Andrew Ng机器学习 四:Neural Networks Learning
背景:跟上一讲一样,识别手写数字,给一组数据集ex4data1.mat,,每个样例都为灰度化为20*20像素,也就是每个样例的维度为400,加载这组数据后,我们会有5000*400的矩阵X(5000个样例),5000*1的矩阵y(表示每个样例所代表的数据)。现在让你拟合出一个模型,使得这个模型能很好的预测其它手写的数字。
(注意:我们用10代表0(矩阵y也是这样),因为Octave的矩阵没有0行)
一:神经网络( Neural Networks)
神经网络脚本ex4.m:
%% Machine Learning Online Class - Exercise Neural Network Learning % Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the
% linear exercise. You will need to complete the following functions
% in this exericse:
%
% sigmoidGradient.m
% randInitializeWeights.m
% nnCostFunction.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
% %% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc %% Setup the parameters you will use for this exercise
input_layer_size = ; % 20x20 Input Images of Digits
hidden_layer_size = ; % hidden units
num_labels = ; % labels, from to
% (note that we have mapped "" to label ) %% =========== Part : Loading and Visualizing Data =============
% We start the exercise by first loading and visualizing the dataset.
% You will be working with a dataset that contains handwritten digits.
% % Load Training Data
fprintf('Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n') load('ex4data1.mat');
m = size(X, ); % Randomly select data points to display
sel = randperm(size(X, ));
sel = sel(:); displayData(X(sel, :)); fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; %% ================ Part : Loading Parameters ================
% In this part of the exercise, we load some pre-initialized
% neural network parameters. fprintf('\nLoading Saved Neural Network Parameters ...\n') % Load the weights into variables Theta1(25x401) and Theta2(10x26)
load('ex4weights.mat'); % Unroll parameters
nn_params = [Theta1(:) ; Theta2(:)]; %% ================ Part : Compute Cost (Feedforward) ================
% To the neural network, you should first start by implementing the
% feedforward part of the neural network that returns the cost only. You
% should complete the code in nnCostFunction.m to return cost. After
% implementing the feedforward to compute the cost, you can verify that
% your implementation is correct by verifying that you get the same cost
% as us for the fixed debugging parameters.
%
% We suggest implementing the feedforward cost *without* regularization
% first so that it will be easier for you to debug. Later, in part , you
% will get to implement the regularized cost.
%
fprintf('\nFeedforward Using Neural Network ...\n') % Weight regularization parameter (we set this to here).
lambda = ; J = nnCostFunction(nn_params, input_layer_size, hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, X, y, lambda); fprintf(['Cost at parameters (loaded from ex4weights): %f '...
'\n(this value should be about 0.287629)\n'], J); fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; %% =============== Part : Implement Regularization ===============
% Once your cost function implementation is correct, you should now
% continue to implement the regularization with the cost.
% fprintf('\nChecking Cost Function (w/ Regularization) ... \n') % Weight regularization parameter (we set this to here).
lambda = ; J = nnCostFunction(nn_params, input_layer_size, hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, X, y, lambda); fprintf(['Cost at parameters (loaded from ex4weights): %f '...
'\n(this value should be about 0.383770)\n'], J); fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; %% ================ Part : Sigmoid Gradient ================
% Before you start implementing the neural network, you will first
% implement the gradient for the sigmoid function. You should complete the
% code in the sigmoidGradient.m file.
% fprintf('\nEvaluating sigmoid gradient...\n') g = sigmoidGradient([- -0.5 0.5 ]);
fprintf('Sigmoid gradient evaluated at [-1 -0.5 0 0.5 1]:\n ');
fprintf('%f ', g);
fprintf('\n\n'); fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; %% ================ Part : Initializing Pameters ================
% In this part of the exercise, you will be starting to implment a two
% layer neural network that classifies digits. You will start by
% implementing a function to initialize the weights of the neural network
% (randInitializeWeights.m) fprintf('\nInitializing Neural Network Parameters ...\n') initial_Theta1 = randInitializeWeights(input_layer_size, hidden_layer_size);
initial_Theta2 = randInitializeWeights(hidden_layer_size, num_labels); % Unroll parameters
initial_nn_params = [initial_Theta1(:) ; initial_Theta2(:)]; %% =============== Part : Implement Backpropagation ===============
% Once your cost matches up with ours, you should proceed to implement the
% backpropagation algorithm for the neural network. You should add to the
% code you've written in nnCostFunction.m to return the partial
% derivatives of the parameters.
%
fprintf('\nChecking Backpropagation... \n'); % Check gradients by running checkNNGradients
checkNNGradients; fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; %% =============== Part : Implement Regularization ===============
% Once your backpropagation implementation is correct, you should now
% continue to implement the regularization with the cost and gradient.
% fprintf('\nChecking Backpropagation (w/ Regularization) ... \n') % Check gradients by running checkNNGradients
lambda = ;
checkNNGradients(lambda); % Also output the costFunction debugging values
debug_J = nnCostFunction(nn_params, input_layer_size, ...
hidden_layer_size, num_labels, X, y, lambda); fprintf(['\n\nCost at (fixed) debugging parameters (w/ lambda = %f): %f ' ...
'\n(for lambda = 3, this value should be about 0.576051)\n\n'], lambda, debug_J); fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; %% =================== Part : Training NN ===================
% You have now implemented all the code necessary to train a neural
% network. To train your neural network, we will now use "fmincg", which
% is a function which works similarly to "fminunc". Recall that these
% advanced optimizers are able to train our cost functions efficiently as
% long as we provide them with the gradient computations.
%
fprintf('\nTraining Neural Network... \n') % After you have completed the assignment, change the MaxIter to a larger
% value to see how more training helps.
options = optimset('MaxIter', ); % You should also try different values of lambda
lambda = ; % Create "short hand" for the cost function to be minimized
costFunction = @(p) nnCostFunction(p, ...
input_layer_size, ...
hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, X, y, lambda); % Now, costFunction is a function that takes in only one argument (the
% neural network parameters)
[nn_params, cost] = fmincg(costFunction, initial_nn_params, options); % Obtain Theta1 and Theta2 back from nn_params
Theta1 = reshape(nn_params(:hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + )), ...
hidden_layer_size, (input_layer_size + )); Theta2 = reshape(nn_params(( + (hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + ))):end), ...
num_labels, (hidden_layer_size + )); fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; %% ================= Part : Visualize Weights =================
% You can now "visualize" what the neural network is learning by
% displaying the hidden units to see what features they are capturing in
% the data. fprintf('\nVisualizing Neural Network... \n') displayData(Theta1(:, :end)); fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; %% ================= Part : Implement Predict =================
% After training the neural network, we would like to use it to predict
% the labels. You will now implement the "predict" function to use the
% neural network to predict the labels of the training set. This lets
% you compute the training set accuracy. pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X); fprintf('\nTraining Set Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(pred == y)) * );
ex4.m
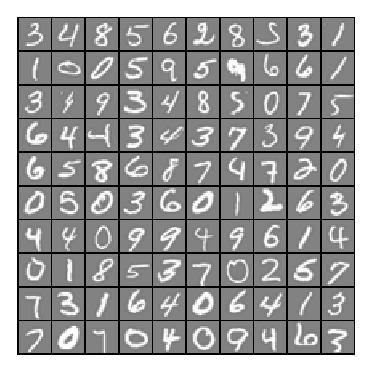
1,通过可视化数据,可以看到如下图所示:
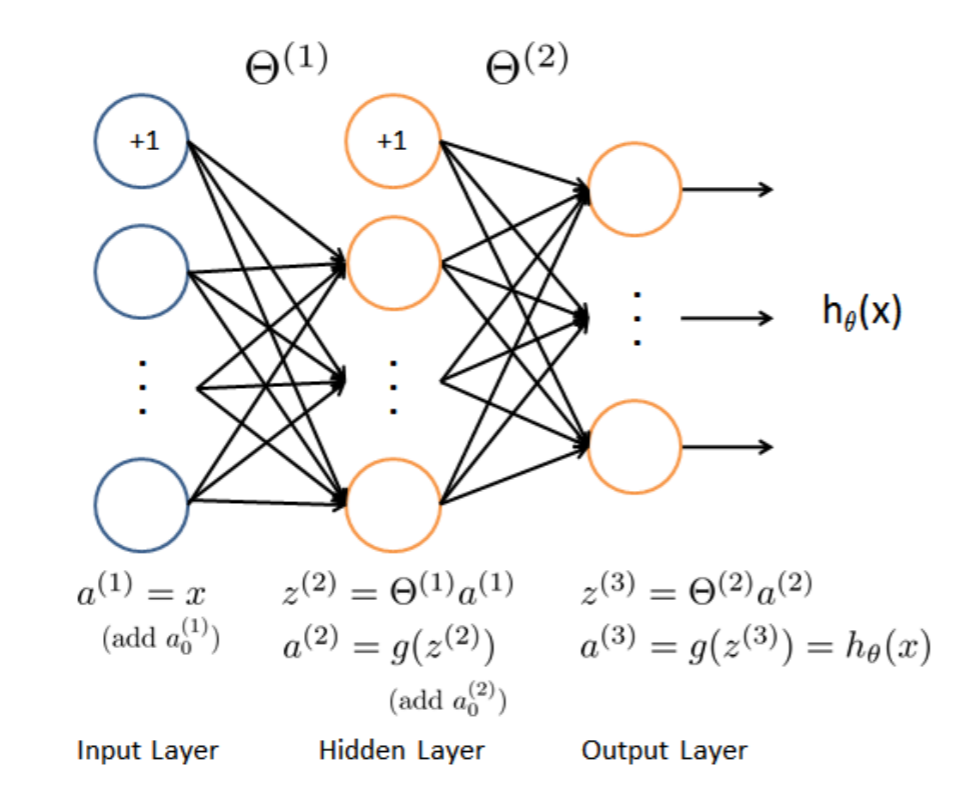
2,前向传播代价函数(Feedforward and cost function)
$J(\Theta)=-\frac{1}{m}\sum_{i=1}^{m}\sum_{k=1}^{K}[y^{(i)}_k(log(h_\Theta(x^{(i)}))_k)+(1-y^{(i)}_k)log(1-(h_{\Theta}(x^{(i)}))_k)]$
$+\frac{\lambda }{2m}\sum_{l=1}^{L-1}\sum_{i=1}^{s_l}\sum_{j=1}^{s_l+1}(\Theta_{ji}^{l})^{2}$
注意:$(h_\Theta(x^{(i)}))_k=a^{(3)}_k$,第k个输出单元。
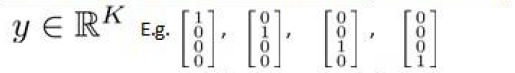
该代价函数正则化时忽略偏差项,最里层的循环$
Andrew Ng机器学习 四:Neural Networks Learning的更多相关文章
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 5) Neural Networks Learning
本栏目内容来自Andrew NG老师的公开课:https://class.coursera.org/ml/class/index 一般而言, 人工神经网络与经典计算方法相比并非优越, 只有当常规方法解 ...
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 4) Neural Networks Representation
Andrew NG的Machine learning课程地址为:https://www.coursera.org/course/ml 神经网络一直被认为是比较难懂的问题,NG将神经网络部分的课程分为了 ...
- [C4] Andrew Ng - Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter tuning, Regularization and Optimization
About this Course This course will teach you the "magic" of getting deep learning to work ...
- 斯坦福大学公开课机器学习: neural networks learning - autonomous driving example(通过神经网络实现自动驾驶实例)
使用神经网络来实现自动驾驶,也就是说使汽车通过学习来自己驾驶. 下图是通过神经网络学习实现自动驾驶的图例讲解: 左下角是汽车所看到的前方的路况图像.左上图,可以看到一条水平的菜单栏(数字4所指示方向) ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 9_Neural Networks learning
神经网络的学习(Neural Networks: Learning) 9.1 代价函数 Cost Function 参考视频: 9 - 1 - Cost Function (7 min).mkv 假设 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(四)之神经网络
Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(四)之神经网络 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请指明转载地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/fydeblog/p/7365730.html 前言 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程11之使用machine learning的建议
Andrew Ng机器学习课程11之使用machine learning的建议 声明:引用请注明出处http://blog.csdn.net/lg1259156776/ 2015-9-28 艺少
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—编程作业 Programming Exercise 4—反向传播神经网络
课程笔记 Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 9_Neural Networks learning 作业说明 Exercise 4,Week 5,实现反向传播 ba ...
- Machine Learning - 第5周(Neural Networks: Learning)
The Neural Network is one of the most powerful learning algorithms (when a linear classifier doesn't ...
随机推荐
- sigaction和实时信号sigqueue
sigaction函数sigaction函数的功能是用于改变进程接收到特定信号后的行为.int sigaction(int signum, const struct sigaction *act,st ...
- Jenkenis报错:该jenkins实例似乎已离线
使用运行war的形式安装jenkins,因为伟大的墙出现,“该jenkins实例似乎已离线” 问题 解决方法: 1. 保留此离线页面,重新开启一个浏览器tab标签页 2.输入输入网址http://lo ...
- jmap使用
今天写的服务在处理大文件是出现Java heap space错误,因此结识了jmap jmap是JDK自带的一个工具,可以做jvm性能调优 可以生成dump文件,查询finalize执行队列.Java ...
- 【视频开发】【Live555】摄像头采集,264编码,live555直播(0)
参看 有关live555 1.首先需要修改live555,定义从 内存中直接获取source而不是从文件读取source的类. 自己实现的类命名为 H264FramedLiveSource /* ...
- SpringBoot系列教程JPA之delete使用姿势详解
原文: 190702-SpringBoot系列教程JPA之delete使用姿势详解 常见db中的四个操作curd,前面的几篇博文分别介绍了insert,update,接下来我们看下delete的使用姿 ...
- TCP/IP学习笔记4--网络地址
"他强由他强,清风拂山岗.他横由他横,明月照大江.世间诸事,敞开心扉,顺其自然." -- 张大千 地址具有两个特性: 1:唯一性 同一个通信网络中的任意两个通信主体不能具有相同的地 ...
- Spark 系列(二)—— Spark开发环境搭建
一.安装Spark 1.1 下载并解压 官方下载地址:http://spark.apache.org/downloads.html ,选择 Spark 版本和对应的 Hadoop 版本后再下载: 解压 ...
- IDENTITY、SCOPE_IDENTITY、IDENT_CURRENT的分析
https://www.cnblogs.com/daihuiquan/archive/2013/03/18/2956845.html IDENT_CURRENT.IDENTITY.SCOPE_IDEN ...
- ubuntu配置Selenium+Chromedriver
1.下载并安装最新的Google Chrome版本执行如下命令: wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_curren ...
- Bean管理学习笔记
1.BeanFactory 介绍 1.1 首先什么是Bean? 1.Bean在Spring技术中是基于组件 2.他是Spring容器管理的最基本最常见的单元.在spring的应用场合中,bean可以是 ...
