ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛-B,F,G
学长写的
F. Fantastic Graph
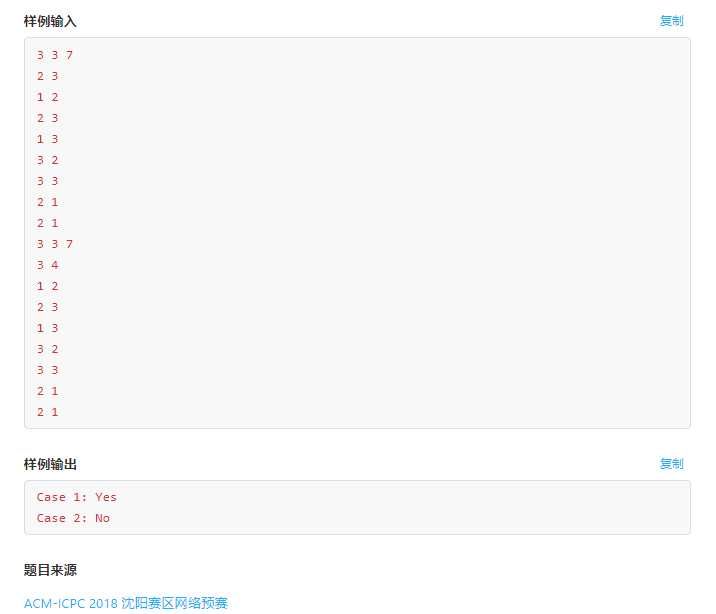
"Oh, There is a bipartite graph.""Make it Fantastic."
X wants to check whether a bipartite graph is a fantastic graph. He has two fantastic numbers, and he wants to let all the degrees to between the two boundaries. You can pick up several edges from the current graph and try to make the degrees of every point to between the two boundaries. If you pick one edge, the degrees of two end points will both increase by one. Can you help X to check whether it is possible to fix the graph?
Input
There are at most 3030 test cases.
For each test case,The first line contains three integers NN the number of left part graph vertices, MM the number of right part graph vertices, and KK the number of edges ( 1 \le N \le 20001≤N≤2000,0 \le M \le 20000≤M≤2000,0 \le K \le 60000≤K≤6000 ). Vertices are numbered from 11 to NN.
The second line contains two numbers L, RL,R (0 \le L \le R \le 300)(0≤L≤R≤300). The two fantastic numbers.
Then KK lines follows, each line containing two numbers UU, VV (1 \le U \le N,1 \le V \le M)(1≤U≤N,1≤V≤M). It shows that there is a directed edge from UU-th spot to VV-th spot.
Note. There may be multiple edges between two vertices.
Output
One line containing a sentence. Begin with the case number. If it is possible to pick some edges to make the graph fantastic, output "Yes" (without quote), else output "No" (without quote).
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define fi first
#define se second
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 6e3+32;
int n,m,k;
int du[2000+42];
int du2[2000+32];
int L,R;
const int MX = 4000+54;
const int MXE = 19000+43;
struct MaxFlow
{
struct Edge
{
int v, w, nxt;
} edge[MXE],edge2[MXE];
int tot, num, s, t;
int head[MX];
void init()
{
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
tot = 0;
}
void add(int u, int v, int w)
{
edge[tot].v = v;
edge[tot].w = w;
edge[tot].nxt = head[u];
head[u] = tot++;
edge[tot].v = u;
edge[tot].w = 0;
edge[tot].nxt = head[v];
head[v] = tot++;
}
int d[MX], vis[MX], gap[MX];
void bfs()
{
memset(d, 0, sizeof(d));
memset(gap, 0, sizeof(gap));
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
queue<int>q;
q.push(t);
vis[t] = 1;
while (!q.empty())
{
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = edge[i].nxt)
{
int v = edge[i].v;
if (!vis[v])
{
d[v] = d[u] + 1;
gap[d[v]]++;
q.push(v);
vis[v] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int last[MX];
int dfs(int u, int f)
{
if (u == t) return f;
int sap = 0;
for (int i = last[u]; ~i; i = edge[i].nxt)
{
int v = edge[i].v;
if (edge[i].w > 0 && d[u] == d[v] + 1)
{
last[u] = i;
int tmp = dfs(v, min(f - sap, edge[i].w));
edge[i].w -= tmp;
edge[i ^ 1].w += tmp;
sap += tmp;
if (sap == f) return sap;
}
}
if (d[s] >= num) return sap;
if (!(--gap[d[u]])) d[s] = num;
++gap[++d[u]];
last[u] = head[u];
return sap;
}
int solve(int st, int ed, int n)
{
int flow = 0;
num = n;
s = st;
t = ed;
bfs();
memcpy(last, head, sizeof(head));
while (d[s] < num) flow += dfs(s, inf);
return flow;
}
} F;
int S,T;
void update(int u,int v,int L,int R)
{
F.add(u,v,R-L);
F.add(S, v, L);
F.add(u, T, L);
}
pair<int,int>Q[6000+53];
int main()
{
int ka = 1;
while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k))
{
F.init();
S = n+m+2;
T = n+m+3;
F.add(n+m+1, 0, INF);
for(int i = 0;i<=max(n,m);i++){
du[i] = du2[i] = 0;
}
scanf("%d%d",&L,&R);
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++){
update(0,i,L,R);
}
for(int i = n+1;i<=n+m;i++)
{
update(i,n+m+1,L,R);
}
for(int i = 0;i<k;i++){
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
Q[i].first = u;
Q[i].second = v;
du[u]++;
du2[v]++;
F.add(u, v+n, 1);
}
printf("Case %d: ",ka++);
int ret = F.solve(S, T, T + 11);
if(ret != (n+m)*L) puts("No");
else puts("Yes");
}
}
B. Call of Accepted
You and your friends are at the table, playing an old and interesting game - the Call of Cthulhu.
There is a mechanism in the game: rolling the dice. You use a notation to communicate the type of dice that needs to be rolled - the operator "\mathop{\rm d}d". "x\mathop{\rm d}yxdy" means that an yy-sided dice should be rolled xx times and the sum of the results is taken.
Formally, for any two integers x, yx,y satisfying x \geq 0x≥0 and y \geq 1y≥1 , "x\mathop{\rm d}yxdy" means the sum of xx random integers in the range of [1, y][1,y]. It's obvious that either x < 0x<0 or y < 1y<1 makes the expression x\ {\rm d}\ yx d y illegal. For example: "2\mathop{\rm d}62d6" means that rolling a 66-sided dice 22 times. At this time, the result can be at least [1, 1] = 2[1,1]=2, and at most [6, 6] = 12[6,6]=12. The results of rolling can be used extensively in many aspects of the game. For example, an "1\mathop{\rm d}1001d100" can be used to determine whether an action with a percentage probability is successful, and a "3\mathop{\rm d}6+33d6+3 * 22" can be used to calculate the total damage when being attacked by 33 monsters simultaneously. In particular, the precedence of "\mathop{\rm d}d" is above "*". Since the operator "\mathop{\rm d}d" does not satisfy the associative law, it's necessary to make sure that "\mathop{\rm d}d" is right-associative.
Now the game has reached its most exciting stage. You are facing the Great Old One - Cthulhu. Because the spirit has been greatly affected, your sanity value needs to be deducted according to the result of rolling. If the sanity value loses too much, you will fall into madness. As a player, you want to write a program for knowing the minimum and maximum loss of sanity value before rolling, in order to make a psychological preparation.
The oldest and strongest emotion of mankind is fear, and the oldest and strongest kind of fear is fear of the unknown. ----H. P. Lovecraft
Input
There are multiple sets of input, at most 3030 cases.
Each set of input contains a string of only '+', '-', '*', 'd', '(', ')' and integers without spaces, indicating the expression of this sanity loss. The length of the expression will be at most 100100.
It is guaranteed that all expressions are legal, all operators except for '(' and ')' are binary, and all intermediate results while calculating are integers in the range of [-2147483648, 2147483647][−2147483648,2147483647].
The most merciful thing in the world, I think, is the inability of the human mind to correlate all its contents. We live on a placid island of ignorance in the midst of black seas of infinity, and it was not meant that we should voyage far. ----H. P. Lovecraft
Output
For each set of data, output a line of two integers separated by spaces, indicating the minimum and maximum possible values of the sanity loss.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define lson l,m,rt<<1
#define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1
#define x first
#define y second
#define rep(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<(b);++i)
#define per(i,a,b) for(int i=a-1;i>=(b);--i)
#define fuck(x) cout<<'['<<#x<<' '<<(x)<<']'
#define sub(x,y) x=((x)-(y)<0)?(x)-(y)+mod:(x)-(y)
#define clr(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define eps 1e-10
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef vector<int> VI;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef unsigned int ui;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll INFLL = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int MX = 2e6 + 5;
vector<string>pre, s;
string str;
bool isoperator(string op) {
if(op == "+" || op == "-" || op == "*" || op == "d") return 1;
return 0;
}
int priority(string op) {
if(op == "#") return -1;
if(op == "(") return 0;
if(op == "+" || op == "-") return 1;
if(op == "*") return 2;
if(op == "d") return 3;
return -1;
}
void postfix() {
stack<string> OPTR; //运算符栈
stack<string> OPND; //数据栈
OPTR.push("#");
rep(i, 0, pre.size()) {
if (pre[i] == "(") OPTR.push(pre[i]);
else if(pre[i] == ")") {
while(OPTR.top() != "(") {
OPND.push(OPTR.top());
OPTR.pop();
}
OPTR.pop();
} else if (isoperator(pre[i])) {
while(!OPTR.empty() && (priority(pre[i]) < priority(OPTR.top()) || priority(pre[i]) == priority(OPTR.top()) && pre[i] != "d")) {
OPND.push(OPTR.top());
OPTR.pop();
}
OPTR.push(pre[i]);
} else OPND.push(pre[i]);
}
while(OPTR.top() != "#") {
OPND.push(OPTR.top());
OPTR.pop();
}
OPTR.pop();
//利用操作符栈逆序即可得到后缀表达式
while(!OPND.empty()) {
OPTR.push(OPND.top());
OPND.pop();
}
s.clear();
while(!OPTR.empty()) {
s.push_back(OPTR.top());
OPTR.pop();
}
}
bool is_dig(char ch) {return ch >= '0' && ch <= '9';}
void pre_solve() {
pre.clear();
rep(i, 0, str.length()) {
if(is_dig(str[i])) {
rep(j, i, str.length()) {
if(!is_dig(str[j])) {
pre.push_back(str.substr(i, j - i));
i = j - 1;
break;
}
if(j == str.length() - 1) {
pre.push_back(str.substr(i, j - i + 1));
i = j;
break;
}
}
} else pre.push_back(str.substr(i, 1));
}
}
ll str_to_int(string st) {
ll ret = 0;
rep(i, 0, st.length()) ret = ret * 10 + st[i] - '0';
return ret;
}
struct node {
ll l, r;
node(ll l = 0, ll r = 0): l(l), r(r) {}
node(string st) {l = r = str_to_int(st);}
node operator-(const node& _A)const {
return node(l - _A.r, r - _A.l);
}
node operator+(const node& _A)const {
return node(l + _A.l, r + _A.r);
}
node operator*(const node& _A)const {
node ret;
ll a = l * _A.l;
ll b = l * _A.r;
ll c = r * _A.l;
ll d = r * _A.r;
ret.l = min(min(a, b), min(c, d));
ret.r = max(max(a, b), max(c, d));
return ret;
}
node operator/(const node& _A)const {
node ret;
ll l1 = max(l, 0ll), r1 = r;
ret.l = l1, ret.r = r1 * _A.r;
return ret;
}
};
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif // local
while(cin >> str) {
pre_solve();
postfix();
stack<node>stk;
node a, b;
rep(i, 0, s.size()) if(isoperator(s[i])) {
b = stk.top(); stk.pop();
a = stk.top(); stk.pop();
// printf("[%lld %lld]\n", a.l, a.r);
// printf("[%lld %lld]\n", b.l, b.r);
if(s[i] == "-") a = a - b;
if(s[i] == "+") a = a + b;
if(s[i] == "*") a = a * b;
if(s[i] == "d") a = a / b;
stk.push(a);
} else stk.push(node(s[i]));
a = stk.top();
printf("%lld %lld\n", a.l, a.r);
}
return 0;
}
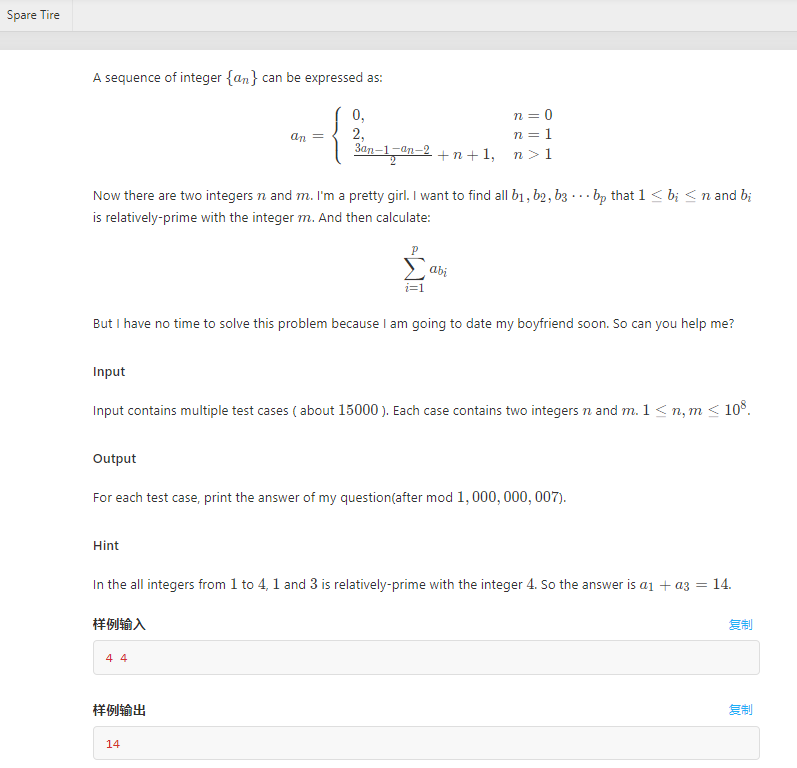
G.Spare time
\(a_{n} = a_{n-1}+2\times n\)
\(a_{n} = (a_{n}-a_{n-1})+(a_{n-1}-a_{n-2})+...+(a_{2}-a_{1})+a_{1} = n\times (n+1)\)
\(S_{n} = \sum_{i=1}^n i\times(i+1) = n\times(n+1)/2 + n\times(n+1)\times(2n+1)/6\)
利用容斥思想,如当\(m=6\)时,有\(2\),\(3\)两个质因子。既然要求与\(m\)互素的下标的数之和,我们枚举素因子的倍数,二进制枚举最简的倍数。
当枚举到\(2\)时,要删去\(2(2*1),4(2*2),6(2*3)\);当枚举到\(3\)时,要删去\(3(3*1),6(3*2)\);(注意到\(6\)被删了两次);当枚举到\(6\)时,要加上\(6\)哦。
容斥:
令\(tmp = tot*get\_num1(cnt)+tot*tot*get\_num2(cnt);\)
tmp = tot*get_num1(cnt)+tot*tot*get_num2(cnt);
若tot是偶数个质因子的倍数,答案加上这个数及其倍数的贡献,即tmp。
若tot是奇数个质因子的倍数,答案减去这个数及其倍数的贡献,即tmp。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const LL MOD = (LL)1e9 + 7;
LL n, m, inv2, inv6;
vector<int> ve;
LL inv(LL t){
return t == 1LL? 1LL: (MOD-MOD/t)*inv(MOD%t)%MOD;
}
LL get_num1(LL n){
return n*(n+1)%MOD*inv2%MOD;
}
LL get_num2(LL n){
return n*(n+1)%MOD*(2*n%MOD+1)%MOD*inv6%MOD;
}
int main(){
inv2 = inv(2), inv6 = inv(6);
while(~scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m)){
ve.clear();
int tm = m;
for(int i = 2; (LL)i * i <= m && i <= n; ++i){
if(tm % i == 0){
ve.push_back(i);
while(tm % i == 0)tm /= i;
}
if(tm == 1)break;
}
if(tm != 1)ve.push_back(tm);
int len = ve.size(), state = 1 << len;
LL ans = (get_num1(n)+get_num2(n))%MOD;
ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < state; ++i){
LL tot = 1, cnt;
int num = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < len; ++j){
if(i&(1<<j)){
++num;
tot *= ve[j];
}
}
cnt = n/tot;
//printf("*%lld %lld %d\n", tot,cnt,num);
if(num % 2 == 0){
ans = (ans+ tot*tot%MOD*get_num2(cnt)%MOD+tot*get_num1(cnt)%MOD)%MOD;
}else{
ans = (ans- tot*tot%MOD*get_num2(cnt)%MOD-tot*get_num1(cnt)%MOD)%MOD;
ans = (ans + MOD)%MOD;
}
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
#### HDU6397容斥
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MXN = 3e5 + 6;
const int MXT = 1e5 + 5;
const int mod = 998244353;
LL n, m, k;
LL f[MXN], invF[MXN];
LL niyuan(int t) {
return t == 1? 1: (mod-mod/t)*niyuan(mod%t)%mod;
}
LL ksm(LL a, int b) {
LL ans = 1;
while(b) {
if(b&1) ans = ans * a %mod;
b >>= 1;
a = a * a %mod;
}
return ans;
}
void init() {
f[0] = 1; invF[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < MXN; ++i) f[i] = f[i-1] * i % mod;
//invF[MXN-1] = niyuan(f[MXN-1]);
invF[MXN-1] = ksm(f[MXN-1], mod-2);
for(int i = MXN-2; i >= 1; --i) invF[i] = invF[i+1]*(i+1)%mod;
}
LL COMB(LL n, LL m) {
if(n < m) return 0;
return f[n] * invF[m] % mod * invF[n-m] % mod;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
//freopen("E://ADpan//in.in", "r", stdin);
#endif
init();
int tim;
scanf("%d", &tim);
while(tim--) {
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &n, &m, &k);
LL ans = COMB(k+m-1,m-1), tmp;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
tmp = COMB(k+m-i*n-1, m-1) * COMB(m, i) % mod;
if(i & 1) ans = (ans - tmp + mod)%mod;
else ans = (ans + tmp)%mod;
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
/*
字母xi=[0,n-1],问有多少个长度为m的单词,其和为k
*/
ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛-B,F,G的更多相关文章
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 K Supreme Number(规律)
https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/31452 题意 给出一个n (2 ≤ N ≤ 10100 ),找到最接近且小于n的一个数,这个数需要满足每位上的数字构成的集合的每个非空子集 ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛-K:Supreme Number
Supreme Number A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 11 that cannot be formed ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛-D:Made In Heaven(K短路+A*模板)
Made In Heaven One day in the jail, F·F invites Jolyne Kujo (JOJO in brief) to play tennis with her. ...
- 图上两点之间的第k最短路径的长度 ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 D. Made In Heaven
131072K One day in the jail, F·F invites Jolyne Kujo (JOJO in brief) to play tennis with her. Howe ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 J树分块
J. Ka Chang Given a rooted tree ( the root is node 11 ) of NN nodes. Initially, each node has zero p ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 K. Supreme Number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 11 that cannot be formed by multiplying ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 F. Fantastic Graph
"Oh, There is a bipartite graph.""Make it Fantastic." X wants to check whether a ...
- Fantastic Graph 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 F题
题意: 二分图 有k条边,我们去选择其中的几条 每选中一条那么此条边的u 和 v的度数就+1,最后使得所有点的度数都在[l, r]这个区间内 , 这就相当于 边流入1,流出1,最后使流量平衡 解析: ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 F Fantastic Graph(贪心或有源汇上下界网络流)
https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/31447 题意 一个二分图,左边N个点,右边M个点,中间K条边,问你是否可以删掉边使得所有点的度数在[L,R]之间 分析 最大流不太会.. ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 沈阳赛区网络预赛 B Call of Accepted(表达式求值)
https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/31443 题意 给出一个表达式,求最小值和最大值. 表达式中的运算符只有'+'.'-'.'*'.'d',xdy 表示一个 y 面的骰子 ro ...
随机推荐
- 【记录】spring boot 图片上传与显示
问题:spring boot 使用的是内嵌的tomcat, 文件上传指定目录时不知道文件上传到哪个地方,不知道访问路径. //部署到服务器的tomcat上时通常使用这种方式request.getSer ...
- Delphi 类(TObject、TPersistent、TComponent、TControl、TWinControl、TCustomControl、TGraphicControl、TInterfacedObject)简单介绍
TObject: VCL中所有类的根类,即是说:VCL中所有的类/组件/控件都是从TObject中继承而来.TObject类中定义了基本的 构造方法和析构方法. TPersistent: ...
- 阿里云高磊:API网关加速能力聚合与生态集成
导读:本文中,阿里云高级技术专家高磊(花名:埃兰)将聚焦API网关加速能力聚合与生态集成,讲述API如何实现系统间的衔接和API网关的产品升级进程,重点展示了一些新功能.新体验和新变化. 大家下午好, ...
- Java中链接MS SQL 数据库用法详解
一.第一种方法: 使用JDBC-ODBC的桥方式 JDBC-ODBC桥连接器是用JdbcOdbc.class 和一个用于访问ODBC驱动程序的本地库实现的,对于Windows平台,该本地库是一个动态链 ...
- BZOJ 1303: [CQOI2009]中位数图(思路题)
传送门 解题思路 比较好想的思路题.首先肯定要把原序列转化一下,大于\(k\)的变成\(1\),小于\(k\)的变成\(-1\),然后求一个前缀和,还要用\(cnt[]\)记录一下前缀和每个数出现了几 ...
- linux 创建多级目录 mkdir -p
原文地址:http://www.dutor.net/index.php/2010/06/cmd-mkdir-p/ mkdir的-p选项允许你一次性创建多层次的目录,而不是一次只创建单独的目录.例如,我 ...
- 20、Linux命令对服务器磁盘进行监控
服务器磁盘性能测试也是一个比较有意思的过程.首先我们要弄清楚磁盘储存哪些内容,这里推荐鸟哥的私房菜 我们不仅要推算出磁盘什么时候被占满,也要监控磁盘的读写速度.也就是我们常说的 I/O df -h ...
- PAT_A1075#PAT Judge
Source: PAT A1075 PAT Judge (25 分) Description: The ranklist of PAT is generated from the status lis ...
- pta作业1
7-1 打印沙漏 (20 分) 本题要求你写个程序把给定的符号打印成沙漏的形状.例如给定17个“*”,要求按下列格式打印 ***** *** * *** ***** 所谓“沙漏形状”,是指每行输出奇数 ...
- Hbase时间同步
如果Hbase的时间没有同步,启动主节点会起来,子节点的regionServer就不会起来. 错误日志如下: aused by: org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.RemoteW ...