SpringBoot学习(三):日志
1、日志框架
小张;开发一个大型系统;
1、System.out.println("");将关键数据打印在控制台;去掉?写在一个文件?
2、框架来记录系统的一些运行时信息;日志框架 ; zhanglogging.jar;
3、高大上的几个功能?异步模式?自动归档?xxxx? zhanglogging-good.jar?
4、将以前框架卸下来?换上新的框架,重新修改之前相关的API;zhanglogging-prefect.jar;
5、JDBC---数据库驱动;
写了一个统一的接口层;日志门面(日志的一个抽象层);logging-abstract.jar;
给项目中导入具体的日志实现就行了;我们之前的日志框架都是实现的抽象层;
市面上的日志框架;
JUL、JCL、Jboss-logging、logback、log4j、log4j2、slf4j....
| 日志门面 (日志的抽象层) | 日志实现 |
|---|---|
| Log4j JUL(java.util.logging) Log4j2 Logback |
左边选一个门面(抽象层)、右边来选一个实现;
日志门面: SLF4J;
日志实现:Logback;
SpringBoot:底层是Spring框架,Spring框架默认是用JCL;‘
**==SpringBoot选用 SLF4j和logback;==**
2、SLF4j使用
1、如何在系统中使用SLF4j https://www.slf4j.org
以后开发的时候,日志记录方法的调用,不应该来直接调用日志的实现类,而是调用日志抽象层里面的方法;
给系统里面导入slf4j的jar和 logback的实现jar
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorld.class);
logger.info("Hello World");
}
}
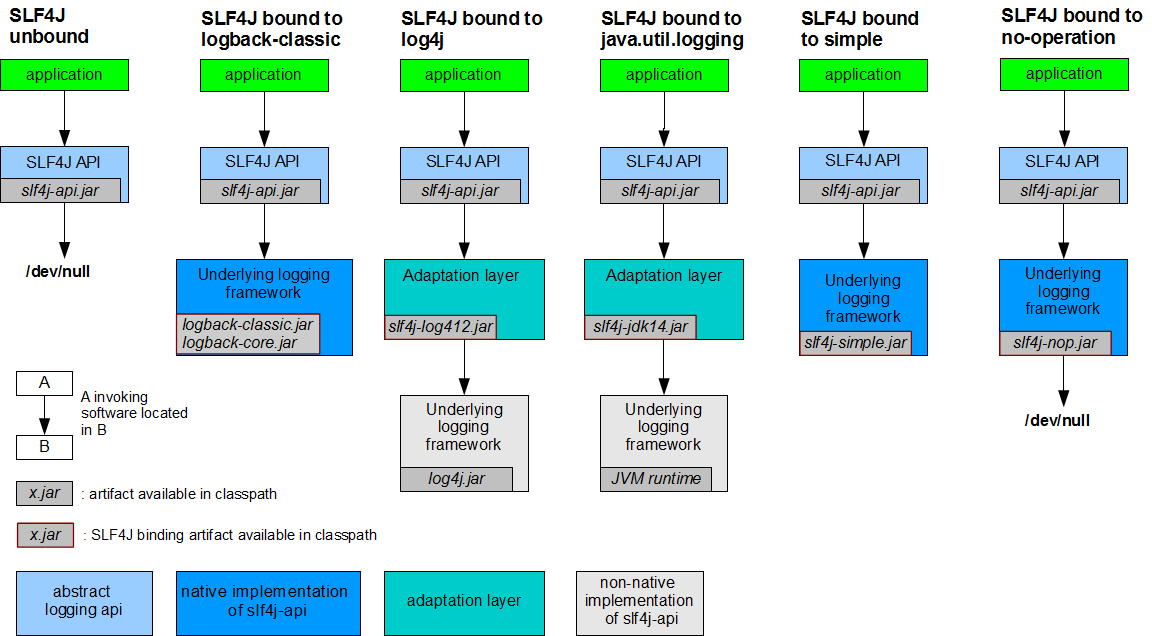
**如何让系统中所有的日志都统一到slf4j;**
==1、将系统中其他日志框架先排除出去;==
==2、用中间包来替换原有的日志框架;==
==3、我们导入slf4j其他的实现==
3、SpringBoot日志关系
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
SpringBoot使用它来做日志功能;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</dependency>
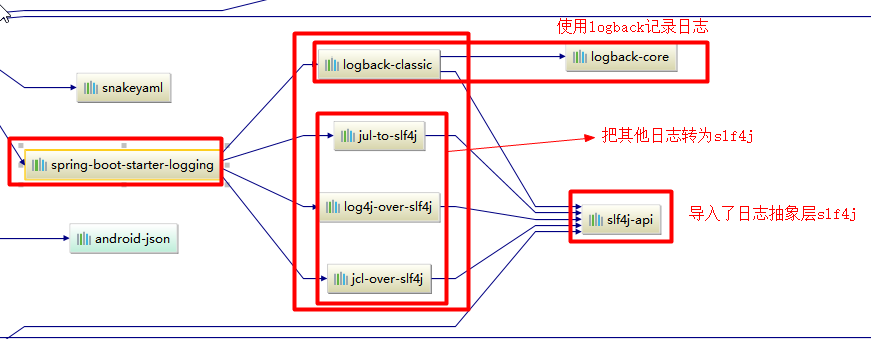
总结:
1)、SpringBoot底层也是使用slf4j+logback的方式进行日志记录
2)、SpringBoot也把其他的日志都替换成了slf4j;
3)、中间替换包?
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public abstract class LogFactory {
static String UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION_IN_JCL_OVER_SLF4J = "http://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#unsupported_operation_in_jcl_over_slf4j";
static LogFactory logFactory = new SLF4JLogFactory();
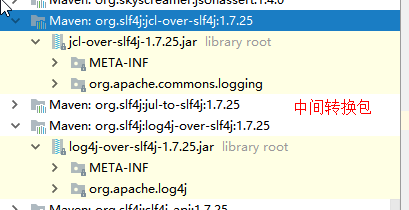
4)、如果我们要引入其他框架?一定要把这个框架的默认日志依赖移除掉?
Spring框架用的是commons-logging;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
==SpringBoot能自动适配所有的日志,而且底层使用slf4j+logback的方式记录日志,引入其他框架的时候,只需要把这个框架依赖的日志框架排除掉即可;==
4、日志使用;
1、默认配置
SpringBoot默认帮我们配置好了日志;
//记录器
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
//System.out.println(); //日志的级别;
//由低到高 trace<debug<info<warn<error
//可以调整输出的日志级别;日志就只会在这个级别以以后的高级别生效
logger.trace("这是trace日志...");
logger.debug("这是dNebug日志...");
//SpringBoot默认给我们使用的是info级别的,没有指定级别的就用SpringBoot默认规定的级别;root级别
logger.info("这是info日志...");
logger.warn("这是warn日志...");
logger.error("这是error日志...")
}
日志输出格式:
%d表示日期时间,
%thread表示线程名,
%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度
%logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。
%msg:日志消息,
%n是换行符
-->
%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
SpringBoot修改日志的默认配置
logging.level.com.atguigu=trace
#logging.path=
# 不指定路径在当前项目下生成springboot.log日志
# 可以指定完整的路径;
#logging.file=G:/springboot.log # 在当前磁盘的根路径下创建spring文件夹和里面的log文件夹;使用 spring.log 作为默认文件
logging.path=/spring/log
# 在控制台输出的日志的格式
logging.pattern.console=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n
# 指定文件中日志输出的格式
logging.pattern.file=%d{yyyy-MM-dd} === [%thread] === %-5level === %logger{50} ==== %msg%n
| logging.file | logging.path | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| (none) | (none) | 只在控制台输出 | |
| 指定文件名 | (none) | my.log | 输出日志到my.log文件 |
| (none) | 指定目录 | /var/log | 输出到指定目录的 spring.log 文件中 |
2、指定配置
给类路径下放上每个日志框架自己的配置文件即可;SpringBoot就不使用他默认配置的了
| Logging System | Customization |
|---|---|
| Logback | logback-spring.xml, logback-spring.groovy, logback.xml or logback.groovy |
| Log4j2 | log4j2-spring.xml or log4j2.xml |
| JDK (Java Util Logging) | logging.properties |
logback.xml:直接就被日志框架识别了;
logback-spring.xml:日志框架就不直接加载日志的配置项,由SpringBoot解析日志配置,可以使用SpringBoot的高级Profile功能
<springProfile name="staging">
<!-- configuration to be enabled when the "staging" profile is active -->
可以指定某段配置只在某个环境下生效
</springProfile>
<appender name="stdout" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<!--
日志输出格式:
%d表示日期时间,
%thread表示线程名,
%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度
%logger{50} 表示logger名字最长50个字符,否则按照句点分割。
%msg:日志消息,
%n是换行符
-->
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<springProfile name="dev">
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ----> [%thread] ---> %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</springProfile>
<springProfile name="!dev">
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} ==== [%thread] ==== %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</springProfile>
</layout>
</appender>
如果使用logback.xml作为日志配置文件,还要使用profile功能,会有以下错误
no applicable action for [springProfile]
5、切换日志框架
可以按照slf4j的日志适配图,进行相关的切换;
slf4j+log4j的方式;
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
</exclusion>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>log4j-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</dependency>
切换为log4j2
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency> <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-log4j2</artifactId>
</dependency>
SpringBoot学习(三):日志的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot学习(1) - 日志
package com.study.spring_boot_log; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.spr ...
- SpringBoot入门 (三) 日志配置
上一篇博文记录了再springboot项目中读取属性文件中配置的属性,本文学习在springboot项目中记录日志. 日志记录在项目中是很常见的一个功能了,对排查问题有很大帮助,也可以做分类分析及统计 ...
- SpringBoot学习(三)-->Spring的Java配置方式之读取外部的资源配置文件并配置数据库连接池
三.读取外部的资源配置文件并配置数据库连接池 1.读取外部的资源配置文件 通过@PropertySource可以指定读取的配置文件,通过@Value注解获取值,具体用法: @Configuration ...
- 尚硅谷springboot学习17-SpringBoot日志
SpringBoot使用它来做日志功能: <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> < ...
- Springboot学习:日志
介绍 市面上的日志框架: JUL.JCL.Jboss-logging.logback.log4j.log4j2.slf4j.... 日志门面 (日志的抽象层) 日志实现 JCL(Jakarta Com ...
- springboot学习三:整合jsp
在pom.xml加入jstl <!--springboot tomcat jsp 支持开启--> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache. ...
- springboot学习4使用日志:logback
springboot学习4使用日志:logback 一.基本知识说明 SpringBoot默认使用logback作为日志框架 ,所以引入起步依赖后就可以直接使用logback,不需要其他依赖. Spr ...
- Java开发学习(三十五)----SpringBoot快速入门及起步依赖解析
一.SpringBoot简介 SpringBoot 是由 Pivotal 团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化 Spring 应用的初始搭建以及开发过程. 使用了 Spring 框架后已经简化了我 ...
- Java开发学习(三十六)----SpringBoot三种配置文件解析
一. 配置文件格式 我们现在启动服务器默认的端口号是 8080,访问路径可以书写为 http://localhost:8080/books/1 在线上环境我们还是希望将端口号改为 80,这样在访问的时 ...
随机推荐
- 关于在vuejs中动态加载不确定数量和内容的组件的解决方案
在做一个门户项目的时候,客户要求需要进行私人化定制,每个人进入首页的时候可以自定义首页显示的版块 要在4.50个组件中显示随机N个组件按照每个人选定的顺序排列.需求说完了,接下来说说解决方案: htm ...
- UNITY->(width*height)style Inventory
项目过后对项目功能进行记录,(width*height)风格背包实现细节,包含对物体的存放,装备,替换,对未知装备的鉴定,物体前缀的获取,项目类型为tcg+rpg,背包的作用主要为游戏中的物品的获取存 ...
- 洛谷$P4099\ [HEOI2013]\ SAO\ dp$
正解:树形$dp$ 解题报告: 传送门$QwQ$. 考虑设$f_i$表示点$i$的子树内的拓扑序排列方案数有多少个. 发现这样不好合并儿子节点和父亲节点.于是加一维,设$f_{i,j}$表示点$i$的 ...
- 20行Python代码爬取王者荣耀全英雄皮肤
引言王者荣耀大家都玩过吧,没玩过的也应该听说过,作为时下最火的手机MOBA游戏,咳咳,好像跑题了.我们今天的重点是爬取王者荣耀所有英雄的所有皮肤,而且仅仅使用20行Python代码即可完成. 准备工作 ...
- 高德API对接
<?php class GaoDeAPI { private $key = '123456789'; # 你应用key /** * 地址转经纬度 */ public function getTr ...
- 微信公众号 唤醒手机导航APP 一看就懂 复制即用
公司自研发框架,基本上没啥看不懂的 基本都是直接复制用就好了!希望能帮助到需要的朋友! 新建俩个同级文件用来保存 jsapi_ticket 和 access_token的文件 命名:jsapi_tic ...
- Web 3D是否需要WebAssembly?
大家好,本文讨论了Web 3D是否需要WebAssembly,结论是: 对于使用原生3D技术的程序员,需要: 对于使用Javascript语言的前端程序员,不需要,有其它方法可以达到接近WebAssd ...
- cassandra中的ACID,与RDBMS中的事务有何不同?
Cassandra中的ACID标准 Apache Cassandra不遵循具有回滚或锁定机制的ACID(原子性,一致性,隔离性,持久性)事务,而是提供原子,隔离和持久的事务,并具有最终和可调的一致性, ...
- Redis入门--1.安装Redis
redis是什么? 是完全开源免费的,用c语言编写的,是一个单线程,高性能的(key/value)内存数据库,基于内存运行并支持持久化的nosql数据库 redis能干嘛? 主要是用来做缓存,但不仅仅 ...
- HTML 图片(image) 左右滑动
1.需求 需要用简单动画的形式将一组图片进行展示,图片数量不固定 2.效果如下: 3.思路 说到动画,首先想到使用-webkit-transition:;因为这个最简单好用,首先将图片都放在左侧,然后 ...
