DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19

代码:
% Analog Signal
Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signal
Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; x = exp(-1000*abs(n*Ts)); % Discrete-time Fourier Transform
%Wmax = 2*pi*2000;
K = 500; k = 0:1:K; w = pi*k/K; % index array k for frequencies
X = x * exp(-j*n'*w); magX = abs(X); angX = angle(X); realX = real(X); imagX = imag(X);
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
%% START X's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
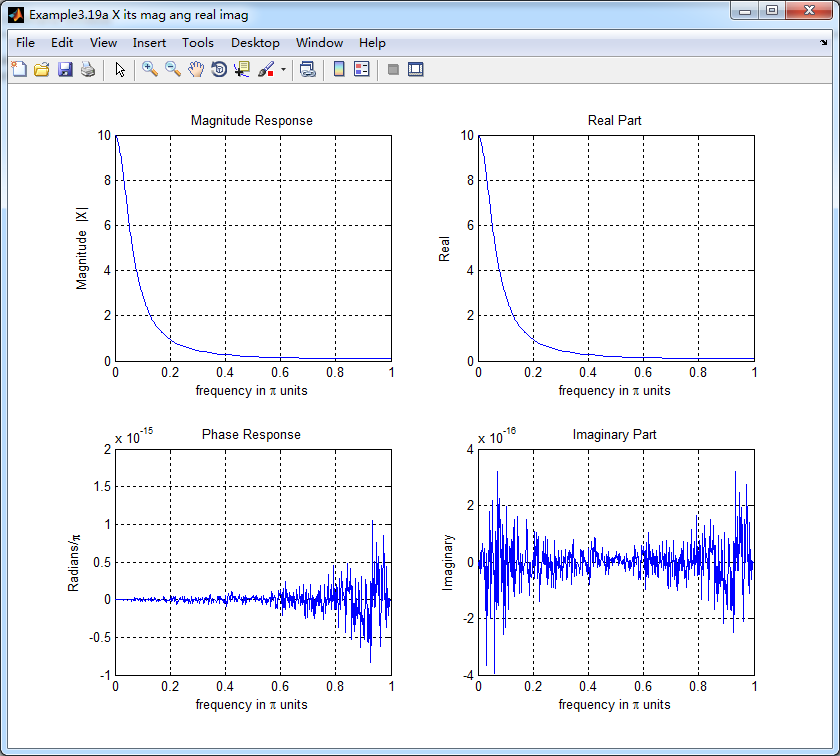
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example3.19a X its mag ang real imag');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magX); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angX/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realX); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagX); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
%% END X's mag ang real imag
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------- X = real(X); w = [-fliplr(w), w(2:K+1)]; % Omega from -Wmax to Wmax
X = [fliplr(X), X(2:K+1)]; % X over -Wmax to Wmax interval
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
%%
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
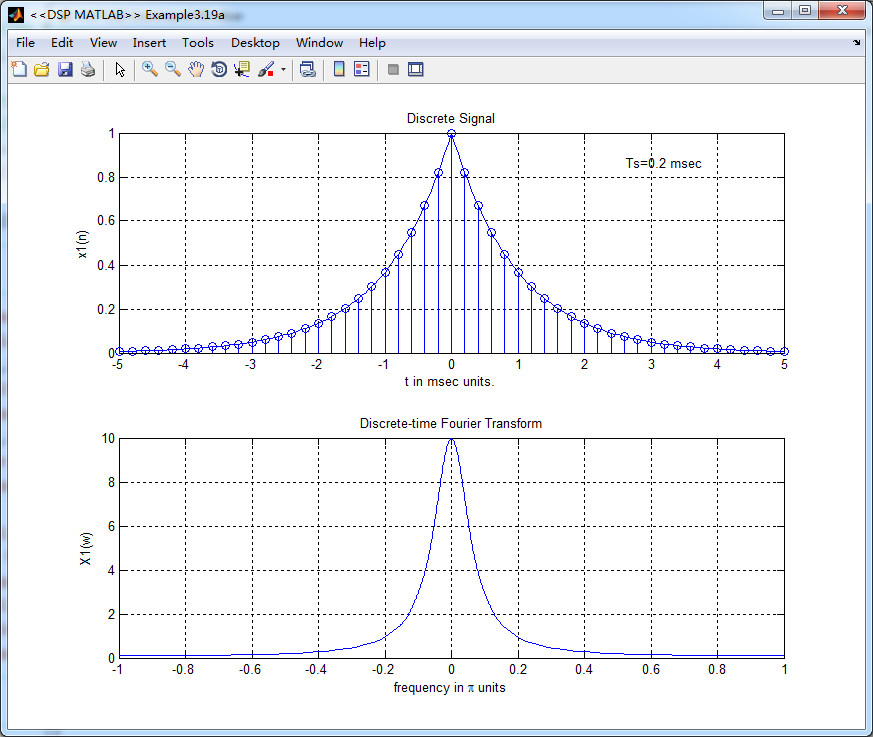
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', '<<DSP MATLAB>> Example3.19a');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(t*1000,xa); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Discrete Signal');
xlabel('t in msec units.'); ylabel('x1(n)'); hold on;
stem(n*Ts*1000,x); gtext('Ts=0.2 msec'); hold off; subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, X); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Discrete-time Fourier Transform');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('X1(w)'); %% -------------------------------------------------------------------
%%
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
运行结果:
b
代码:
% Analog Signal
Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signal
%Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; x = exp(-1000*abs(n*Ts));
Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; x = exp(-1000*abs(n*Ts)); % Discrete-time Fourier Transform
%Wmax = 2*pi*2000;
K = 500; k = 0:1:K; w = pi*k/K; % index array k for frequencies
X = x * exp(-j*n'*w); magX = abs(X); angX = angle(X); realX = real(X); imagX = imag(X);
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
%% START X's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
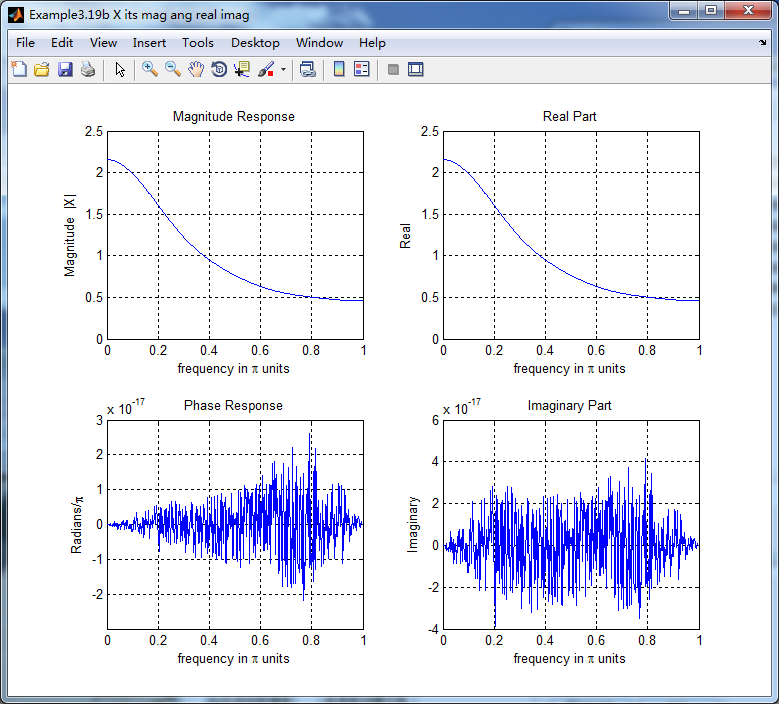
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example3.19b X its mag ang real imag');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magX); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angX/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realX); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagX); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
%% END X's mag ang real imag
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------- X = real(X); w = [-fliplr(w), w(2:K+1)]; % Omega from -Wmax to Wmax
X = [fliplr(X), X(2:K+1)]; % X over -Wmax to Wmax interval
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
%%
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
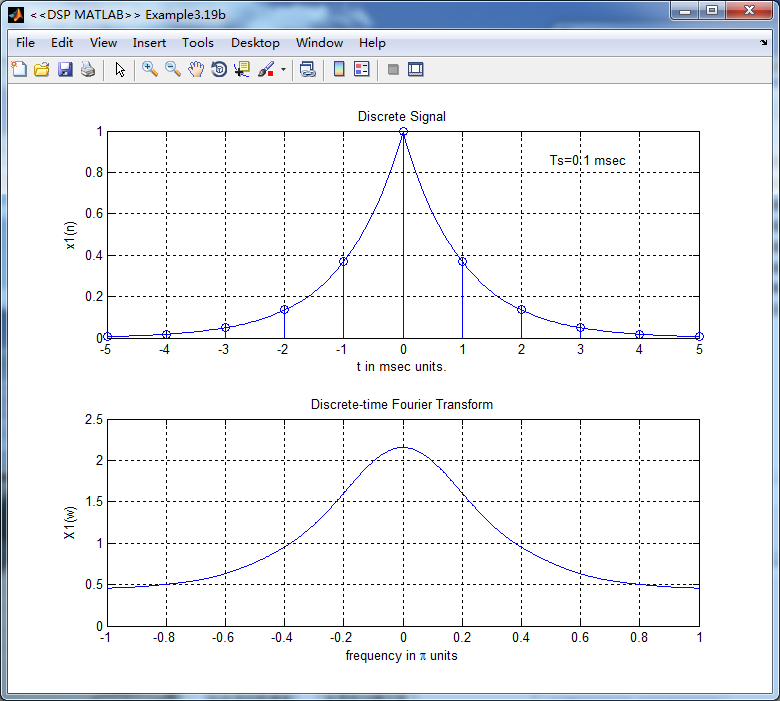
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', '<<DSP MATLAB>> Example3.19b');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); plot(t*1000,xa); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Discrete Signal');
xlabel('t in msec units.'); ylabel('x1(n)'); hold on;
stem(n*Ts*1000,x); gtext('Ts=0.1 msec'); hold off; subplot(2,1,2); plot(w/pi, X); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Discrete-time Fourier Transform');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('X1(w)'); %% -------------------------------------------------------------------
%%
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
运行结果:
DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.17
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.15
上代码: subplot(1,1,1); b = 1; a = [1, -0.8]; n = [0:100]; x = cos(0.05*pi*n); y = filter(b,a,x); figur ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.13
上代码: w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; % freqency between 0 and +pi, [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. H = ex ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12
用到的性质 代码: n = -5:10; x = sin(pi*n/2); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi , ...
随机推荐
- 【python】lxml处理命名空间
有如下xml <A xmlns="http://This/is/a/namespace"> <B>dataB1</B> <B>dat ...
- 25个增强iOS应用程序性能的提示和技巧(中级篇)(2)
25个增强iOS应用程序性能的提示和技巧(中级篇)(2) 2013-04-16 14:42 破船之家 beyondvincent 字号:T | T 本文收集了25个关于可以提升程序性能的提示和技巧,分 ...
- 如何用Endnote导入你要用的格式
在Google搜索某一个期刊名 ens格式的文件,下载,然后放入endnote的文件夹中(C:\Program Files (x86)\EndNote X7\Styles) 然后将其导入即可
- iOS 动态计算文本内容的高度
关于ios 下动态计算文本内容的高度,经过查阅和网上搜素,现在看到的有以下几种方法: 1. // 获取字符串的大小 ios6 - (CGSize)getStringRect_:(NSString* ...
- vs2013中项目依赖项的作用
依赖项就是设定项目所以来的项目,以决定具体生成解决方案时,项目编译的顺序(一般一个解决方案会有很多项目组成). 通常来说,依赖项取决于这个项目引用的组件和项目,系统可以自己决定. 作用就是让系统知道你 ...
- python基础——使用元类
python基础——使用元类 type() 动态语言和静态语言最大的不同,就是函数和类的定义,不是编译时定义的,而是运行时动态创建的. 比方说我们要定义一个Hello的class,就写一个hello. ...
- Swift - 状态栏颜色显示(字体、背景)
ios上状态栏 就是指的最上面的20像素高的部分 状态栏分前后两部分,要分清这两个概念,后面会用到: 前景部分:就是指的显示电池.时间等部分: 背景部分:就是显示黑色或者图片的背景部分: 如下图:前景 ...
- Swift - 懒加载(lazy initialization)
Swift中是存在和OC一样的懒加载机制的,在程序设计中,我们经常会使用 懒加载 ,顾名思义,就是用到的时候再开辟空间 懒加载 格式: lazy var 变量: 类型 = { 创建变量代码 }() 懒 ...
- 理解KMP算法
母串:S[i] 模式串:T[i] 标记数组:Next[i](Next[i]表示T[0~i]最长前缀/后缀数) 先来讲一下最长前缀/后缀的概念 例如有字符串T[6]=abcabd接下来讨论的全部是真前缀 ...
- Loadrunner之HTTP接口测试脚本实例
接口测试的原理是通过测试程序模拟客户端向服务器发送请求报文,服务器接收请求报文后对相应的报文做出处理然后再把应答报文发送给客户端,客户端接收应答报文结果与预期结果进行比对的过程,接口测试可以通过Jav ...
