foreach="l.pro ...
- 一个struts2程序
1.index.jsp 2.struts.xml 3.Loginaction.java package action; import java.io.File; import java.io.File ...
- 20155204 王昊《网络对抗技术》EXP2 后门原理与实践
20155204 王昊<网络对抗技术>EXP2 后门原理与实践 一.实验内容 准备工作(试用ncat.socat) 1. 使用netcat获取主机操作Shell,cron启动. 明确目标: ...
- python 穷举法 算24点(史上最简短代码)
本来想用回溯法实现 算24点.题目都拟好了,就是<python 回溯法 子集树模板 系列 -- 7.24点>.无奈想了一天,没有头绪.只好改用暴力穷举法. 思路说明 根据四个数,三个运算符 ...
- PHP 练习(租房子)
一.题目要求 二.题目做法 1.建立数据库 2.封装类文件 <?php class DBDA { public $fuwuqi="localhost"; //服务器地址 pu ...
- angularJs 技巧总结及最佳实践
强烈建议通读官方wiki文档,里面包含了FAQ,最佳实践,深入理解最核心的Directive及Scope等文章, 基础 1. 使用ng-repeat指令,为防止重复值发生的错误.加上track by ...
- md5加密,同样的代码得到不同的加密结果(已解决)
场景: 开发环境(windows下)调用第三方接口验签通过,发测试环境(linux下)后死活验签通过不了 原因: md5是一项成熟的加密技术,问题应该在代码里,查了查感觉可能是字符编码的问题,导致加签 ...
