SPAN, RSPAN, ERSPAN

该文档摘自:Home > CCIE Routing and Switching Study Group > Discussions
由 Deben 于 2015-2-6 上午6:50 创建,最后由 Deben 于 2015-2-6 上午9:51 修改。
SPAN, RSPAN, ERSPAN

Switch port Analyzer (SPAN) is an efficient, high performance traffic monitoring system. It directs or mirrors traffic from a source port or VLAN to a destination port. This is sometimes referred to as session monitoring. SPAN is used for troubleshooting connectivity issues and calculating network utilization and performance, among many others. There are three types of SPANs supported on Cisco products …
a. SPAN or local SPAN.
b. Remote SPAN (RSPAN).
c. Encapsulated remote SPAN (ERSPAN).
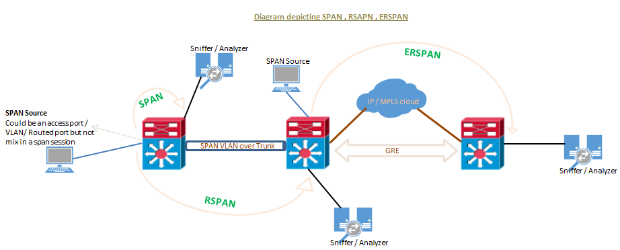
SPAN / traffic mirroring / port mirroring is used for many purposes, below includes some.
- Implementing IDS/IPS in promiscuous mode.
- VOIP call recording solutions.
- Security compliance reasons to monitor and analyze traffic.
- Troubleshooting connection issues, monitoring traffic.
Regardless the SPAN type running, SPAN source can be any type of port i.e. a routed port, physical switch port, an access port, trunk, VLAN (all active ports are monitored of the switch), an EtherChannel (either a port or entire port-channel interfaces) etc. Note that a port configured for SPAN destination CANNOT be part of a SPAN source VLAN.
SPAN sessions support the monitoring of ingress traffic (ingress SPAN), egress traffic (egress SPAN), or traffic flowing in both directions.
- Ingress SPAN (RX) copies traffic received by the source ports and VLANs to the destination port. SPAN copies the traffic before any modification (for example before any VACL or ACL filter, QoS or ingress or egress policing).
- Egress SPAN (TX) copies traffic transmitted from the source ports and VLANs to the destination port. All relevant filtering or modification by VACL or ACL filter, QoS or ingress or egress policing actions are taken before the switch forwards traffic to SPAN destination port.
- When the both keyword is used, SPAN copies the network traffic received and transmitted by the source ports and VLANs to the destination port.
- SPAN/RSPAN usually ignores CDP, STP BPDU, VTP, DTP and PAgP frames. However these traffic types can be forwarded if the encapsulation replicate command is configured.
SPAN or Local SPAN
SPAN mirrors traffic from one or more interface on the switch to one or more interfaces on the same switch; hence SPAN is mostly referred to as LOCAL SPAN.
Guidelines or restrictions to local SPAN:
- Both Layer 2 switched ports and Layer 3 ports can be configured as source or destination ports.
- The source can be either one or more ports or a VLAN, but not a mix of these.
- Trunk ports are valid source ports mixed with non-trunk source ports.
- Up to 64 SPAN destination ports can be configured on a switch.
- When we configure a destination port, its original configuration is overwritten. If the SPAN configuration is removed, the original configuration on that port is restored.
- When configure a destination port, the port is removed from any EtherChannel bundle if it were part of one. If it were a routed port, the SPAN destination configuration overrides the routed port configuration.
- Destination ports do not support port security, 802.1x authentication, or private VLANs.
- A port can act as the destination port for only one SPAN session.
- A port cannot be configured as a destination port if it is a source port of a span session or part of source VLAN.
- Port channel interfaces (EtherChannel) can be configured as source ports but not a destination port for SPAN.
- Traffic direction is “both” by default for SPAN sources.
- Destination ports never participate in a spanning-tree instance. Cannot support DTP, CDP etc. Local SPAN includes BPDUs in the monitored traffic, so any BPDUs seen on the destination port are copied from the source port. Hence never connect a switch to this type of SPAN as it could cause a network loop.
- When VLAN is configured as SPAN source (mostly referred to as VSPAN) with both ingress and egress options configured, forward duplicate packets from the source port only if the packets get switched in the same VLAN. One copy of the packet is from the ingress traffic on the ingress port, and the other copy of the packet is from the egress traffic on the egress port.
- VSPAN monitors only traffic that leaves or enters Layer 2 ports in the VLAN.
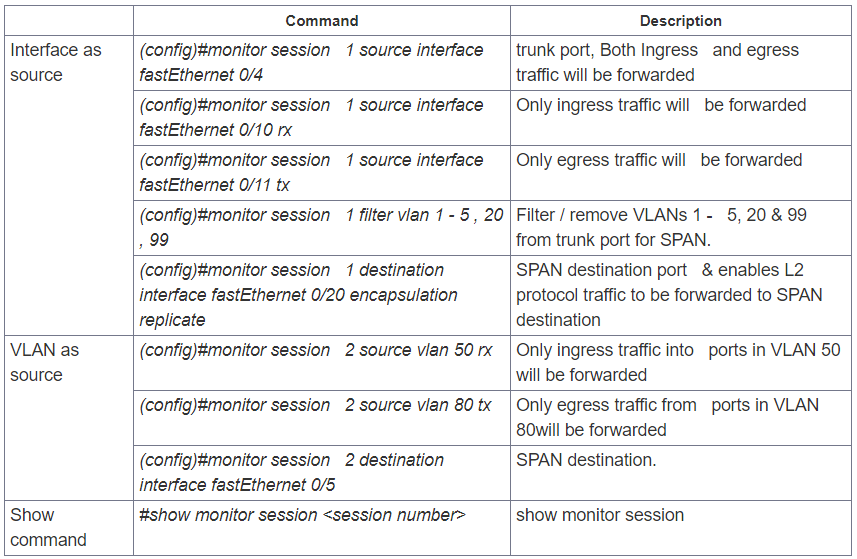
Remote SPAN (RSPAN)
Remote SPAN (RSPAN) is similar to SPAN, but it supports source ports, source VLANs, and destination ports on different switches, which provide remote monitoring traffic from source ports distributed over multiple switches and allows destination centralize network capture devices. Each RSPAN session carries the SPAN traffic over a user-specified dedicated RSPAN VLAN in all participating switches. This VLAN is then trunked to other switches, allowing the RSPAN session traffic to be transported across multiple switches and delivered to destination capturing station. RSPAN consists of an RSPAN source session, an RSPAN VLAN, and an RSPAN destination session.
Guidelines or restrictions to RSPAN:
- A specific VLAN must be configured for SPAN destination which will traverse across the intermediate switches via trunk links toward destination port.
- Can create same source type – at least one port or at least one VLAN but cannot be the mix.
- The destination for the session is RSPAN VLAN rather than the single port in switch, so all ports in RSPAN VLAN will receive the mirrored traffic.
- Configure any VLAN as an RSPAN VLAN as long as all participating network devices support configuration of RSPAN VLANs, and use the same RSPAN VLAN for each RSPAN session
- VTP can propagate configuration of VLANs numbered 1 through 1024 as RSPAN VLANs , must manually configure VLANs numbered higher than 1024 as RSPAN VLANs on all source, intermediate, and destination network devices.
- MAC address learning is disabled in the RSPAN VLAN.

Encapsulated remote SPAN (ERSPAN)
Encapsulated remote SPAN (ERSPAN) brings generic routing encapsulation (GRE) for all captured traffic and allows it to be extended across Layer 3 domains.
ERSPAN is a Cisco proprietary feature and is available only to Catalyst 6500, 7600, Nexus, and ASR 1000 platforms to date. The ASR 1000 supports ERSPAN source (monitoring) only on Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and port-channel interfaces.
Guidelines or restrictions to ERSPAN:
- ERSPAN source sessions do not copy ERSPAN GRE-encapsulated traffic from source ports. Each ERSPAN source session can have either ports or VLANs as sources, but not both.
- Regardless of any configured MTU size, ERSPAN creates Layer 3 packets that can be as long as 9,202 bytes. ERSPAN traffic might be dropped by any interface in the network that enforces an MTU size smaller than 9,202 bytes.
- ERSPAN does not support packet fragmentation. The "do not fragment" bit is set in the IP header of ERSPAN packets. ERSPAN destination sessions cannot reassemble fragmented ERSPAN packets.
- The ERSPAN ID differentiates the ERSPAN traffic arriving at the same destination IP address from various different ERSPAN source sessions; configured ERSPAN ID must match on source and destination devices.
- For a source port or a source VLAN, the ERSPAN can monitor the ingress, egress, or both ingress and egress traffic. By default, ERSPAN monitors all traffic, including multicast and Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) frames.
- Tunnel interface supported as source ports for an ERSPAN source session are GRE, IPinIP, SVTI, IPv6, IPv6 over IP tunnel, Multipoint GRE (mGRE) and Secure Virtual Tunnel Interfaces (SVTI).
- The filter VLAN option is not functional in an ERSPAN monitoring session on WAN interfaces.
- ERSPAN on Cisco ASR 1000 Series Routers supports only Layer 3 interfaces. Ethernet interfaces are not supported on ERSPAN when configured as Layer 2 interfaces.
- When a session is configured through the ERSPAN configuration CLI, the session ID and the session type cannot be changed. To change them, you must first use the no form of the configuration command to remove the session and then reconfigure the session.
- Cisco IOS XE Release 3.4S :- Monitoring of non-IPsec-protected tunnel packets is supported on IPv6 and IPv6 over IP tunnel interfaces only to ERSPAN source sessions, not to ERSPAN destination sessions.
- Cisco IOS XE Release 3.5S, support was added for the following types of WAN interfaces as source ports for a source session: Serial (T1/E1, T3/E3, DS0) , Packet over SONET (POS) (OC3, OC12) and Multilink PPP ( multilink, pos, and serial keywords were added to the source interface command).

Using ERSPAN as Local SPAN:
To use ERSPAN to monitor traffic through one or more ports or VLANs in same device, we must have to create an ERSPAN source and ERSPAN destination sessions in same device, data flow takes place inside the router, which is similar to that in local SPAN.
The following factors are applicable while using ERSPAN as a local SPAN:
- Both sessions have the same ERSPAN ID.
- Both sessions have the same IP address. This IP address is the routers own IP address; that is, the loopback IP address or the IP address configured on any port.
|
(config)# monitor session 10 type erspan-source |
|
(config-mon-erspan-src)# source interface Gig0/0/0 |
|
(config-mon-erspan-src)# destination |
|
(config-mon-erspan-src-dst)# ip address 10.10.10.1 |
|
(config-mon-erspan-src-dst)# origin ip address 10.10.10.1 |
|
(config-mon-erspan-src-dst)# erspan-id 100 |
SPAN, RSPAN, ERSPAN的更多相关文章
- Cisco交换机SPAN&RSPAN调试实录
Cisco交换机SPAN&RSPAN设置实录 本文出自 "李晨光原创技术博客" 博客,请务必保留此出处http://chenguang.blog.51cto.com/3 ...
- Openvswitch手册(1): 架构,SSL, Manager, Bridge
Openvswitch是一个virutal swtich, 支持Open Flow协议,当然也有一些硬件Switch也支持Open Flow协议,他们都可以被统一的Controller管理,从而实现物 ...
- openvswith Frequently Asked Questions
Open vSwitch <http://openvswitch.org> 参考地址:http://git.openvswitch.org/cgi-bin/gitweb.cgi?p=ope ...
- [转载]抓包,端口镜像,monitor session命令(转)
原文地址:抓包,端口镜像,monitor session命令(转)作者:浮云皓月 一.SPAN简介 SPAN技术主要是用来监控交换机上的数据流,大体分为两种类型,本地SPAN和远程SPAN. --Lo ...
- Open vSwitch安装及配置
一. Open vSwitch简介 1.1概述 Open vSwitch是一个高质量的.多层虚拟交换机,使用开源Apache 2.0许可协议,由Nicira Networks开发,主要实现代码为可移植 ...
- 从三个开源项目认识OpenFlow交换机 - OVS
在SDN/NFV的网络革新技术浪潮的引领下,催生了诸多数据面开源方案的诞生.业界知名度较高的有OVS(Open vSwitch).FD.io (Fast Data I/O).ODP(Open Data ...
- Openvswitch手册(4): Mirror
这一节我们来分析Mirror Mirror就是配置一个bridge,将某些包发给指定的mirrored ports 对于包的选择: select_all,所有的包 select_dst_port se ...
- VMware vSphere 5.x 与 vSphere 6.0各版本功能特性对比
各版本中的新特性及功能对比: VMware vSphere 5.0 VMware vSphere 5.1 VMware vSphere 5.5 VMware vSphere 6.0 ESXi 5. ...
- OpenStack若干概念
近期在部署OpenStack时涉及到各个服务之间的诸多概念,这里简要记录其中的一些作为备忘. 服务(service) 在OpenStack中,一个服务有若干端点,用户通过端点访问服务并使用服务提供的功 ...
随机推荐
- 整理收集的一些常用java工具类
1.json转换工具 package com.taotao.utils; import java.util.List; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonPr ...
- Rider代码格式设置
单选注释格式设置: File/Settings(Ctrl+Alt+S/Command+Option+S)/Code Style/C#选择Other
- 两个map合并
两个map合并所用函数为:putAll package myProject; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class ...
- 关于#progma comment 中库文件相对路径问题 (转)
最近做一个验证程序的对话框编程,因为里面要要用到静态链接库,所以就稍微的学习了下静态链接库知识,学习的过程中感觉到了自己所了解的东西实在是少的可怜,更加坚定了自己要更加上进的决心,要把以前所丢掉的都给 ...
- mysql创建用户后无法访问数据库的问题
1.停止mysql服务器 sudo service mysql stop 2.启动mysql服务 sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables 3.登陆 mysql mys ...
- C++-POJ1200-Crazy Search[hash]
由于已经给出字符只有NC种,故可以把子串视为一个NC进制的数,以此构造hash函数就可以了 #include <set> #include <map> #include < ...
- win 下 docker 环境配置
声明 此文只针对 win7.win10 家庭版等用户操作系统,因为这些系统无法使用 windows 的 Hyper-V 虚拟技术.只能借助于 Virtual Box 虚拟机来使用 docker. Do ...
- scss(sass)
- 计算系数(NOIP2011提高LuoguP1313)
一道数论好题,知识点涉及扩展欧几里得,快速幂,逆元,二项式定理,模运算,组合数等. (别问为啥打了快速幂不用费马小求逆元...我就练习下扩欧) (数据就应该再加大些卡掉n^2递推求组合数的) #inc ...
- softmax-Fork
softmax和分类模型 内容包含: softmax回归的基本概念 如何获取Fashion-MNIST数据集和读取数据 softmax回归模型的从零开始实现,实现一个对Fashion-MNIST训练集 ...
