第十四章 Java常用类
| 14、常用类 | |
| 14.1 字符串相关的类 | 1课时 |
| 14.2 JDK 8之前时间日期API | 1课时 |
| 14.3 JDK8中新时间日期API | 1课时 |
| 14.4 JDK8中的Optional类 | 1课时 |
| 14.5 Math类 | 1课时 |
| 14.6 BigInteger 类与BigDecimal类 | 1课时 |
##14-1 字符串相关的类









案例
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import org.junit.Test;
public class StringTest {
@Test
public void test4(){
String s1 = "javaEE";
String s2 = "hadoop";
String s3 = "javaEEhadoop";
String s4 = "javaEE" + "hadoop";
//s5 - s8 :凡是声明为变量做连接运算的,都需要重新开辟空间。
String s5 = s1 + "hadoop";
String s6 = "javaEE" + s2;
String s7 = s1 + s2;
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//true
System.out.println(s3 == s5);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s6);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s7);//false
System.out.println(s5 == s6);//false
System.out.println(s5 == s7);//false
System.out.println(s6 == s7);//false
String s8 = s1 + "hadoop";
System.out.println(s5 == s8);//false
//intern():得到的字符串对象以后,通过调用intern(),判断现有的字符串常量池中是否已经存在了当前内容
//的字符串。如果存在,则直接引用现成的字符串。
String s9 = s6.intern();
System.out.println(s3 == s9);//true
}
//一个小问题
@Test
public void test3(){
String s1 = null;
s1 = "";
s1 += "hello";
System.out.println(s1);//nullhello --->hello
}
/**
* String:代表着不可变的字符序列。
*
* 1.String类的声明
* public final class String implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence
* ①String声明为final,不可被继承。
* ②实现Serializable:表明String可序列化。浏览器/客户端<--->服务器端 进程1<---->进程2
* "{name=Tom,age=12}" JSON:本质就是String
* ③String重写了hashCode()/equals():常常将Map的key声明为String型。
* ④实现Comparable接口:String可以比较大小。
* ⑤实现CharSequence接口:String的底层声明了char[] value数组。
*
* 2.如何理解String的不可变性:
* ①向现有的字符串后添加新的字符串,必须声明新的字符串空间
* ②将现有的字符串替换为新的字符串,必须声明新的字符串空间
* ③只替换现有字符串中的指定某个字符,也必须声明新的字符串空间
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
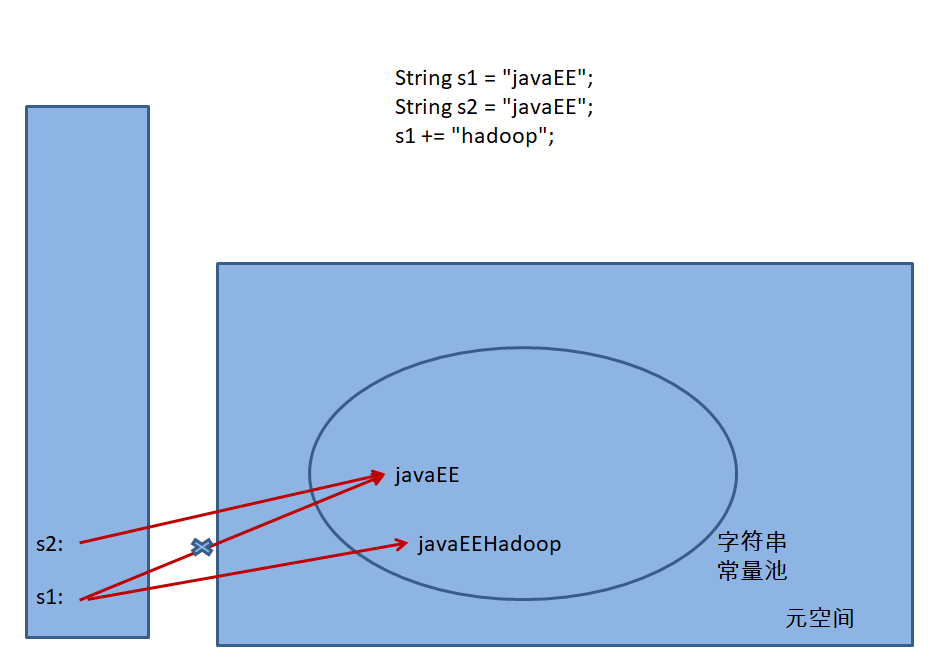
String s1 = "javaEE";
String s2 = "javaEE";
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
s1 += "hadoop";
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println("**********************");
String s3 = "beijing";
String s4 = "beijing";
s3 = "shanghai";
System.out.println(s3);//shanghai
System.out.println(s4);//beijing
System.out.println("**********************");
String s5 = "hello";
String s6 = s5.replace('l', 't');
System.out.println(s6);//hetto
System.out.println(s5);//hello
}
/**
* String:字符串
*
*
* 1.字符串声明的数据,会存储在字符串常量池中。第一次声明时,需要创建相应的字符串。之后,如果声明的变量,其
* 值与之前存在的字符串内容相同,则直接引用现成的字符串。
*
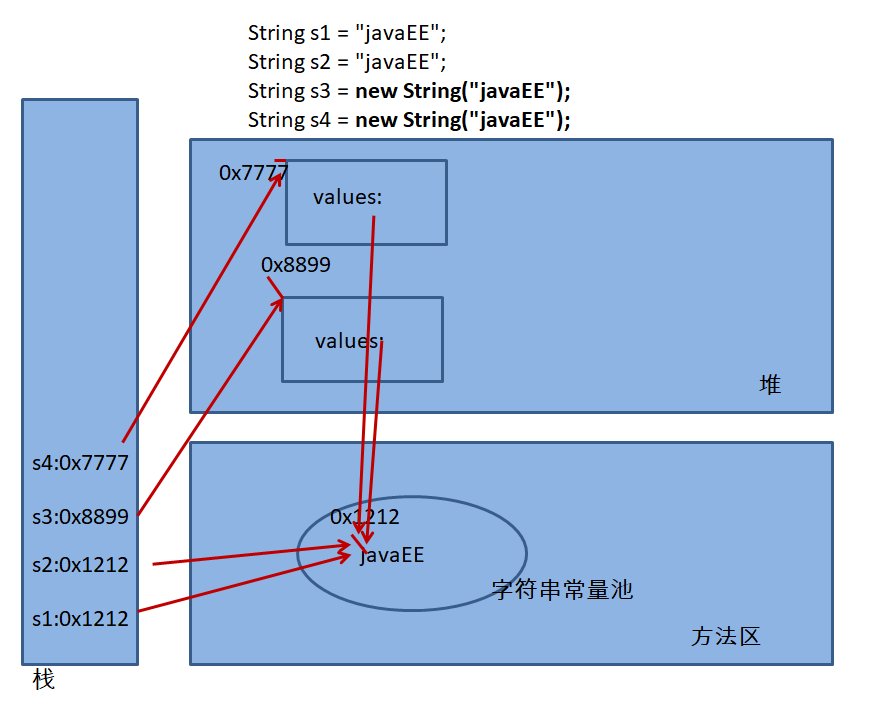
* 2.面试题:String s3 = new String("javaEE");创建的对象,在内存中生成了几个对象?
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
String s1 = "javaEE";
String s2 = "javaEE";
String s3 = new String("javaEE");
String s4 = new String("javaEE");
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true
System.out.println(s1 == s3);//false
System.out.println(s1 == s4);//false
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//false
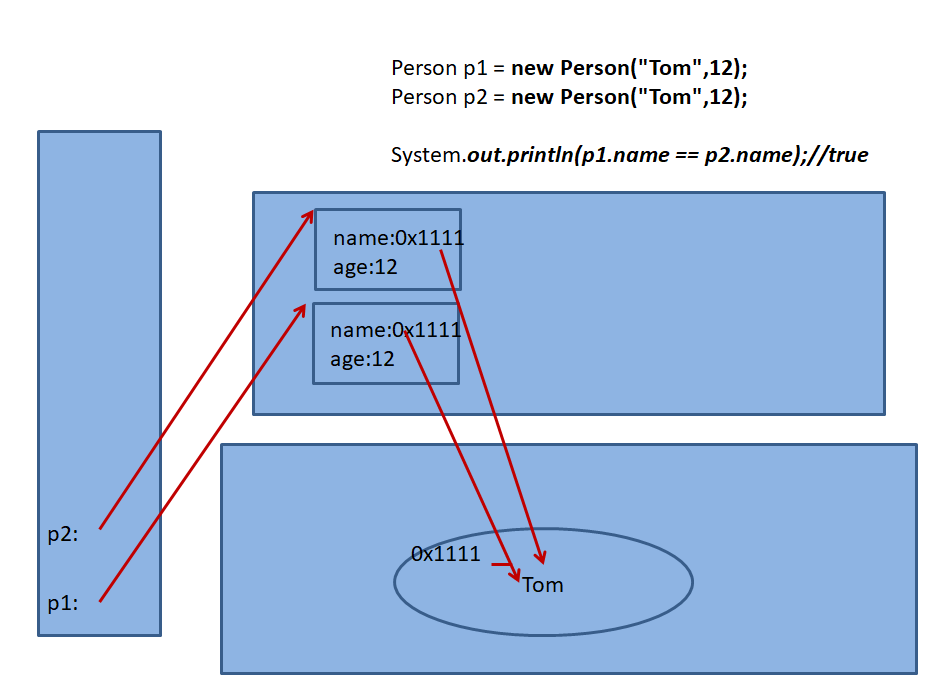
//判断:
Person p1 = new Person("Tom",12);
Person p2 = new Person("Tom",12);
System.out.println(p1.name == p2.name);//true
System.out.println(p1.name == "Tom");//true
}
}
public class StringTest {
/*
* String中常用的方法有哪些?
* length();charAt(int index);equals();compareTo(String str);
* startsWith();endsWith();con0tains();indexOf();lastIndexOf();
*
*
* String类与其它结构的转换:
* 1.String 与包装类、基本数据类型变量间的转换
* String-->包装类、基本数据类型:调用包装类Xxx的parseXxx(String s)方法
* String s = "123";
* 包装类、基本数据类型 -->String:调用String的valueOf(xxx xxx);
*
* 2.String 与 字节数组间的转换
* String --> 字节数组:调用String类的getBytes()
* 字节数组-->String:new String(byte[] buffer,startIndex,length)
*
* 3.String 与 字符数组间的转换
* String --> 字符数组:调用String类的toCharArray()
* 字符数组 -->String:new String(char[] cbuf,startIndex,length)
*
*
*/
/*
public String substring(int startpoint):返回当前字符串中从startPoint位置开始,到末尾的子字符串。
public String substring(int start,int end):返回当前字符串中从startPoint位置开始,到end结束的左闭右开区间的子字符串。
pubic String replace(char oldChar,char newChar):将字符串中指定的所有oldChar替换为newChar.
public String replaceAll(String old,String new):将字符串中指定的所有old替换为new.
public String trim():去除字符串首尾的空格
public String concat(String str):连接两个字符串
public boolean contains(CharSequence s):判断当前字符串中是否包含s.
public String[] split(String regex)
根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串。
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
String[] fakeFileData = {"justin\t64/5/26\t0939002302\t5433343","momor\t68/7/23\t0939100391\t5432343" };
for(String data : fakeFileData) {
String[] tokens = data.split("\t");
//\t为字符串的分割符号。
for(String token : tokens) {
System.out.print(token + "\t| ");}
System.out.println();
}
}
@Test
public void test2(){
String str = "嘻嘻哈哈啦啦咕咕";
String substring = str.substring(2);
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(substring);
System.out.println(str.substring(2, 5));
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("IT", "ET"));
String str1 = " hell o ";
String str2 = str1.trim();
System.out.println("------" + str1 + "------");
System.out.println("------" + str2 + "------");
System.out.println(str.contains("嘻嘻"));
}
/*
public int length():返回当前字符串的长度
public char charAt(int index):获取指定索引位置的字符
public boolean equals(Object anObject):比较两个字符串内容是否相等。
public int compareTo(String anotherString):比较两个字符串的大小
public int indexOf(String s):返回s在当前字符串中首次出现的位置。如果不存在,返回-1.
public int indexOf(String s ,int startpoint):
public int lastIndexOf(String s):返回s在当前字符串中末次出现的位置。如果不存在,返回-1.
public int lastIndexOf(String s ,int startpoint):
public boolean startsWith(String prefix):判断当前的字符串是否以指定的prefix字符串开始的
public boolean endsWith(String suffix):判断当前的字符串是否以指定的suffix字符串结束的
public boolean regionMatches(int firstStart,String other,int otherStart ,int length)
*
*
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
String str = "beijing";
System.out.println(str.length());
System.out.println(str.charAt(0));
// System.out.println(str.charAt(7));//越界
String str1 = new String("beijing");
System.out.println(str.equals(str1));
String str2 = "bbeijing";
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("i"));
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("i",3));
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("beij"));
String str3 = "bbjingcd";
System.out.println(str1.regionMatches(3, str3, 2, 4));
}
}


import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.Test;
public class StringDemo {
/*
*
5.对字符串中字符进行自然顺序排序。
提示:
1)字符串变成字符数组。
2)对数组排序,选择,冒泡,Arrays.sort();
3)将排序后的数组变成字符串
*
*
*/
@Test
public void test5(){
String s = "dsaffvfwqefscer";
char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(charArray);
String sortedStr = new String(charArray);
System.out.println(sortedStr);
}
/*
* 4.获取两个字符串中最大相同子串。比如:
str1 = "abcwerthelloyuiodef";str2 = "cvhellobnm"
提示:将短的那个串进行长度依次递减的子串与较长的串比较。
*
*
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
String str1 = "abcwerthelloyuiodef";
String str2 = "cvhellobnmiodef";
List<String> list = getMaxSameString1(str1,str2);
System.out.println(list);
}
public List<String> getMaxSameString1(String str1,String str2){
String maxStr = (str1.length() > str2.length())? str1 : str2;
String minStr = (str1.length() > str2.length())? str2 : str1;
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
int len = minStr.length();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){//0 1 2 3 4 此层循环决定要去几个字符
for(int x = 0,y = len - i;y <= len;x++,y++){
if(maxStr.contains(minStr.substring(x, y))){
list.add(minStr.substring(x, y));
}
}
// if(list.size() != 0){
// return list;
// }
}
return null;
}
public String getMaxSameString(String str1,String str2){
String maxStr = (str1.length() > str2.length())? str1 : str2;
String minStr = (str1.length() > str2.length())? str2 : str1;
int len = minStr.length();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){//0 1 2 3 4 此层循环决定要去几个字符
for(int x = 0,y = len - i;y <= len;x++,y++){
if(maxStr.contains(minStr.substring(x, y))){
return minStr.substring(x, y);
}
}
}
return null;
}
/*
*3. 获取一个字符串在另一个字符串中出现的次数。
比如:获取“ab”在 “abkkcadkabkebfkabkskab”
中出现的次数
*
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
String son = "ab";
son = "kab";
String mother = "abkkcadkabkebfkabkskab";
int count = getCount(mother,son);
System.out.println(count);
}
//判断son字符串在mother字符串中出现的次数
public int getCount(String mother,String son){
int count = 0;
if(mother.length() >= son.length()){
//方式一:
// int index = 0;
// while((index = mother.indexOf(son)) != -1){
// count++;
// mother = mother.substring(index + son.length());
// }
//方式二:比方式一效率高
int index = 0;
while((index = mother.indexOf(son, index)) != -1){
count++;
index += son.length();
}
return count;
}
return 0;
}
@Test
public void test2(){
String s = "abcdefg";
String s1 = reverse2(s,2,5);
System.out.println(s1);//abfedcg
}
//2.将一个字符串进行反转。将字符串中指定部分进行反转。比如将“abcdefg”反转为”abfedcg”
//方式三:
public String reverse2(String str,int start,int end){
StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer(str.length());
s.append(str.substring(0, start));
for(int i = end;i >= start;i--){
s.append(str.charAt(i));
}
s.append(str.substring(end + 1));
return s.toString();
}
//方式二:效率最低
public String reverse1(String str,int start,int end){
//取第一部分
String s = str.substring(0, start);
//取第二部分
for(int i = end;i >= start;i--){
s += str.charAt(i);
}
//取第三部分
s += str.substring(end + 1);
return s;
}
//方式一:使用数组
public String reverse(String str,int start,int end){
char[] charArray = str.toCharArray();
for(int i = start,j = end;i < j;i++,j--){
char temp = charArray[i];
charArray[i] = charArray[j];
charArray[j] = temp;
}
return new String(charArray);
}
@Test
public void test1(){
String s = " hell oo ";
s = " ";
s = "a ";
s = " b";
String trimS = trim(s);
System.out.println("-------" + trimS + "-----");
}
//1.模拟一个trim方法,去除字符串两端的空格。
public String trim(String s){
if(s != null){
int start = 0;//首索引
int end = s.length() - 1;//最后一个索引
while(start <= end && s.charAt(start) == ' '){
start++;
}
//得到首次出现非空格的索引:start
while(start <= end && s.charAt(end) == ' '){
end--;
}
//从后往前数,首次出现非空格的索引:end
return s.substring(start, end + 1);
}
return null;
}
}






案例
import org.junit.Test;
/**
*
* StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder的使用
*/
public class StringBufferBuilderTest {
/*
* 测试String 、StringBuffer 、 StringBuilder三者的效率
*
* 从效率高到低: StringBuilder > StringBuffer > String
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
long startTime = 0L;
long endTime = 0L;
String text = new String();
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer("");
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("");
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0;i<80000;i++){
buffer.append(String.valueOf(i));
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("StringBuffer的执行时间:"+(endTime-startTime));
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0;i<80000;i++){
builder.append(String.valueOf(i));
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("StringBuilder的执行时间:"+(endTime-startTime));
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0;i<80000;i++){
text = text + i;
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("String的执行时间:"+(endTime-startTime));
}
/**
* StringBuffer中的方法:
StringBuffer append(String s), StringBuffer append(int n) ,
StringBuffer append(Object o) , StringBuffer append(char n),
StringBuffer append(long n), StringBuffer append(boolean n),
StringBuffer insert(int index, String str)
public StringBuffer reverse()
StringBuffer delete(int startIndex, int endIndex):删除当前可变字符串中从startIndex到endIndex结束的左闭右开区间的数据。
public char charAt(int n )
public void setCharAt(int n ,char ch)
StringBuffer replace( int startIndex ,int endIndex, String str)
public int indexOf(String str)
public String substring(int start,int end)
public int length()
*
* 总结:
* 增:append(Xxx xxx)
* 删:delete(int startIndex, int endIndex)
* 改:setCharAt(int n ,char ch) / replace( int startIndex ,int endIndex, String str)
* 查:charAt(int n)
* 插:insert(int index, String str)
* 长度:length()
* 遍历:使用for + charAt()
*
*
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer("helloworld");
// StringBuffer s2 = s1.delete(2, 5);
// System.out.println(s1);
// System.out.println(s2);
StringBuffer s3 = s1.replace(2, 5, "ccc");
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s3);
}
/**
*
*
* 面试题:
* String:不可变的字符序列;底层使用char[]存储
* StringBuffer:可变的字符序列;线程安全的,效率低;底层使用char[]存储
* StringBuilder:可变的字符序列;线程不安全的,效率高,(jdk 5.0新增);底层使用char[]存储
*
* 类比:String --->数组; StringBuffer --->Vector StringBuilder --->ArrayList
* ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
* list.add(123);//new Object[10];
* ....
* 扩容:1.5倍的方式扩容。
*
*
* 这里:
* String str = new String();//new char[0];
* str.length();
*
* String str1 = new String("abc");//new char[]{'a','b','c'};
*
* 对比:
* StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer();//char[] value = new char[16]
*
* StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer(10);//char[] value = new char[10]
*
* s1.append("abc");//value[0] = 'a',value[1] = 'b',value[2] = 'c';
* ...
* 每次添加时,都需要判断底层的char[]是否能够盛装下新要添加的字符串。
* 如果不能盛装下,需要扩容。默认扩容为原来的2倍 + 2.
*
* 启示:
* StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer(int capacity);开发中建议使用此构造器。
*
*
*
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
String str = new String();
System.out.println(str.length());
}
}
14-2 JDK8之前时间日期API








import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* jdk 8 之前 日期+时间 API的使用
*
*/
public class TimeTest {
/**
* java.util.Calendar(日历)类的使用
*
* @throws ParseException
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
//1.实例化
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
//get()
int day = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(day);
//set()
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 20);
day = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(day);
//add()
calendar.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, -2);
day = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(day);
//日历 --->日期
Date date = calendar.getTime();
System.out.println(date);
//使用指定的Date对象,来设置calendar
Date date1 = new Date();
calendar.setTime(date1);
day = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(day);
}
/*
* 练习一:
* 如何将字符串的"2014-1-16"数据转换为java.sql.Date对象?
*
*
* 练习二:“三天打渔,两天晒网” 从 1990-1-1开始实施。
* 判断1990-1-1之后xxxx-xx-xx日是打渔?晒网?
* 比如:2017-08-15
* 方式一:1990-1-1 ---> 2016-12-31 + 2017-1-1 ----->2017-8-15 计算出总天数
* 计算的总天数为sumDays.
* sumDays % 5 == 1,2,3 :打渔
* sumDays % 5 == 4,0 :晒网
*
* 方式二:1990-1-1 ---->java.util.Date: date1
* 2017-08-15 ------>java.util.Date :date2
*
* sumDays = (date2.getTime() - date1.getTime()) / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) + 1
*
*
*/
@Test
public void testExer() throws ParseException{
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
String info = "2014-1-16";
Date date = sdf.parse(info);
// System.out.println(date);
java.sql.Date date1 = new java.sql.Date(date.getTime());
System.out.println(date1);
}
/**
* java.text.SimpleDateFormat类
*
* 1.SimpleDateFormat的作用:
* 格式化:日期--->文本
* 解析:格式化的逆过程,文本 --->日期
*
* 2.SimpleDateFormat实例化
* @throws ParseException
*
*/
@Test
public void test3() throws ParseException{
//1.使用默认构造器
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();
//格式化:String format(Date date):
Date date = new Date();
String dateStr = sdf.format(date);
System.out.println(dateStr);//17-8-15 下午2:20
//解析: Date parse(String dateStr)
Date date1 = sdf.parse("17-8-15 下午2:18");
System.out.println(date1);
//2.使用带参数的构造器
// SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("EEE, d MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss Z");
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
//格式化
String dateStr1 = sdf1.format(date);
System.out.println(dateStr1);//2017-08-15 02:24:40
//解析
Date date2 = sdf1.parse("2017-08-15 02:24:40");
System.out.println(date2);
}
/**
* java.util.Date类
* |----java.sql.Date类
*
* 1.java.util.Date类:
* 如何实例化:两个构造器
* 常用方法:toString() / getTime();
*
* 2.java.sql.Date类:与数据表中的Date类型的变量对应。
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
//构造器一:获取系统当前时间对应的Date对象
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date.toString());
//getTime():返回当前日期对应的毫秒数:当前时间与1970-1-1 00:00:00直接的毫秒数
System.out.println(date.getTime());
//构造器二:获取毫秒数所对应的Date对象
Date date1 = new Date(1502768492941L);
System.out.println(date1);
System.out.println("************如下的是java.sql.Date*********************");
//实例化:
java.sql.Date date2 = new java.sql.Date(1502768492941L);
System.out.println(date2.toString());//2017-08-15
System.out.println(date2.getTime());
//小练习:如何将java.util.Date转换为java.sql.Date
//情形一:
Date date3 = new java.sql.Date(153145234532L);
// date3 = new Date();//会报异常
java.sql.Date date4 = (java.sql.Date) date3;
System.out.println(date4);
//情形二:
System.out.println();
Date date5 = new Date();
java.sql.Date date6 = new java.sql.Date(date5.getTime());
System.out.println(date6);
}
@Test
public void test1(){
//用来返回当前时间与1970年1月1日0时0分0秒之间以毫秒为单位的时间差。
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(currentTimeMillis);
}
}
14-3 JDK8中新时间日期API

闰秒,是指为保持协调世界时接近于世界时时刻,由国际计量局统一规定在年底或年中(也可能在季末)对协调世界时增加或减少1秒的调整。由于地球自转的不均匀性和长期变慢性(主要由潮汐摩擦引起的),会使世界时(民用时)和原子时之间相差超过到±0.9秒时,就把协调世界时向前拨1秒(负闰秒,最后一分钟为59秒)或向后拨1秒(正闰秒,最后一分钟为61秒); 闰秒一般加在公历年末或公历六月末。
目前,全球已经进行了27次闰秒,均为正闰秒。












import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.OffsetDateTime;
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.format.FormatStyle;
import java.time.temporal.Temporal;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAccessor;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjusters;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Set;
import org.junit.Test;
public class JDK8TimeTest {
//7.DateTimeFormatter:日期时间的格式化工具 -----重要
//类似于:SimpleDateFormat
@Test
public void test9(){
// 预定义的标准格式。如:ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;ISO_LOCAL_DATE
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
String formatDateTime = dateTimeFormatter.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(formatDateTime);
// 本地化相关的格式。如:ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.MEDIUM)
//FormatStyle.MEDIUM / FormatStyle.LONG :适用于LocalDateTime
//FormatStyle.FULL / FormatStyle.SHORT : 适用于LocalDate / LocalTime
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter1 = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.MEDIUM);
//格式化:DateTime ---->文本
String formatDateTime1 = dateTimeFormatter1.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(formatDateTime1);//2017-8-15 17:04:50
//解析:文本 --->DateTime
TemporalAccessor temporalAccessor = dateTimeFormatter1.parse("2017-8-15 17:04:50");
System.out.println(temporalAccessor);
// 自定义的格式。如:ofPattern(“yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss E”)
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
//格式化:DateTime ---->文本
String dateTimeStr = dateTimeFormatter2.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(dateTimeStr);//2017-08-15 05:07:33
//解析:文本 --->DateTime
TemporalAccessor temporalAccessor1 = dateTimeFormatter2.parse("2017-08-15 05:07:33");
System.out.println(temporalAccessor1);
}
//6.TemporalAdjuster:时间校正器
@Test
public void test8(){
//获取当前日期的下一个周日是哪天?
TemporalAdjuster temporalAdjuster = TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.SUNDAY);
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now().with(temporalAdjuster);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
//获取下一个工作日是哪天?
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now().with(new TemporalAdjuster(){
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
LocalDate date = (LocalDate)temporal;
if(date.getDayOfWeek().equals(DayOfWeek.FRIDAY)){
return date.plusDays(3);
}else if(date.getDayOfWeek().equals(DayOfWeek.SATURDAY)){
return date.plusDays(2);
}else{
return date.plusDays(1);
}
}
});
System.out.println("下一个工作日是:" + localDate);
}
//5.Period:用于计算两个“日期”间隔,以年、月、日衡量
@Test
public void test7(){
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2028, 3, 18);
Period period = Period.between(localDate, localDate1);
System.out.println(period);
System.out.println(period.getYears());
System.out.println(period.getMonths());
System.out.println(period.getDays());
Period period1 = period.withYears(2);
System.out.println(period1);
}
//4.Duration:用于计算两个“时间”间隔,以秒和纳秒为基准
@Test
public void test6(){
LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.now();
LocalTime localTime1 = LocalTime.of(15, 23, 32);
//between():静态方法,返回Duration对象,表示两个时间的间隔
Duration duration = Duration.between(localTime1, localTime);
System.out.println(duration);
System.out.println(duration.getSeconds());
System.out.println(duration.getNano());
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2016, 6, 12, 15, 23, 32);
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2017, 6, 12, 15, 23, 32);
Duration duration1 = Duration.between(localDateTime1, localDateTime);
System.out.println(duration1.toDays());
}
//3. ZonedDateTime:带时区的日期时间
@Test
public void test5(){
//now():获取本时区的ZonedDateTime对象
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
System.out.println(zonedDateTime);
//now(ZoneId id):获取指定时区的ZonedDateTime对象
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime1 = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Tokyo"));
System.out.println(zonedDateTime1);
}
//3. ZoneId:类中包含了所有的时区信息
@Test
public void test4(){
//getAvailableZoneIds():获取所有的ZoneId
Set<String> zoneIds = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();
for(String s : zoneIds){
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println();
//获取“Asia/Tokyo”时区对应的时间
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Tokyo"));
System.out.println(localDateTime);
}
//2. Instant:时间点 -----重要
//类似:Date
@Test
public void test3(){
//now():得到Instant的实例
Instant instant = Instant.now();//表示自1970年1月1日0时0分0秒(UTC)开始的秒数
System.out.println(instant);
//atOffset():得到带偏移量的日期时间
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = instant.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));
System.out.println(offsetDateTime);
//得到时间戳
long milli = instant.toEpochMilli();
System.out.println(milli);//1502785241830
//根据毫秒数,得到时间点的对象
Instant instant2 = Instant.ofEpochMilli(milli);
System.out.println(instant2);
}
//1. LocalDate / LocalTime / LocalDateTime -----重要
//理解为对Calendar
@Test
public void test2(){
//实例化
//now()
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.now();
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(localDate);
System.out.println(localTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
//of()
LocalDate localDate2 = LocalDate.of(2017, 8, 15);
System.out.println(localDate2);
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = LocalDateTime.of(2017, 8, 15, 11, 11, 23);
System.out.println(localDateTime2);
System.out.println();
//getXxx():
System.out.println(localDateTime.getDayOfYear());
System.out.println(localDateTime.getDayOfMonth());
System.out.println(localDateTime.getDayOfWeek());
System.out.println(localDateTime.getMonth());
System.out.println(localDateTime.getMonthValue());
System.out.println(localDateTime.getHour());
System.out.println(localDateTime.getMinute());
//withXxx():体现了不可变性
LocalDateTime localDateTime3 = localDateTime.withDayOfMonth(20);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime3);
LocalDateTime localDateTime4 = localDateTime.withHour(12);
System.out.println(localDateTime4);
//plus()
//minus()
LocalDateTime localDateTime5 = localDateTime.plusDays(3);
System.out.println(localDateTime5);
LocalDateTime localDateTime6 = localDateTime.minusMinutes(20);
System.out.println(localDateTime6);
boolean isBefore = localDateTime.isBefore(localDateTime6);
System.out.println(isBefore);//false
boolean isAfter = localDateTime.isAfter(localDateTime6);
System.out.println(isAfter);//true
//isLeapYear():
System.out.println(localDate.isLeapYear());
LocalDate localDate3 = localDate.minusYears(1);
System.out.println(localDate3.isLeapYear());
}
@Test
public void test1(){
Date date = new Date(2017-1900, 8 - 1, 15);
System.out.println(date);
}
}
14-4 JDK8中的Optional类


public class Girl {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Girl(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Girl [name=" + name + "]";
}
}
public class Man {
private Girl girl;
public Man(Girl girl) {
super();
this.girl = girl;
}
public Girl getGirl() {
return girl;
}
public void setGirl(Girl girl) {
this.girl = girl;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Man [girl=" + girl + "]";
}
public Man() {
super();
}
}
import java.util.Optional;
import org.junit.Test;
public class ManTest {
// Optional使用的练习
@Test
public void test3(){
String name = getGirlName2(new Man(new Girl("迪丽热巴")));
System.out.println(name);
name = getGirlName2(new Man());
System.out.println(name);
name = getGirlName2(null);
System.out.println(name);
}
public String getGirlName2(Man man){
Optional<Man> op = Optional.ofNullable(man);
Man man1 = op.orElse(new Man(new Girl("佟老师")));//man1一定是非空的
Girl girl = man1.getGirl();
Optional<Girl> op1 = Optional.ofNullable(girl);
Girl girl1 = op1.orElse(new Girl("苍老师"));//girl1一定是非空的
return girl1.getName();
}
@Test
public void test2(){
String name = getGirlName1(new Man());
System.out.println(name);
}
public String getGirlName1(Man man){
if(man != null){
Girl girl = man.getGirl();
if(girl != null){
return girl.getName();
}
}
return "苍老师";
}
@Test
public void test1() {
//原来的方式可能存在空指针异常。
// String name = getGirlName(null);
String name = getGirlName(new Man());
System.out.println(name);
}
public String getGirlName(Man man){
return man.getGirl().getName();
}
}
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* Optional类使用的测试
*
* Optional:是一个封装了具体类型数据的容器。
* 其中,具体的类型:通过Optional的泛型体现。
* 具体类型的数据:通过Optional内部的T value体现
*/
public class OptionalTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
//返回一个没有封装任何数据的Optional对象
// Optional<Object> op = Optional.empty();
// System.out.println(op);
//
// //isPresent():判断内部的数据是否存在
// if(op.isPresent()){
// //get():返回Optional对象内部封装的数据
// System.out.println(op.get());
// }else{
// System.out.println("内部木有数据");
// }
System.out.println("**********************");
//of(T t):当t为null时,报异常。建议不用此方法
Optional<String> op = Optional.of("beijing");
// Optional<String> op = Optional.of(null);
System.out.println(op);
//isPresent():判断内部的数据是否存在
if(op.isPresent()){
//get():返回Optional对象内部封装的数据
System.out.println(op.get());
}else{
System.out.println("内部木有数据");
}
System.out.println("**********************");
// Optional<String> op1 = Optional.ofNullable("beijing");
Optional<String> op1 = Optional.ofNullable(null);
System.out.println(op1);
//isPresent():判断内部的数据是否存在
if(op1.isPresent()){
//get():返回Optional对象内部封装的数据
System.out.println(op1.get());
}else{
// System.out.println("内部木有数据");
//orElse(T t):如果调用对象包含值,返回该值,否则返回t
String str = op1.orElse("xxxxx");
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("**********************");
//总结:"beijing"位置的对象如果不为空,则返回此对象。如果为空,返回"shanghai"对应的对象。
//进而,通过使用Optional能够规避空指针的异常。
Optional<String> op2 = Optional.ofNullable("beijing");
String str1 = op2.orElse("shanghai");
System.out.println(str1);
}
}
14-5 Math类


import java.io.IOException;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import org.junit.Test;
public class OtherTest {
/*
* Integer类作为int的包装类,能存储的最大整型值为2^31−1,
* BigInteger类的数值范围较Integer类、Long类的数值范围要大得多,可以支持任意精度的整数。
*
* 在商业计算中,要求数字精度比较高,故用到java.math.BigDecimal类。BigDecimal类支持任何精度的定点数。
*
*
*/
@Test
public void testBigInteger(){
BigInteger bi = new BigInteger("12433241123");
BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal("12435.351");
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("11");
System.out.println(bi);
//System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2));
System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));
System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2,15,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));
}
//规则:var + 0.5 之后,截断。
// 11.6 + 0.5 = 12.1
// 11.4 + 0.5 = 11.9
@Test
public void test2() {
long l = Math.round(-11.5); // -11.5 + 0.5 = -11
System.out.println(l);
long l1 = Math.round(-11.4);// -11.4 + 0.5 = -10.9
System.out.println(l1);
long l2 = Math.round(-11.6);// - 11.6 + 0.5 = -11.1
System.out.println(l2);
}
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
String str = "学java";
System.out.println(str.getBytes("UTF-8").length);
System.out.println(str.getBytes("GBK").length);
}
}
14-6 BigInteger与BigDecimal类



虚拟机内存解析移步
第十四章 Java常用类的更多相关文章
- 前端(十四)—— JavaScript常用类:Number、Date类、字符串、数组、Math类、正则
JS常用类:Number类.Date类.Math类.字符串.数组.正则 一.Number 1.常用数字 整数:10 小数:3.14 科学计数法:1e5 | 1e-5 正负无穷:Infinity | - ...
- java 面向对象编程 --第十二章 JDK常用类
1. 系统类 java.lang包 System类 sys.out;sys.exit;sys.gc; sys.currentTimeMillis();----得到从1970-01-01到当前时间 ...
- Java面向对象笔记 • 【第6章 Java常用类】
全部章节 >>>> 本章目录 6.1 Object类 6.1.1 Object类概述 6.1.2 Object的常用方法 6.1.3 实践练习 6.2 String类和St ...
- 第13章 Java常用类
1.自动装箱和自动拆箱 自动装箱:基本类型就自动的封装到与它相同类型的包装中:如: 创建一个对象时:Integer i = 100;本质上是编译器编译时为我们添加了:Integer i = new I ...
- VS2010/MFC编程入门之四十四(MFC常用类:定时器Timer)
前面一节鸡啄米讲了CTime类和CTimeSpan类的使用,本节继续讲与时间有关的定时器.定时器并不是一个类,主要考虑到,提起时间的话就不能不说定时器,所以就把它放到CTime和CTimeSpan之后 ...
- Java中的集合(十四) Map的实现类LinkedHashMap
Java中的集合(十四) Map的实现类LinkedHashMap 一.LinkedHashMap的简介 LinkedHashMap是Map接口的实现类,继承了HashMap,它通过重写父类相关的方法 ...
- “全栈2019”Java多线程第三十四章:超时自动唤醒被等待的线程
难度 初级 学习时间 10分钟 适合人群 零基础 开发语言 Java 开发环境 JDK v11 IntelliJ IDEA v2018.3 文章原文链接 "全栈2019"Java多 ...
- “全栈2019”Java多线程第二十四章:等待唤醒机制详解
难度 初级 学习时间 10分钟 适合人群 零基础 开发语言 Java 开发环境 JDK v11 IntelliJ IDEA v2018.3 文章原文链接 "全栈2019"Java多 ...
- “全栈2019”Java多线程第十四章:线程与堆栈详解
难度 初级 学习时间 10分钟 适合人群 零基础 开发语言 Java 开发环境 JDK v11 IntelliJ IDEA v2018.3 文章原文链接 "全栈2019"Java多 ...
随机推荐
- Robot Framework问题记录
robotframework运行时后台报错UnicodeDecodeError UnicodeDecodeError :'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xb2 in ...
- 用docker-compose部署postgres+ postgis
20190411更新.之前写的太啰嗦,也不删了,重新来.小坑还是有的 psql 命令行客户端 因为postgres用docker镜像安装,所以host不需要安装pg,只需要安装客户端 sudo apt ...
- rabbitmq channel参数详解
文章转载自: https://www.cnblogs.com/piaolingzxh/p/5448927.html 部分参数说明有修改 1.Channel 1.1 channel.exchang ...
- ubuntu1404安装搜狗输入法
1.安装fcitx,一种输入法框架 apt-get install fcitx 2.配置使用fcitx 配置中心-语言支持-键盘输入方式系统,选择fcitx 3.登出再登入 4.下载sougou安装d ...
- pta-3
一:实验代码 include <stdio.h> int main() { char ch; int income=0; int unhappy, sad, glad; unhappy = ...
- SpringBoot之依赖注入DI
相关注解: @Component @Service @Controller @Repository --------------------------------------------- @Inj ...
- laravel orwhere的使用
- laravel 实现增 与查
//调用模型层 <?phpnamespace App;use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Mod ...
- PostgreSQL work_mem理解
官方说法: work_mem (integer) Specifies the amount of memory to be used by internal sort operations and h ...
- Django框架(五)
九.Django与Ajax 一.Ajax简介 AJAX(Asynchronous Javascript And XML)翻译成中文就是“异步Javascript和XML”.即使用Javascript语 ...
