HashMap的底层原理
简单说: 底层原理就是采用数组加链表:

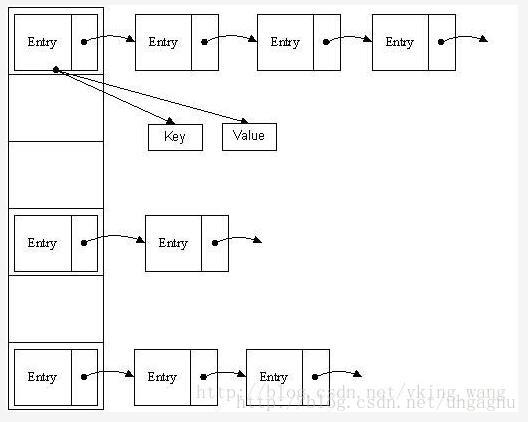
两张图片很清晰地表明存储结构:
既然是线性数组,为什么能随机存取?这里HashMap用了一个小算法,大致是这样实现:
// 存储时:
int hash = key.hashCode(); // 这个hashCode方法这里不详述,只要理解每个key的hash是一个固定的int值
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
Entry[index] = value;
// 取值时:
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = hash % Entry[].length;
return Entry[index];
HashMap的底层原理的更多相关文章
- HashMap的底层原理(jdk1.7.0_79)
前言 在Java中我们最常用的集合类毫无疑问就是Map,其中HashMap作为Map最重要的实现类在我们代码中出现的评率也是很高的. 我们对HashMap最常用的操作就是put和get了,那么你知道它 ...
- 谈一下HashMap的底层原理是什么?
底层原理:Map + 无序 + 键唯一 + 哈希表 (数组+Entry)+ 存取值 1.HashMap是Map接口的实现类.实现HashMap对数据的操作,允许有一个null键,多个null值. Co ...
- HashMap的底层原理 cr:csdn:zhangshixi
1. HashMap概述: HashMap是基于哈希表的Map接口的非同步实现.此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用null值和null键.此类不保证映射的顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变 ...
- 深度解析HashMap集合底层原理
目录 前置知识 ==和equals的区别 为什么要重写equals和HashCode 时间复杂度 (不带符号右移) >>> ^异或运算 &(与运算) 位移操作:1<&l ...
- 浅谈HashMap 的底层原理
本文整理自漫画:什么是HashMap? -小灰的文章 .已获得作者授权. HashMap 是一个用于存储Key-Value 键值对的集合,每一个键值对也叫做Entry.这些个Entry 分散存储在一个 ...
- HashMap 的底层原理
1. HashMap的数据结构 数据结构中有数组和链表来实现对数据的存储,但这两者基本上是两个极端. 数组 数组存储区间是连续的,占用内存严重,故空间复杂的很大.但数组的二分查找时间复杂度小,为O(1 ...
- 最简单的HashMap底层原理介绍
HashMap 底层原理 1.HashMap底层概述 2.JDK1.7实现方式 3.JDK1.8实现方式 4.关键名词 5.相关问题 1.HashMap底层概述 在JDK1.7中HashMap采用的 ...
- HashMap的底层实现原理
HashMap的底层实现原理1,属性static final int MAX_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;//1073741824(十进制)0100000000000000000 ...
- HashMap底层原理分析(put、get方法)
1.HashMap底层原理分析(put.get方法) HashMap底层是通过数组加链表的结构来实现的.HashMap通过计算key的hashCode来计算hash值,只要hashCode一样,那ha ...
随机推荐
- Hello China操作系统在Virtual PC上的安装和使用
http://blog.csdn.net/hellochina15/article/details/7253350 本文介绍如何在Windows 7操作系统和Virtual PC 2007虚拟机上安装 ...
- GStreamer 简化 Linux 多媒体开发
Streamer 是 GNOME 桌面环境下用来构建流媒体应用的开源多媒体框架(framework),其目标是要简化音/视频应用程序的开发,目前已经能够被用来处理像 MP3.Ogg.MPEG1.MPE ...
- ASP.NET WebAPI String 传值问题
如果我们再WebAPI中定义了只有一个string参数的WebAPI函数,如下所示: [HttpPost] public string TrackBill(string str) { return s ...
- Coins HDU - 2844
Whuacmers use coins.They have coins of value A1,A2,A3...An Silverland dollar. One day Hibix opened p ...
- UltraEdit 脚本 实现查找替换
UltraEdit中,要实现,脚本查找替换功能,按照下文中的做法稍作修改, 现象很奇怪,有时可以进行查找替换有时不能. http://blog.csdn.net/neareast/article/de ...
- HALCON不支持的设备中,获取图像
HALCON不支持的设备中,获取图像 参考(HALCON手册): Solution_guide_II_A_image_acquisiton.pdf image_acquisition_interf ...
- 彻底禁用Chrome的“请停用以开发者模式运行的扩展程序”提示
前言 作为一个前端程序员,难免会有一些专属自己的小扩展,没必要每一个都发到Chrome应用商店去,虽然可以勾选"开发者模式"来运行本地插件,但是每次启动都会有一个烦人的" ...
- 洛谷P2444 [POI2000]病毒(AC自动机,DFS求环)
洛谷题目传送门 AC自动机入门--yyb巨佬的博客 AC自动机入手经典好题(虽然年代久远) 有了fail指针,trie树就不是原来的树型结构了,我们可以把它叫做trie图,由父节点向子节点连的边和fa ...
- 【ZJOI2008】树的统计(树链剖分)
题面 Description 一棵树上有n个节点,编号分别为1到n,每个节点都有一个权值w.我们将以下面的形式来要求你对这棵树完成一些操作: I. CHANGE u t : 把结点u的权值改为t II ...
- Bzoj5093: 图的价值
题面 Bzoj Sol 一张无向无重边自环的图的边数最多为\(\frac{n(n-1)}{2}\) 考虑每个点的贡献 \[n*2^{\frac{n(n-1)}{2} - (n-1)}\sum_{i=0 ...
