Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) -----CF546
A. Soldier and Bananas
A soldier wants to buy w bananas in the shop. He has to pay k dollars for the first banana, 2k dollars for the second one and so on (in other words, he has to pay i·k dollars for the i-th banana).
He has n dollars. How many dollars does he have to borrow from his friend soldier to buy w bananas?
The first line contains three positive integers k, n, w (1 ≤ k, w ≤ 1000, 0 ≤ n ≤ 109), the cost of the first banana, initial number of dollars the soldier has and number of bananas he wants.
Output one integer — the amount of dollars that the soldier must borrow from his friend. If he doesn't have to borrow money, output 0.
3 17 4
13
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; #define LL __int64
LL n,k,w; int main()
{
int i;
LL sum = ;
scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&k,&n,&w);
for(i = ;i<=w;i++)
sum +=i*k;
if(n>=sum)
printf("0\n");
else
printf("%I64d\n",sum-n); return ;
}
B. Soldier and Badges
Colonel has n badges. He wants to give one badge to every of his n soldiers. Each badge has a coolness factor, which shows how much it's owner reached. Coolness factor can be increased by one for the cost of one coin.
For every pair of soldiers one of them should get a badge with strictly higher factor than the second one. Exact values of their factors aren't important, they just need to have distinct factors.
Colonel knows, which soldier is supposed to get which badge initially, but there is a problem. Some of badges may have the same factor of coolness. Help him and calculate how much money has to be paid for making all badges have different factors of coolness.
First line of input consists of one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3000).
Next line consists of n integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ n), which stand for coolness factor of each badge.
Output single integer — minimum amount of coins the colonel has to pay.
4
1 3 1 4
1
5
1 2 3 2 5
2
In first sample test we can increase factor of first badge by 1.
In second sample test we can increase factors of the second and the third badge by 1.
题意:给你n堆价值,要求得到每堆价值是独一无二的,问你往每堆加多少,最少加多少。
思路:(贪心)先排序,然后以第一个为基准,后面的不大于前面的,就加加;
转载请注明出处:寻找&星空の孩子
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/546/problem/B
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
#include <bitset>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
using namespace std; #define lson 2*i
#define rson 2*i+1
#define LS l,mid,lson
#define RS mid+1,r,rson
#define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++)
#define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--)
#define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
#define W(a) while(a)
#define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b)
#define LL long long
#define N 5000005
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define EXP 1e-8
#define lowbit(x) (x&-x)
const int mod = 1e9+;
#define LL __int64
int n,a[];
int main()
{
int i,j,ans;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
ans = ;
int sum1 = ,sum2 = ;
for(i = ; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sum1+=a[i];
}
sort(a+,a++n);
sum2 = a[];
for(i = ; i<=n; i++)
{
if(a[i] == a[i-])
a[i]++;
else if(a[i]<a[i-])
a[i] +=(a[i-]-a[i])+;
sum2+=a[i];
}
printf("%d\n",sum2-sum1);
} return ;
}
C. Soldier and Cards
Two bored soldiers are playing card war. Their card deck consists of exactly n cards, numbered from 1 to n, all values are different. They divide cards between them in some manner, it's possible that they have different number of cards. Then they play a "war"-like card game.
The rules are following. On each turn a fight happens. Each of them picks card from the top of his stack and puts on the table. The one whose card value is bigger wins this fight and takes both cards from the table to the bottom of his stack. More precisely, he first takes his opponent's card and puts to the bottom of his stack, and then he puts his card to the bottom of his stack. If after some turn one of the player's stack becomes empty, he loses and the other one wins.
You have to calculate how many fights will happen and who will win the game, or state that game won't end.
First line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 10), the number of cards.
Second line contains integer k1 (1 ≤ k1 ≤ n - 1), the number of the first soldier's cards. Then follow k1 integers that are the values on the first soldier's cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
Third line contains integer k2 (k1 + k2 = n), the number of the second soldier's cards. Then follow k2 integers that are the values on the second soldier's cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
All card values are different.
If somebody wins in this game, print 2 integers where the first one stands for the number of fights before end of game and the second one is 1 or 2 showing which player has won.
If the game won't end and will continue forever output - 1.
4
2 1 3
2 4 2
6 2
3
1 2
2 1 3
-1
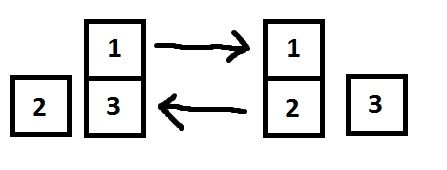
First sample:
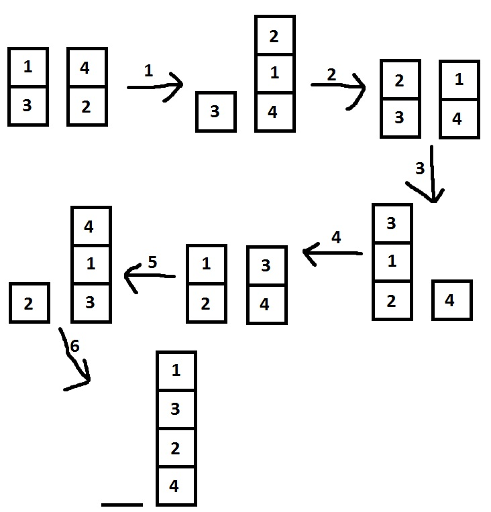
Second sample:
题意:给一个n(<=10)表示两人手中共有n张牌,接下来一行表示第1个人有k1张牌,k1 v1[1] v1[2]......v1[k1], v1[i]表示第i 张牌的大小,第三行表示第2个人有k2张牌,k2 v2[1] v2[2]......v2[k2], v2[i]表示第i 张牌的大小。每一轮,两人从牌顶部各出一张,谁出的牌大则两张牌归谁,放入到自己牌的底部,直到其中一个人手中没有牌出,则那个人输了。问需要多少轮,哪个人赢了。如果没有解则输出-1.
思路:(模拟题)直接模拟一下过程,主要是标记一下两个人手中牌的状态,用map<string,map<string,bool> >vist 标记一下。
转载请注明出处:寻找&星空の孩子
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/546/problem/C
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
#include <bitset>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
using namespace std; #define lson 2*i
#define rson 2*i+1
#define LS l,mid,lson
#define RS mid+1,r,rson
#define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++)
#define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--)
#define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
#define W(a) while(a)
#define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b)
#define LL long long
#define N 5000005
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define EXP 1e-8
#define lowbit(x) (x&-x)
const int mod = 1e9+; map<string,map<string,int> > vis;
int n;
int k1,k2;
int a[],b[],c[];
char s1[],s2[]; int main()
{
int i,j,k;
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%d",&k1);
for(i = ; i<k1; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
c[i] = a[i];
}
scanf("%d",&k2);
for(i = ; i<k2; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
c[k1+i] = b[i];
}
sort(c,c+k1+k2);
for(i = ; i<k1; i++)
{
for(j = ; j<k1+k2; j++)
{
if(a[i]==c[j])
s1[i] = j+'';
}
}
s1[k1] = '\0';
for(i = ; i<k2; i++)
{
for(j = ; j<k1+k2; j++)
{
if(b[i]==c[j])
s2[i] = j+'';
}
}
s2[k2] = '\0';
vis[s1][s2] = ;
int ans = ;
while(k1&&k2)
{
int p1 = s1[],p2 = s2[];
// printf("[%d %d %d %d]\n",p1,p2,k1,k2); /* printf("(1):");
for(i = 0; i<k1; i++)
printf("%c ",s1[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("(2):");
for(i = 0; i<k2; i++)
printf("%c ",s2[i]);
printf("\n");*/
if(p1>p2)
{
for(i = ; i<k2; i++)
s2[i] = s2[i+];
k2--;
for(i = ; i<k1; i++)
s1[i] = s1[i+];
s1[k1-] = p2;
s1[k1] = p1;
k1++;
s2[k2] = s1[k1] = '\0';
}
else
{
for(i = ; i<k1; i++)
s1[i] = s1[i+];
k1--;
for(i = ; i<k2; i++)
s2[i] = s2[i+];
s2[k2-] = p1;
s2[k2] = p2;
k2++;
s2[k2] = s1[k1] = '\0';
}
/* printf("(1):");
for(i = 0; i<k1; i++)
printf("%c ",s1[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("(2):");
for(i = 0; i<k2; i++)
printf("%c ",s2[i]);
printf("\n");*/
if(vis[s1][s2])
{
ans = -;
break;
}
//printf("%d %d\n",k1,k2);
ans++;
vis[s1][s2] = ;
}
printf("%d",ans);
if(ans!=-)
{
if(k1)
printf("");
else
printf("");
}
printf("\n"); return ;
}
D. Soldier and Number Game
Two soldiers are playing a game. At the beginning first of them chooses a positive integer n and gives it to the second soldier. Then the second one tries to make maximum possible number of rounds. Each round consists of choosing a positive integer x > 1, such that n is divisible by x and replacing n with n / x. When n becomes equal to 1 and there is no more possible valid moves the game is over and the score of the second soldier is equal to the number of rounds he performed.
To make the game more interesting, first soldier chooses n of form a! / b! for some positive integer a and b (a ≥ b). Here by k! we denote the factorial of k that is defined as a product of all positive integers not large than k.
What is the maximum possible score of the second soldier?
First line of input consists of single integer t (1 ≤ t ≤ 1 000 000) denoting number of games soldiers play.
Then follow t lines, each contains pair of integers a and b (1 ≤ b ≤ a ≤ 5 000 000) defining the value of n for a game.
For each game output a maximum score that the second soldier can get.
2
3 1
6 3
2
5
题意:n=a!/b!问你n的素数因子的个数。
思路:素数打表;
转载请注明出处:寻找&星空の孩子
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/546/problem/D
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
#include <bitset>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
using namespace std; #define lson 2*i
#define rson 2*i+1
#define LS l,mid,lson
#define RS mid+1,r,rson
#define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++)
#define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--)
#define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
#define W(a) while(a)
#define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b)
#define LL long long
#define N 5000005
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define EXP 1e-8
#define lowbit(x) (x&-x)
const int mod = 1e9+;
int p[N];
int a[N];
int prime[];
LL sum[N];
void init()
{ for(int i=; i<; ++i)
prime[i] = INF;
prime[] = ;
int num = ;
for(int i=; i<; ++i)
{
int x = ;
while(i%prime[x] && prime[x] <= i) ++x;
if( !(i%prime[x]) )
a[i] = prime[x];
else
{
prime[++num] = i;
a[i] = i;
}
}
a[] =;
for(int i=; i< N; ++i)
{
int x = ;
while(i%prime[x] && prime[x] <= i) ++x;
if( !(i%prime[x]) )
a[i] = prime[x];
else
a[i] = i;
}
p[] = ;
for(int i=; i <N; ++i)
p[i] = p[i/a[i]] + ;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
init();
sum[] = ;
// printf("%d\n",p[4]);
for(i = ; i<=; i++)
{
sum[i] = sum[i-]+p[i];
// printf("%d %I64d\n",i,sum[i]);
}
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&i,&j);
// printf("%d %d %I64d %I64d\n",i,j+1,sum[i],sum[j+1]);
if(i == j)
printf("0\n");
else
printf("%I64d\n",sum[i]-sum[j]);
} return ;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
#include <bitset>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
using namespace std; #define lson 2*i
#define rson 2*i+1
#define LS l,mid,lson
#define RS mid+1,r,rson
#define UP(i,x,y) for(i=x;i<=y;i++)
#define DOWN(i,x,y) for(i=x;i>=y;i--)
#define MEM(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
#define W(a) while(a)
#define gcd(a,b) __gcd(a,b)
#define LL long long
#define N 5000005
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define EXP 1e-8
#define lowbit(x) (x&-x)
const int mod = 1e9+;
int p[N];
bool v[N];
int a[N];
int prime[N/];
LL sum[N];
void init()
{
for(int i=; i<N; ++i)
a[i] = i;
int num=-;
for(int i=; i<N; ++i)
{
if(!v[i]) prime[++num] = i;
for(int j=; j<=num && i*prime[j] < N; ++j)
{
int t = i*prime[j];
v[t] =;
if(a[t] > prime[j]) a[t] = prime[j];
if(i%prime[j] == ) break;
}
}
p[] = ;
for(int i=; i <N; ++i)
p[i] = p[i/a[i]] + ;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
init();
sum[] = ;
for(i = ; i<=; i++)
{
sum[i] = sum[i-]+p[i];
}
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&i,&j);
if(i == j)
printf("0\n");
else
printf("%I64d\n",sum[i]-sum[j]);
} return ;
}
E. Soldier and Traveling
In the country there are n cities and m bidirectional roads between them. Each city has an army. Army of the i-th city consists of aisoldiers. Now soldiers roam. After roaming each soldier has to either stay in his city or to go to the one of neighboring cities by at moving along at most one road.
Check if is it possible that after roaming there will be exactly bi soldiers in the i-th city.
First line of input consists of two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 100, 0 ≤ m ≤ 200).
Next line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100).
Next line contains n integers b1, b2, ..., bn (0 ≤ bi ≤ 100).
Then m lines follow, each of them consists of two integers p and q (1 ≤ p, q ≤ n, p ≠ q) denoting that there is an undirected road between cities p and q.
It is guaranteed that there is at most one road between each pair of cities.
If the conditions can not be met output single word "NO".
Otherwise output word "YES" and then n lines, each of them consisting of n integers. Number in the i-th line in the j-th column should denote how many soldiers should road from city i to city j (if i ≠ j) or how many soldiers should stay in city i (if i = j).
If there are several possible answers you may output any of them.
4 4
1 2 6 3
3 5 3 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 2
YES
1 0 0 0
2 0 0 0
0 5 1 0
0 0 2 1
2 0
1 2
2 1
NO
题意:给你一张无向图,每个点有一定数量的人,通过移动可以去邻接点(但是只能移动一次)问你是否能从初始状态移动到目标状态;
思路:网络流+最大流;
转载请注明出处:寻找&星空の孩子
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/546/problem/E
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define captype int const int MAXN = ; //点的总数
const int MAXM = ; //边的总数
const int INF = <<;
struct EDG{
int to,next;
captype cap,flow;
} edg[MAXM];
int eid,head[MAXN];
int gap[MAXN]; //每种距离(或可认为是高度)点的个数
int dis[MAXN]; //每个点到终点eNode 的最短距离
int cur[MAXN]; //cur[u] 表示从u点出发可流经 cur[u] 号边
int pre[MAXN];
int mapt[][]; void init(){
eid=;
memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
memset(mapt,,sizeof(mapt));
}
//有向边 三个参数,无向边4个参数
void addEdg(int u,int v,captype c,captype rc=){
edg[eid].to=v; edg[eid].next=head[u];
edg[eid].cap=c; edg[eid].flow=; head[u]=eid++; edg[eid].to=u; edg[eid].next=head[v];
edg[eid].cap=rc; edg[eid].flow=; head[v]=eid++;
}
captype maxFlow_sap(int sNode,int eNode, int n){//n是包括源点和汇点的总点个数,这个一定要注意
memset(gap,,sizeof(gap));
memset(dis,,sizeof(dis));
memcpy(cur,head,sizeof(head));
pre[sNode] = -;
gap[]=n;
captype ans=; //最大流
int u=sNode;
while(dis[sNode]<n){ //判断从sNode点有没有流向下一个相邻的点
if(u==eNode){ //找到一条可增流的路
captype Min=INF ;
int inser;
for(int i=pre[u]; i!=-; i=pre[edg[i^].to]) //从这条可增流的路找到最多可增的流量Min
if(Min>edg[i].cap-edg[i].flow){
Min=edg[i].cap-edg[i].flow;
inser=i;
}
for(int i=pre[u]; i!=-; i=pre[edg[i^].to]){ edg[i].flow+=Min;
edg[i^].flow-=Min; //可回流的边的流量 if(edg[i].to==eNode||edg[i].to==sNode||edg[i^].to==eNode||edg[i^].to==sNode)
continue;
if(edg[i].cap>){
int tu, tv;
tu=edg[i^].to; tv=edg[i].to-(n-)/;
mapt[tu][tv]+=Min;
}
else{
int tu, tv;
tu=edg[i].to; tv=edg[i^].to-(n-)/;
mapt[tu][tv]-=Min;
} }
ans+=Min;
u=edg[inser^].to;
continue;
}
bool flag = false; //判断能否从u点出发可往相邻点流
int v;
for(int i=cur[u]; i!=-; i=edg[i].next){
v=edg[i].to;
if(edg[i].cap-edg[i].flow> && dis[u]==dis[v]+){
flag=true;
cur[u]=pre[v]=i;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
u=v;
continue;
}
//如果上面没有找到一个可流的相邻点,则改变出发点u的距离(也可认为是高度)为相邻可流点的最小距离+1
int Mind= n;
for(int i=head[u]; i!=-; i=edg[i].next)
if(edg[i].cap-edg[i].flow> && Mind>dis[edg[i].to]){
Mind=dis[edg[i].to];
cur[u]=i;
}
gap[dis[u]]--;
if(gap[dis[u]]==) return ans; //当dis[u]这种距离的点没有了,也就不可能从源点出发找到一条增广流路径
//因为汇点到当前点的距离只有一种,那么从源点到汇点必然经过当前点,然而当前点又没能找到可流向的点,那么必然断流
dis[u]=Mind+;//如果找到一个可流的相邻点,则距离为相邻点距离+1,如果找不到,则为n+1
gap[dis[u]]++;
if(u!=sNode) u=edg[pre[u]^].to; //退一条边
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
int n,m ,s , t , u,v,c[],tc;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)>){
init();
s=;
t=*n+;
int ans=;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++){
scanf("%d",&c[i]);
ans+=c[i];
addEdg(s,i,c[i]);
addEdg(i,i+n,c[i]);
}
int sum=;
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&tc); sum+=tc;
addEdg(i+n,t,tc);
}
while(m--){
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
addEdg(u,v+n,c[u]);
addEdg(v,u+n,c[v]);
}
if(ans!=sum){
printf("NO\n"); continue;
}
ans -= maxFlow_sap(s,t,t+);
if(ans==){
printf("YES\n");
for(int i=; i<=n; i++){
for(int j=; j<n; j++)
printf("%d ",mapt[i][j]);
printf("%d\n",mapt[i][n]);
}
}
else
printf("NO\n");
}
}
Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) -----CF546的更多相关文章
- DP+埃氏筛法 Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) D. Soldier and Number Game
题目传送门 /* 题意:b+1,b+2,...,a 所有数的素数个数和 DP+埃氏筛法:dp[i] 记录i的素数个数和,若i是素数,则为1:否则它可以从一个数乘以素数递推过来 最后改为i之前所有素数个 ...
- queue+模拟 Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) C. Soldier and Cards
题目传送门 /* 题意:两堆牌,每次拿出上面的牌做比较,大的一方收走两张牌,直到一方没有牌 queue容器:模拟上述过程,当次数达到最大值时判断为-1 */ #include <cstdio&g ...
- 贪心 Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) B. Soldier and Badges
题目传送门 /* 题意:问最少增加多少值使变成递增序列 贪心:排序后,每一个值改为前一个值+1,有可能a[i-1] = a[i] + 1,所以要 >= */ #include <cstdi ...
- 水题 Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) A. Soldier and Bananas
题目传送门 /* 水题:ans = (1+2+3+...+n) * k - n,开long long */ #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm ...
- 数学+DP Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) D. Soldier and Number Game
题目传送门 /* 题意:这题就是求b+1到a的因子个数和. 数学+DP:a[i]保存i的最小因子,dp[i] = dp[i/a[i]] +1;再来一个前缀和 */ /***************** ...
- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) D. Soldier and Number Game 数学 质因数个数
D. Soldier and Number Game Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/conte ...
- codeforces水题100道 第五题 Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) A. Soldier and Bananas (math)
题目链接:http://www.codeforces.com/problemset/problem/546/A题意:一个人现在有n元,它买第i根香蕉需要i*k元,问他要买w根香蕉的话,需要问他的朋友借 ...
- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) E. Soldier and Traveling 最大流
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/546/E E. Soldier and Traveling time limit per test1 s ...
- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) C. Soldier and Cards 水题
C. Soldier and Cards Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/546 ...
随机推荐
- c# 字符串中多个连续空格转为一个空格
#region 字符串中多个连续空格转为一个空格 /// <summary> /// 字符串中多个连续空格转为一个空格 /// </summary> /// <param ...
- Java核心技术卷一基础知识-第8章-事件处理-读书笔记
第8章 事件处理 本章内容: * 事件处理基础 * 动作 * 鼠标事件 * AWT事件继承层次 8.1 事件处理基础 在AWT所知的事件范围内,完全可以控制事件从事件源(event source)例如 ...
- 吴恩达机器学习笔记26-样本和直观理解1(Examples and Intuitions I)
从本质上讲,神经网络能够通过学习得出其自身的一系列特征.在普通的逻辑回归中,我们被限制为使用数据中的原始特征
- Eclipse 使用前常用设置
1.常用设置的位置 Eclipse中一般的设置都是在这个位置进行设置的: 2.设置字体类型和大小 一般可以设置成这样代码比较清晰:Consolas + 常规 + 小四 3.设置各种编码 设置工作空间的 ...
- Day2:html和css
Day2:html和css 表格是一种常用的标签,表格结构,做到能够合并单元格. 表格的属性: 属性名 说明 border 设置表格的边框 cellspacing 设置单元格与单元格边框之间的空白间距 ...
- Python You-Get (送你一个免广告的视频和音乐网站 VIP)
You-get可以在仅仅提供URL情况下就可以实现下载视频.图片.音乐等信息.也可以通过播放器在线观看视频或听音乐,重要的是再也不用烦恼弹出的广告了,如果你想观看视频,但又不想观看广告,并且你还想把视 ...
- python函数学习1
函数1 (1)定义: def 函数名(参数列表) 函数体 (2)参数传递: 在python中,一切都是对象,类型也属于对象,变量是没有类型的. a = [1,2,3] a = "hellow ...
- virtualbox ubuntu 安装 openssh-server
最近为了学 DevOps,自己动手在 virtualbox 上安装 ubuntu 系统,安装完后发现好坑,没办法用 XShell 连接.在线安装 openssh-server 又发现没有配置软件源,手 ...
- [译]ASP.NET Core中使用MediatR实现命令和中介者模式
作者:依乐祝 原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yilezhu/p/9866068.html 在本文中,我将解释命令模式,以及如何利用基于命令模式的第三方库来实现它们,以及如何 ...
- 【原】gulp工作中的实战
写这篇文章的目的是为了以后的项目中懒得再去配gulp,直接可以拿这篇博客中的来用,因为有时候配置还是挺烦人的. gulp相关插件的介绍 用法比较简单,假设大家都会用gulp,下面主要介绍一下一些插件的 ...
