Helvetic Coding Contest 2016 online mirror B1
Description
The zombies are gathering in their secret lair! Heidi will strike hard to destroy them once and for all. But there is a little problem... Before she can strike, she needs to know where the lair is. And the intel she has is not very good.
Heidi knows that the lair can be represented as a rectangle on a lattice, with sides parallel to the axes. Each vertex of the polygon occupies an integer point on the lattice. For each cell of the lattice, Heidi can check the level of Zombie Contamination. This level is an integer between 0and 4, equal to the number of corners of the cell that are inside or on the border of the rectangle.
As a test, Heidi wants to check that her Zombie Contamination level checker works. Given the output of the checker, Heidi wants to know whether it could
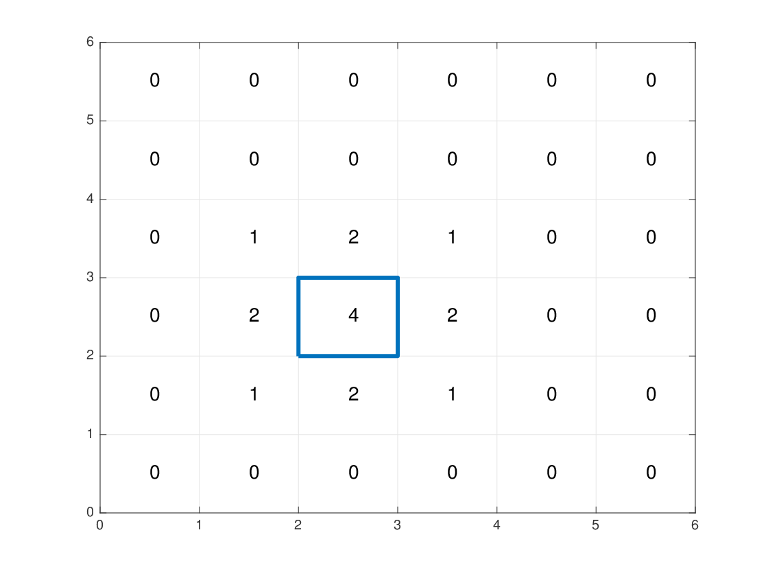
have been produced by a single non-zero area rectangular-shaped lair (with axis-parallel sides).
The first line of each test case contains one integer N, the size of the lattice grid (5 ≤ N ≤ 50). The next N lines each contain N characters, describing the level of Zombie Contamination of each cell in the lattice. Every character of every line is a digit between 0 and 4.
Cells are given in the same order as they are shown in the picture above: rows go in the decreasing value of y coordinate, and in one row cells go in the order of increasing x coordinate. This means that the first row corresponds to cells with coordinates (1, N), ..., (N, N) and the last row corresponds to cells with coordinates (1, 1), ..., (N, 1).
The first line of the output should contain Yes if there exists a single non-zero area rectangular lair with corners on the grid for which checking the levels of Zombie Contamination gives the results given in the input, and No otherwise.
6
000000
000000
012100
024200
012100
000000
Yes
The lair, if it exists, has to be rectangular (that is, have corners at some grid points with coordinates (x1, y1), (x1, y2), (x2, y1), (x2, y2)), has a non-zero area and be contained inside of the grid (that is, 0 ≤ x1 < x2 ≤ N, 0 ≤ y1 < y2 ≤ N), and result in the levels of Zombie Contamination as reported in the input.
1,2,3,4的意思是有几个点和内部接触,比如1只有一个点和4接触,2有两个点和4接触,4就在里面就是4个,就是没有3.。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
string a[1000];
int Mx=-1000,My=-1000,mx=1000,my=1000;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]!='0')
{
Mx=max(Mx,i);
mx=min(mx,i);
My=max(My,j);
my=min(my,j);
}
}
}
if(a[Mx][my]!='1'||a[mx][my]!='1'||a[Mx][My]!='1'||a[mx][My]!='1')
{
puts("No");
return 0;
}
else
{
for(int j=my+1;j<=My-1;j++)
{
// cout<<a[mx][j];
if(a[mx][j]!='2')
{
puts("No");
return 0;
}
}
for(int j=my+1;j<=My-1;j++)
{
// cout<<a[mx][j];
if(a[Mx][j]!='2')
{
puts("No");
return 0;
}
}
for(int i=mx+1;i<=Mx-1;i++)
{
// cout<<a[i][my];
if(a[i][my]!='2')
{
puts("No");
return 0;
}
}
for(int i=mx+1;i<=Mx-1;i++)
{
// cout<<a[i][My];
if(a[i][My]!='2')
{
puts("No");
return 0;
}
}
for(int i=mx+1;i<=Mx-1;i++)
{
for(int j=my+1;j<=My-1;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]!='4')
{
puts("No");
return 0;
}
}
}
}
puts("Yes");
return 0;
}
Helvetic Coding Contest 2016 online mirror B1的更多相关文章
- CF 690C3. Brain Network (hard) from Helvetic Coding Contest 2016 online mirror (teams, unrated)
题目描述 Brain Network (hard) 这个问题就是给出一个不断加边的树,保证每一次加边之后都只有一个连通块(每一次连的点都是之前出现过的),问每一次加边之后树的直径. 算法 每一次增加一 ...
- Helvetic Coding Contest 2016 online mirror A1
Description Tonight is brain dinner night and all zombies will gather together to scarf down some de ...
- Helvetic Coding Contest 2016 online mirror F1
Description Heidi has finally found the mythical Tree of Life – a legendary combinatorial structure ...
- Helvetic Coding Contest 2016 online mirror C2
Description Further research on zombie thought processes yielded interesting results. As we know fro ...
- Helvetic Coding Contest 2016 online mirror D1
Description "The zombies are lurking outside. Waiting. Moaning. And when they come..." &qu ...
- Helvetic Coding Contest 2016 online mirror C1
Description One particularly well-known fact about zombies is that they move and think terribly slow ...
- Helvetic Coding Contest 2019 online mirror (teams allowed, unrated)
http://codeforces.com/contest/1184 A1 找一对整数,使x^x+2xy+x+1=r 变换成一个分式,保证整除 #include<iostream> #in ...
- [Helvetic Coding Contest 2017 online mirror]
来自FallDream的博客,未经允许,请勿转载,谢谢, 第一次在cf上打acm...和同校大佬组队打 总共15题,比较鬼畜,最后勉强过了10题. AB一样的题目,不同数据范围,一起讲吧 你有一个背包 ...
- 【Codeforces】Helvetic Coding Contest 2017 online mirror比赛记
第一次打ACM赛制的团队赛,感觉还行: 好吧主要是切水题: 开场先挑着做五道EASY,他们分给我D题,woc什么玩意,还泊松分布,我连题都读不懂好吗! 果断弃掉了,换了M和J,然后切掉了,看N题: l ...
随机推荐
- Codeforces Round #402 (Div. 2) 阵亡记
好长时间没有打Codeforces了,今天被ysf拉过去打了一场. lrd也来参(nian)加(ya)比(zhong)赛(sheng) Problem A: 我去,这不SB题吗.. 用桶统计一下每个数 ...
- mysql du-master配置
db-server1 my.cnf log_bin = mysql-binbinlog_format = mixedserver_id = 1 read-only = 0#binlog-do-db = ...
- poj 1517 u Calculate e(精度控制+水题)
一.Description A simple mathematical formula for e is e=Σ0<=i<=n1/i! where n is allowed to go t ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(六九):HTTP服务(3):HTTP POST MultiPart
目录(?)[-] 建立测试环境 开发环境导入第三方JAR HTTP Post Multipart小例子 HTTP POST不仅可以通过键值对传递参数,还可以携带更为复杂的参数,例如文件.HTTP Po ...
- nginx利用proxy_cache来缓存文件
为什么要做web cache,我想大家最主要的是解决流量的压力.随着网站流量的提升,如果只是单台机器既处理静态文件,又处理动态脚本,显然效率很难上升,不能处理日益上涨的流量压力.与此同时某些网站的页面 ...
- UE3优化
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/NEOCSL/p/3320510.html 优化问题有很多内容可讲,涉及林林总总.今天我总结一下优化注意的地方. 1.从AnimTree和Skele ...
- 《Kubernetes权威指南第2版》学习(四)kubernetes基本概念和术语
1: etcd是干什么的: 键-值存储仓库,用来配置共享和服务发现. k8s把Node, pod,replication controller, Services看做是资源对象,这些资源对象可以通过K ...
- sql server 表索引碎片处理
DBCC SHOWCONTIG (Transact-SQL) SQL Server 2005 其他版本 更新日期: 2007 年 9 月 15 日 显示指定的表或视图的数据和索引的碎片信息. 重要提示 ...
- wdatePicker时间控件的使用
wdatePicker时间控件的使用 1.引用wdatePicker控件的js <seript src="../../js/My97DatePicker/wdatePicker.js& ...
- Qt 按顺序保存多个文件
void MainWindow::on_pushButtonSnap_clicked() { ]; sprintf(image_name, "%s%d%s", "C:/i ...
