160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists【Easy】【求两个单链表的第一个交点】
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
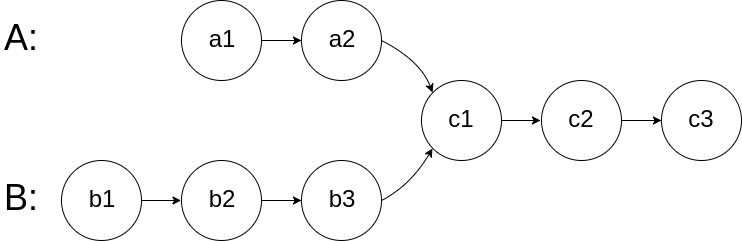
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
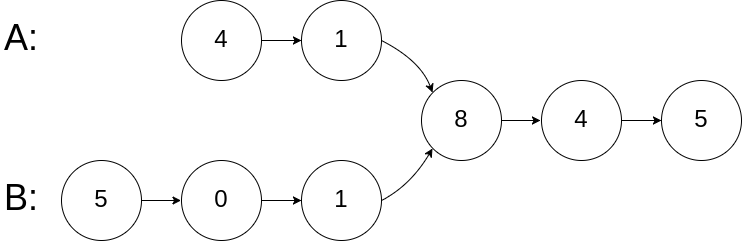
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Example 2:
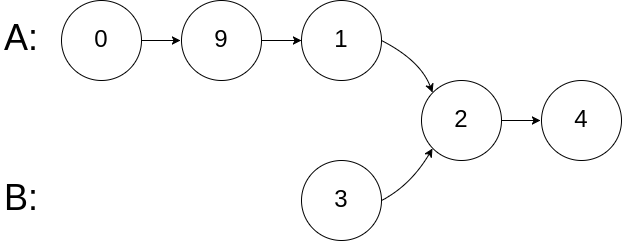
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Reference of the node with value = 2
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:
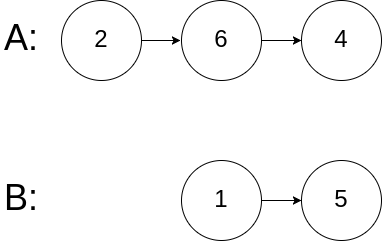
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: null
Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
null. - The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
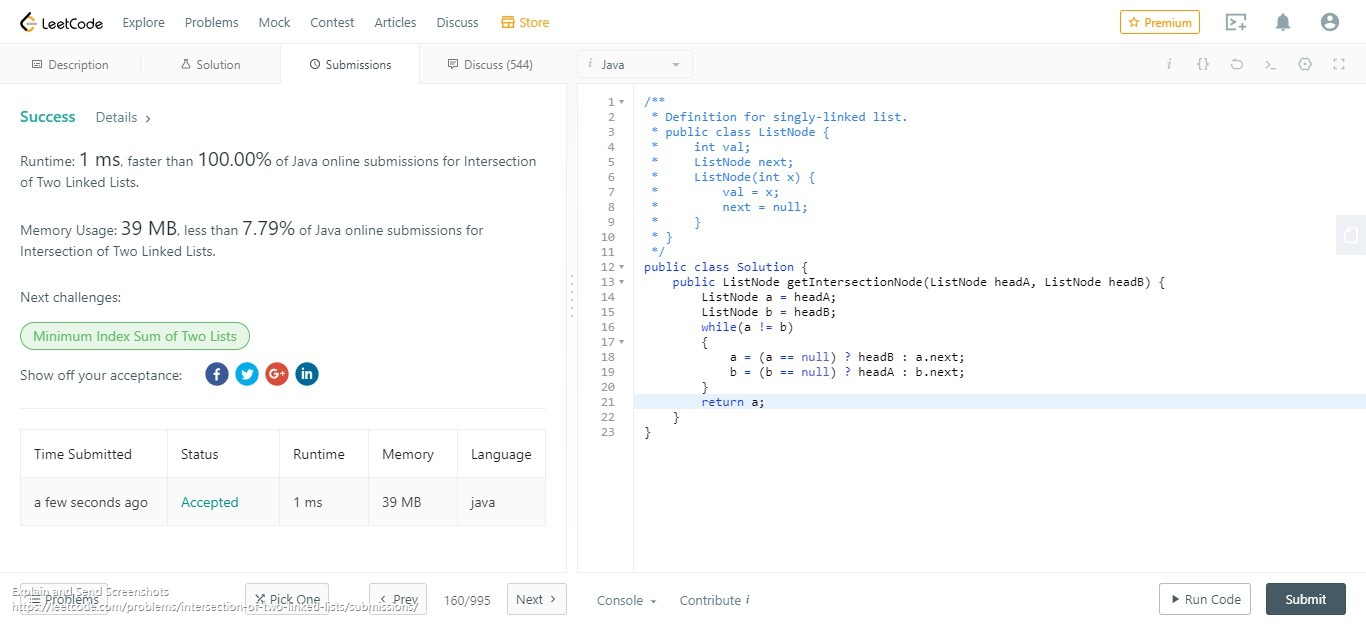
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode a = headA;
ListNode b = headB;
while(a != b)
{
a = (a == null) ? headB : a.next;
b = (b == null) ? headA : b.next;
}
return a;
}
}
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists【Easy】【求两个单链表的第一个交点】的更多相关文章
- 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists(剑指Offer-两个链表的第一个公共结点)
题目: Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins. Fo ...
- LeetCode--LinkedList--160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists(Easy)
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists(Easy) 题目地址https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-li ...
- 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists【easy】
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists[easy] Write a program to find the node at which the intersecti ...
- [LeetCode] 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists 解题思路
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins. For ex ...
- [LeetCode]160.Intersection of Two Linked Lists(2个链表的公共节点)
Intersection of Two Linked Lists Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two s ...
- [LeetCode] 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists 求两个链表的交集
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins. For ex ...
- ✡ leetcode 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists 求两个链表的起始重复位置 --------- java
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins. For ex ...
- LeetCode OJ 160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins. For ex ...
- 【LeetCode】160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
题目: Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins. Fo ...
随机推荐
- hdu 3689 Infinite monkey theorem
Infinite monkey theorem Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/ ...
- 【hdu5217-括号序列】线段树
题意:给一串括号,有2个操作,1.翻转某个括号.2.查询某段区间内化简后第k个括号是在原序列中的位置.1 ≤ N,Q ≤ 200000. 题解: 可以知道,化简后的序列一定是)))((((这种形式的. ...
- Kubernetes: 集群网络配置 - flannel
参考: [ Kubernetes 权威指南 ] Kubernetes 集群搭建可以参考 [ Kubernetes : 多节点 k8s 集群实践 ] 在多个 Node 组成的 Kubernetes 集群 ...
- Centos服务器ssh免密登录以及搭建私有git服务器
一.概述 服务器的免密登录和git服务器的搭建,关键都是要学会把自己用的机器的公钥添加到服务器上,让服务器“认识”你的电脑,从而不需要输入密码就可以远程登录服务器上的用户 免密登录当然是登录root用 ...
- js获取屏幕高度宽度
获取各种屏幕的宽度和高度Javascript: 网页可见区域宽: document.body.clientWidth网页可见区域高: document.body.clientHeight网页可见区域宽 ...
- hdu 1599 find the mincost route (最小环与floyd算法)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1599 find the mincost route Time Limit: 1000/2000 MS ...
- Java面试基础知识1
1.动态绑定是指在执行期间判断所引用对象的实际类型,根据其实际的类型调用其相应的方法. 2.在将超类转换为子类之前,应该使用instanceof进行检查. 3.包含一个或者多个抽象方法的类本身必须被声 ...
- linux percpu机制解析【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/wh8_2011/article/details/53138377 一.概述 每cpu变量是最简单也是最重要的同步技术.每cpu变量主要是数据结构数组, ...
- 64_m1
MAKEDEV-3.24-18.fc26.x86_64.rpm 13-Feb-2017 22:33 101030 MUMPS-5.0.2-8.fc26.i686.rpm 14-Feb-2017 13: ...
- 获取并编译最新的Notepad++源码
获取并编译最新的Notepad++源码 http://blog.csdn.net/u012814856/article/details/68947310 Notepad++源码编译及其分析 http: ...
