[MAUI程序设计]界面多态与实现
.NET MAUI 实现界面多态有很多种方式,今天主要来说说在日常开发中常见的需求该如何应对。
需求一:在不同设备上使用不同 UI 外观
.NET MAUI是一个跨平台的UI框架,可在一个项目中开发Android、iOS、Windows、MacOS等多个平台的应用。在不同设备上我们希望应用的界面或交互方式能够有所不同。
比如在本示例中,我们希望博客条目的菜单使用平台特性的交互方式以方便触屏或鼠标的操作:比如手机设备中博客条目的菜单使用侧滑方式呈现,而在桌面设备中使用右键菜单呈现。
要实现不同平台下的控件外观,我们可以定义一个ContentView控件,然后在不同平台上使用不同的控件模板(ControlTemplate)。
控件模板(ControlTemplate)是我们的老朋友了,早在WPF时代就已经出现了,它可以完全改变一个控件的可视结构和外观,与使用Style改变控件外观样式和行为样式不同,使用Style只能改变控件已有的属性。
定义控件 UI 外观
首先用控件模板定义博客条目的外观,“博客条目”是包含博客标题,内容,以及发布时间等信息的卡片,视觉上呈现圆角矩形的白色不透明卡片效果。
博客条目控件是一个基于ContentView控件
<ContentView xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:service="clr-namespace:Lession1.Models;assembly=Lession1"
x:Class="Lession1.Views.TextBlogView">
<Grid>
<VerticalStackLayout>
<Label Text="{Binding Title}" FontAttributes="Bold">
</Label>
<Label Text="{Binding Content}"
LineBreakMode="WordWrap"></Label>
</VerticalStackLayout>
</Grid>
</ContentView>
在页面的资源中,添加如下两个ControlTemplate模板,分别用于手机设备和桌面设备。
- BlogCardViewPhone用于博客条目在手机设备中的呈现,条目菜单侧滑栏方式展开,我们配置SwipeView控件,作为卡片,用一个Frame框架包裹其内容。设置卡片的阴影,圆角,以及内边距。
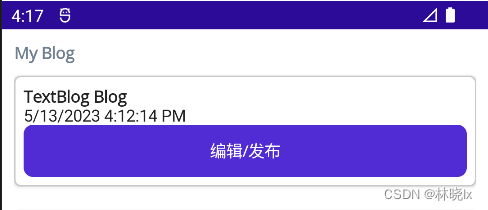
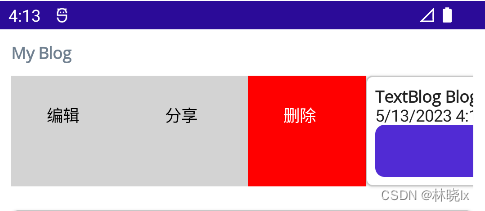
代码如下
<ControlTemplate x:Key="BlogCardViewPhone">
<Grid>
<SwipeView>
<SwipeView.LeftItems>
<SwipeItems>
<SwipeItem Text="编辑"
IconImageSource="delete.png"
BackgroundColor="LightGray" />
<SwipeItem Text="分享"
IconImageSource="delete.png"
BackgroundColor="LightGray" />
<SwipeItem Text="删除"
IconImageSource="delete.png"
BackgroundColor="Red" />
</SwipeItems>
</SwipeView.LeftItems>
<Frame HasShadow="True"
Margin="0,10,0,10"
CornerRadius="5"
Padding="8">
<VerticalStackLayout>
<ContentPresenter />
<Label Text="{TemplateBinding BindingContext.PostTime}"
FontFamily="FontAwesome"></Label>
<Button Text="编辑/发布"
Command="{TemplateBinding BindingContext.SwitchState}" />
</VerticalStackLayout>
</Frame>
</SwipeView>
</Grid>
</ControlTemplate>
- BlogCardViewDesktop用于博客条目在桌面设备中的呈现,条目菜单右键菜单方式展开,我们配置FlyoutBase.ContextFlyout属性,作为卡片,用一个Frame框架包裹其内容。设置卡片的阴影,圆角,以及内边距。
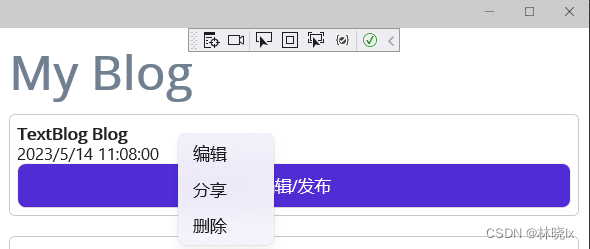
代码如下:
<ControlTemplate x:Key="BlogCardViewDesktop">
<Frame HasShadow="True"
Margin="0,10,0,10"
CornerRadius="5"
Padding="8">
<FlyoutBase.ContextFlyout>
<MenuFlyout>
<MenuFlyoutItem Text="编辑" />
<MenuFlyoutItem Text="分享" />
<MenuFlyoutItem Text="删除" />
</MenuFlyout>
</FlyoutBase.ContextFlyout>
<VerticalStackLayout>
<ContentPresenter />
<Label Text="{TemplateBinding BindingContext.PostTime}"
FontFamily="FontAwesome"></Label>
<Button Text="编辑/发布"
Command="{TemplateBinding BindingContext.SwitchState}" />
</VerticalStackLayout>
</Frame>
</ControlTemplate>
.NET MAUI 提供了ContentPresenter作为模板控件中的内容占位符,用于标记模板化自定义控件或模板化页面要显示的内容将在何处显示。
各平台模板中的<ContentPresenter /> 将显示控件的Content属性,也就是将TextBlogView中定义的内容,放到ContentPresenter处。
<view:TextBlogView ControlTemplate="{StaticResource BlogCardViewPhone}">
</view:TextBlogView>
基于平台自定义配置
.NET MAUI 提供了 OnPlatform 标记扩展和 OnIdiom 标记扩展。以便在不同平台上使用不同的控件模板。
通过 OnPlatform 标记扩展可基于每个平台控件属性:
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Default | 平台的属性的默认值。 |
| Android | 属性在 Android 上应用的值。 |
| iOS | 属性在 iOS 上应用的值。 |
| MacCatalyst | 设置为要在 Mac Catalyst 的值。 |
| Tizen | 属性在 Tizen 平台的值。 |
| WinUI | 属性在 WinUI 的值。 |
通过 OnIdiom 标记扩展可基于设备语义上的控件属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Default | 设备语义的属性的默认值。 |
| Phone | 属性在手机上应用的值。 |
| Tablet | 属性在平板电脑的值。 |
| Desktop | 设置为要在桌面平台的值。 |
| TV | 属性在电视平台的值。 |
| Watch | 属性在可穿戴设备(手表)平台的值。 |
在本示例中,我们使用OnIdiom标记扩展,分别为手机和桌面设备配置不同的模板。
<view:TextBlogView>
<view:TextBlogView.ControlTemplate>
<OnIdiom Phone="{StaticResource BlogCardViewPhone}"
Desktop="{StaticResource BlogCardViewDesktop}">
</OnIdiom>
</view:TextBlogView.ControlTemplate>
</view:TextBlogView>
需求二:在不同数据类别中使用不同的 UI 外观
数据模板(DataTemplate) 可以在支持的控件上(如:CollectionView)定义数据表示形式
可以使用数据模板选择器(DataTemplateSelector) 来实现更加灵活的模板选择。
DataTemplateSelector 可用于在运行时根据数据绑定属性的值来选择 DataTemplate。 这样可将多个 DataTemplate 应用于同一类型的对象,以自定义特定对象的外观。
相对于ControlTemplate方式,DataTemplateSelector是从Xamarin.Forms 2.1引入的新特性。
定义视图 UI 外观
创建两种视图和模板选择器:
- TextBlog: 文本博客
- PhotoBlog: 图片博客
编写文本博客条目展示标题和内容,创建TextBlogView.xaml,定义如下:
<ContentView xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:service="clr-namespace:Lession1.Models;assembly=Lession1"
x:Class="Lession1.Views.TextBlogView">
<Grid>
<VerticalStackLayout>
<Label Text="{Binding Title}" FontAttributes="Bold">
</Label>
<Label Text="{Binding Content}"
LineBreakMode="WordWrap"></Label>
</VerticalStackLayout>
</Grid>
</ContentView>
编写图片博客条目展示标题和博客中图片的缩略图,创建PhotoBlogView.xaml,定义如下:
<ContentView xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:service="clr-namespace:Lession1.Models;assembly=Lession1"
x:Class="Lession1.Views.PhotoBlogView">
<Grid>
<Label Text="{Binding Title}"
FontAttributes="Bold">
</Label>
<StackLayout BindableLayout.ItemsSource="{Binding Images}"
Orientation="Horizontal">
<BindableLayout.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<Image Source="{Binding}"
Aspect="AspectFill"
WidthRequest="44"
HeightRequest="44" />
</DataTemplate>
</BindableLayout.ItemTemplate>
</StackLayout>
</Grid>
</ContentView>

创建数据模板
在页面的资源中,添加各个视图创建数据模板(DataTemplate)类型的资源。
<ContentPage.Resources>
<DataTemplate x:Key="PhotoBlog">
<view:PhotoBlogView>
<view:PhotoBlogView.ControlTemplate>
<OnIdiom Phone="{StaticResource BlogCardViewPhone}"
Tablet="{StaticResource BlogCardViewDesktop}"
Desktop="{StaticResource BlogCardViewDesktop}">
</OnIdiom>
</view:PhotoBlogView.ControlTemplate>
</view:PhotoBlogView>
</DataTemplate>
<DataTemplate x:Key="TextBlog">
<view:TextBlogView>
<view:TextBlogView.ControlTemplate>
<OnIdiom Phone="{StaticResource BlogCardViewPhone}"
Tablet="{StaticResource BlogCardViewDesktop}"
Desktop="{StaticResource BlogCardViewDesktop}">
</OnIdiom>
</view:TextBlogView.ControlTemplate>
</view:TextBlogView>
</DataTemplate>
</ContentPage.Resources>
创建选择器
创建BlogDataTemplateSelector,根据博客的类型,返回不同的数据模板(DataTemplate)对象。
public class BlogDataTemplateSelector : DataTemplateSelector
{
public object ResourcesContainer { get; set; }
protected override DataTemplate OnSelectTemplate(object item, BindableObject container)
{
if (item == null)
{
return default;
}
if (item is Blog)
{
var dataTemplateName = (item as Blog).Type;
if (dataTemplateName == null) { return default; }
if (ResourcesContainer == null)
{
return Application.Current.Resources[dataTemplateName] as DataTemplate;
}
return (ResourcesContainer as VisualElement).Resources[dataTemplateName] as DataTemplate;
}
return default;
}
}
DataTemplate将在页面资源字典中被创建。若没有绑定ResourcesContainer,则在App.xaml中寻找。
同样, 将BlogDataTemplateSelector添加到页面的资源中
<view:BlogDataTemplateSelector x:Key="BlogDataTemplateSelector"
ResourcesContainer="{x:Reference MainContentPage}" />
注意,此时BlogDataTemplateSelector.ResourcesContainer指向MainContentPage,显式设置MainPage对象的名称:x:Name="MainContentPage"
定义数据
我们定义一个Blog类, 用于表示博客条目,包含标题,内容,发布时间,图片等属性。
public class Blog
{
public Blog()
{
PostTime = DateTime.Now;
State = BlogState.Edit;
}
public Guid NoteId { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Type { get; set; }
public BlogState State { get; set; }
public string Content { get; set; }
public List<string> Images { get; set; }
public DateTime PostTime { get; set; }
public bool IsHidden { get; set; }
}
定义博客列表的绑定数据源 ObservableCollection<Blog> Blogs,给数据源初始化一些数据,用于测试。
private async void CreateBlogAction(object obj)
{
var type = obj as string;
if (type == "TextBlog")
{
var blog = new Blog()
{
NoteId = Guid.NewGuid(),
Title = type + " Blog",
Type = type,
Content = type + " Blog Test, There are so many little details that a software developer must take care of before publishing an application. One of the most time-consuming is the task of adding icons to your toolbars, buttons, menus, headers, footers and so on.",
State = BlogState.PreView,
IsHidden = false,
};
this.Blogs.Add(blog);
}
else if (type == "PhotoBlog")
{
var blog = new Blog()
{
NoteId = Guid.NewGuid(),
Title = type + " Blog",
Type = type,
Content = type + " Blog Test",
Images = new List<string>() { "p1.png", "p2.png", "p3.png", "p4.png" },
State = BlogState.PreView,
IsHidden = false,
};
this.Blogs.Add(blog);
}
}
设置博客列表控件CollectionView绑定的数据源为Blogs,并设置数据模板选择器为BlogDataTemplateSelector
<ContentPage.Content>
<Grid Margin="10">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="1*" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<!--标题区域-->
<Label Text="My Blog"
TextColor="SlateGray"
FontSize="Header"
FontAttributes="Bold"></Label>
<CollectionView x:Name="MainCollectionView"
Grid.Row="1"
ItemsSource="{Binding Blogs}"
ItemTemplate="{StaticResource BlogDataTemplateSelector}" />
</Grid>
</ContentPage.Content>
则列表中的每个博客条目将根据博客类型,使用不同的数据模板进行渲染。
效果如下:
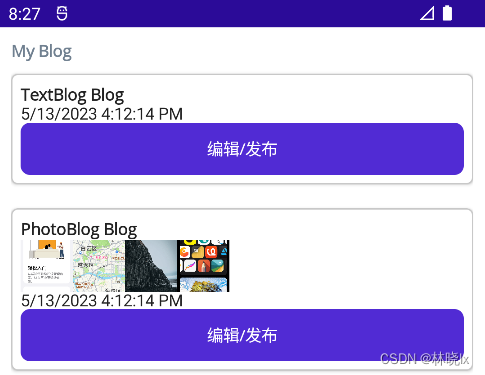
需求三:在不同数据状态中使用不同的 UI 外观
此功能没有一个固定的解决方案,可以根据实际情况,选择合适的方式实现。
比如在本项目中,博客存在编辑和发布两个状态
public enum BlogState
{
Edit,
PreView
}
使用绑定模型更改控件的外观
最简单的方式是用IsVisible来控制控件中元素的显示和隐藏。
在本示例中,TextBlogView需要对编辑中的状态和预览中的状态进行区分。
EnumToBoolConverter是枚举到bool值的转换器,它返回当前绑定对象的State属性与指定的BlogState枚举项是否一致,详情请查看 .NET MAUI 社区工具包
<ContentView xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:service="clr-namespace:Lession1.Models;assembly=Lession1"
x:Class="Lession1.Views.TextBlogView">
<Grid>
<VerticalStackLayout IsVisible="{Binding State, Converter={StaticResource EnumToBoolConverter}, ConverterParameter={x:Static service:BlogState.PreView}}">
<Label Text="{Binding Title}" FontAttributes="Bold">
</Label>
<Label Text="{Binding Content}"
LineBreakMode="WordWrap"></Label>
</VerticalStackLayout>
<VerticalStackLayout IsVisible="{Binding State, Converter={StaticResource EnumToBoolConverter}, ConverterParameter={x:Static service:BlogState.Edit}}">
<Label Text="编辑"
FontAttributes="Bold">
</Label>
<Entry Text="{Binding Title}"
Placeholder="标题"></Entry>
<Editor Text="{Binding Content}"
AutoSize="TextChanges"
Placeholder="内容"></Editor>
</VerticalStackLayout>
</Grid>
</ContentView>
编辑状态:
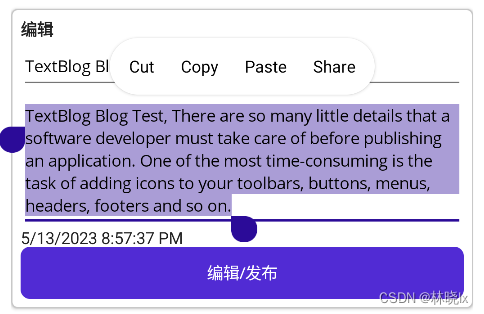
发布状态:

使用视觉状态更改控件的外观
还可以使用定义自定义视觉状态对界面进行控制。
在本示例中,使用VisualStateManager定义了两个视觉状态,分别对应Label的编辑状态和发布状态,当State属性的值发生变化时,会触发对应的视觉状态。
<Label Grid.Row="1">
<VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<VisualStateGroup>
<VisualState Name="BlogPreView">
<VisualState.StateTriggers>
<StateTrigger
IsActive="{Binding State, Converter={StaticResource EnumToBoolConverter}, ConverterParameter={x:Static service:BlogState.PreView}}" />
</VisualState.StateTriggers>
<VisualState.Setters>
<Setter Property="Text"
Value="当前为发布模式" />
</VisualState.Setters>
</VisualState>
<VisualState Name="BlogEdit">
<VisualState.StateTriggers>
<StateTrigger IsActive="{Binding State, Converter={StaticResource EnumToBoolConverter}, ConverterParameter={x:Static service:BlogState.Edit}}" />
</VisualState.StateTriggers>
<VisualState.Setters>
<Setter Property="Text"
Value="当前为编辑模式" />
</VisualState.Setters>
</VisualState>
</VisualStateGroup>
</VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
</Label>
编辑状态:

发布状态:

项目地址
关注我,学习更多.NET MAUI开发知识!
[MAUI程序设计]界面多态与实现的更多相关文章
- 【我要学python】面对对象编程之继承和多态
class animal(object): def run(): print('animal is running...') class dog(animal): def run(self): pri ...
- java学习笔记(详细)
java平台 1.J2SE java开发平台标准版 2.J2EE java开发平台企业版 java程序需要在虚拟机上才可以运行,换言之只要有虚拟机的系统都可以运行java程序.不同系统上要安装对应的虚 ...
- DeltaFish 校园物资共享平台 第三次小组会议
一.想法 娄雨禛: 网页底层开发转移到后端,快速建站,效率高. 可以依照模板进行仿制. 可以考虑只进行页面设计. 但是出现问题不会调试. 所以自己写源码,做出一个大致的样子. 二.上周进度汇报 齐天杨 ...
- Golang核心编程
源码地址: https://github.com/mikeygithub/GoCode 第1章 1Golang 的学习方向 Go 语言,我们可以简单的写成 Golang 1.2Golang 的应用领域 ...
- JAVA(3)
接口注意事项: 1.接口不能被实例化 2.接口中所有的方法都不能有主体 (不能有{ }) 3.一个类可以实现多个接口 4.接口中可以有变量<但变量不能用private和protected修饰& ...
- OpenGL基础图形编程
一.OpenGL与3D图形世界1.1.OpenGL使人们进入三维图形世界 我们生活在一个充满三维物体的三维世界中,为了使计算机能精确地再现这些物体,我们必须能在三维空间描绘这些物体.我们又生活在一个充 ...
- php面向对象之抽像类、接口、final、类常量
一.抽像类(abstract) 在我们实际开发过程中,有些类并不需要被实例化,如前面学习到的一些父类,主要是让子类来继承,这样可以提高代码复用性语法结构: 代码如下 复制代码 ab ...
- C#基本线程同步
0 概述 所谓同步,就是给多个线程规定一个执行的顺序(或称为时序),要求某个线程先执行完一段代码后,另一个线程才能开始执行. 第一种情况:多个线程访问同一个变量: 1. 一个线程写,其它线程读:这种情 ...
- BIOS
转自BIOS BIOS(Basic Input/Output System的缩写.中文:基本输入输出系统),在IBM PC兼容机上,是一种业界标准的固件接口.BIOS这个字眼是在1975第一次由CP/ ...
- ASP.NET 设计模式(转)
Professional ASP.NET Design Patterns 为什么学习设计模式? 运用到ASP.NET应用程序中的设计模式.原则和最佳实践.设计模式和原则支持松散耦合.高内聚的代码,而这 ...
随机推荐
- ESP32 优化 IRAM 内存方法整理 ---ESP32
有以下三种方便的方法来优化 IRAM 内存: 启用 menuconfig -> Compiler option -> Optimization Level -> Optimize f ...
- IDEA学生认证的步骤详解
步骤详解 在上次使用学生认证的方法对jetbrains认证成功之后,咱们在IDEA这里认证一下吧! 一.点击help这里的register 如图所示: 进入这样一个界面: 然后点击左下角的的Log I ...
- Java面试——Netty
一.BIO.NIO 和 AIO [1]阻塞 IO(Blocking I/O):同步阻塞I/O模式,当一条线程执行 read() 或者 write() 方法时,这条线程会一直阻塞直到读取一些数据或者写出 ...
- Leetcode Practice -- 字符串
目录 14. 最长公共前缀 思路解析 151. 反转字符串中的单词 思路解析 125. 验证回文串 思路解析 415. 字符串相加 思路解析 3. 无重复字符的最长子串 思路解析 8. 字符串转换整数 ...
- gralde-plugin->docker-compose的使用
在java web项目中,本地开发经常会需要在本地使用docker启动数据库等之类的服务.gradle提供了一个插件,允许通过gradle task启动docker的容器.在这里我们介绍的一个gral ...
- 【JavaScript快速排序算法】不同版本原理分析
说明 快速排序(QuickSort),又称分区交换排序(partition-exchange sort),简称快排.快排是一种通过基准划分区块,再不断交换左右项的排序方式,其采用了分治法,减少了交换的 ...
- LeetCode 周赛 338,贪心 / 埃氏筛 / 欧氏线性筛 / 前缀和 / 二分查找 / 拓扑排序
本文已收录到 AndroidFamily,技术和职场问题,请关注公众号 [彭旭锐] 提问. 大家好,我是小彭. 上周末是 LeetCode 第 338 场周赛,你参加了吗?这场周赛覆盖的知识点很多,第 ...
- MySQL事务还没提交,Canal就能读到消息了?
[问题描述] 开发有天碰到一个很奇怪的问题,他的场景是这样子的: 通过Canal来订阅MySQL的binlog, 当捕获到有数据变化时,回到数据库,反查该数据的明细,然后做进一步处理. 有一次,他碰到 ...
- 学习docker看此文足以
什么是 Docker Docker 最初是 dotCloud 公司创始人 在法国期间发起的一个公司内部项目,它是基于 dotCloud 公司多年云服务技术的一次革新,并于 ,主要项目代码在 上进行 ...
- SpringIOC注入
在lagou的训练营的学习历程 SpringIOC实例化Bean的三种方式:1.使用无参构造器2.静态方法3.实例化方法.他要先实例化创建类(和2的区别),再调用. XML注入属性DI依赖注入,根据实 ...
