Java 计算两点间的全部路径(二)
一、有向线段,存储开始点与结束点
/**
* 有方向的线段
*
* @author Gm
*
*/
public class DirectionLine implements Cloneable {
private String beginNode;
private String endNode;
public DirectionLine(String beginNode, String endNode) {
this.beginNode = beginNode;
this.endNode = endNode;
}
public String toString() {
return beginNode + "->" + endNode;
}
public String getBeginNode() {
return beginNode;
}
public void setBeginNode(String beginNode) {
this.beginNode = beginNode;
}
public String getEndNode() {
return endNode;
}
public void setEndNode(String endNode) {
this.endNode = endNode;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
DirectionLine dl = (DirectionLine) obj;
if (this.getBeginNode().equals(dl.getBeginNode()) && this.getEndNode().equals(dl.getEndNode())) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public Object clone() {
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
三、过滤无效节点
public class Graph {
List<DirectionLine> directionLines = null; // 已知的路径(有向线,包含:开始点、结束点)
List<String> visitedList = new ArrayList<String>(); // 存放已经访问过点的节点
Set<String> resultSet = new HashSet<String>(); // 目的访问路径(点的集合)
Set<DirectionLine> loopList = new HashSet<DirectionLine>(); // 已知的回路(有向线,包含:开始点、结束点)
public Graph(List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
this.directionLines = directionLines;
}
public List<DirectionLine> getDirectionLines() {
return directionLines;
}
public void setDirectionLines(List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
this.directionLines = directionLines;
}
public List<String> getVisitedList() {
return visitedList;
}
public void setVisitedList(List<String> visitedList) {
this.visitedList = visitedList;
}
public Set<String> getResultSet() {
return resultSet;
}
public void setResultSet(Set<String> resultSet) {
this.resultSet = resultSet;
}
public Set<DirectionLine> getLoopList() {
return loopList;
}
public void setLoopList(Set<DirectionLine> loopList) {
this.loopList = loopList;
}
/**
* 路径遍历的核心算法
*
* @param startNode
* @param endNode
*/
public void getAllPaths(String startNode, String endNode) {
visitedList.add(startNode);
// System.out.println("访问的起点->终点:" + startNode + "->" + endNode);
for (int z = 0; z < directionLines.size(); z++) {
// System.out.println("遍历次数:" + z + ",路径:" + directionLines.get(z).toString());
if (directionLines.get(z).getBeginNode().equals(startNode)) { // 寻找找以startNode开始的路径
if (directionLines.get(z).getEndNode().equals(endNode)) { // 如果以endNode结尾,则为一条有效路径
resultSet.add(visitedList.toString().substring(0, visitedList.toString().lastIndexOf("]")) + "," + endNode + "]");
continue;
}
// System.out.println("已访问过的节点:" + visitedList.toString());
if (!visitedList.contains(directionLines.get(z).getEndNode())) {// 此节点仍未遍历,则继续迭代
getAllPaths(directionLines.get(z).getEndNode(), endNode);
} else {// 证明存在回路
loopList.add(directionLines.get(z));
}
}
}
visitedList.remove(startNode);
}
}
public class MapVisit {
/**
* 构造初始化路径--已知
*
*/
public List<DirectionLine> init() {
List<DirectionLine> directionLines = new ArrayList<DirectionLine>();
String str = CommonUtil.readToString("room_layout2.json");
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(str);
for (Entry<String, Object> entry : jsonObject.entrySet()) {
String startNode = "node" + entry.getKey();
JSONObject child_nodes = JSONObject.parseObject(entry.getValue().toString());
for (Entry<String, Object> child_entry : child_nodes.entrySet()) {
String endNode = "node" + child_entry.getKey();
// System.out.println(startNode + ":" + endNode);
directionLines.add(new DirectionLine(startNode, endNode));
}
}
return directionLines;
}
/**
* 判断所有路径中是否有以beginNode节点为起点的基本路径
*
* @param beginNode
* @param directionLines
* @return
*/
public boolean existBeginNode(String beginNode, List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
boolean result = false;
for (DirectionLine dl : directionLines) {
if (dl.getBeginNode().equals(beginNode)) {
result = true;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 判断所有路径中是否有以end节点为终点的基本路径
*
* @param endNode
* @param directionLines
* @return
*/
public boolean existEndNode(String endNode, List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
boolean result = false;
for (DirectionLine dl : directionLines) {
if (dl.getEndNode().equals(endNode)) {
result = true;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 根据路径获取到所有的节点
*
* @param directionLines
* @return
*/
public Set<String> getAllNodes(List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
Set<String> nodes = new HashSet<String>();
for (DirectionLine r : directionLines) {
nodes.add(r.getBeginNode());
nodes.add(r.getEndNode());
}
return nodes;
}
/**
* 获取到需要删除的路径
*
* @param beginNodes
* 无效起始节点
* @param endNodes
* 无效终结点
* @param directionLines
*/
public Set<DirectionLine> deleteDirectionLines(Set<String> beginNodes, Set<String> endNodes, List<DirectionLine> directionLines) {
Set<DirectionLine> set = new HashSet<DirectionLine>();
for (String str : beginNodes) {
for (DirectionLine dl : directionLines) {
if (dl.getBeginNode().equals(str)) {
set.add(dl);
}
if (dl.getBeginNode().equals(str)) {
set.add(dl);
}
}
}
return set;
}
/**
* 过滤掉无用的节点 获取到无效开始节点和无效结束点
*
* @param all
* @param directionLines
* @param beginNodes
* @param endNodes
* @return
*/
public Set<String> filterInvalidNode(Set<String> allNodes, List<DirectionLine> directionLines, Set<String> beginNodes, Set<String> endNodes) {
Set<String> result = new HashSet<String>();
boolean isBegin = true;
boolean isEnd = true;
for (String node : allNodes) {
if (!existEndNode(node, directionLines)) { // 没有以此节点结尾的路径,则证明此节点为无用节点
isBegin = false;
beginNodes.add(node);
} else if (!existBeginNode(node, directionLines)) {// 没有以此节点开头的路径,则证明此节点为无用节点
isEnd = false;
endNodes.add(node);
} else {
result.add(node); // 有用的节点
}
}
if (isBegin == true && isEnd == true) {
return result;
} else {
return filterInvalidNode(result, directionLines, beginNodes, endNodes);
}
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
MapVisit visit = new MapVisit();
List<DirectionLine> directionLines = visit.init();
// 构造基本路径--为已知条件
Set<String> invalidBeginNodes = new HashSet<String>(); // 无效的起始节点
Set<String> invalidEndNodes = new HashSet<String>(); // 无效的结束节点
Set<String> allNodes = visit.getAllNodes(directionLines);
visit.filterInvalidNode(allNodes, directionLines, invalidBeginNodes, invalidEndNodes); // 获取到无效开始节点和无效结束点
Set<DirectionLine> invalidRoads = visit.deleteDirectionLines(invalidBeginNodes, invalidEndNodes, directionLines); // 获取需要删除的路径
directionLines.removeAll(invalidRoads); // 删除无效的路径
// System.out.println(directionLines.toString());
Graph pra = new Graph(directionLines);
String begin = "node12"; // 起始点
String end = "node1"; // 终结点
// 获取所有有效路径
pra.getAllPaths(begin, end);
Iterator<String> it = pra.getResultSet().iterator();
System.out.println("-----------------从" + begin + "至" + end + "的有效路径如下-----------------");
while (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}
四、数据集
{"1":{"2":1},"2":{"1":1,"3":1,"19":1},"3":{"2":1,"4":1,"9":1},"4":{"3":1,"5":1},"5":{"4":1},"6":{"9":1},"7":{"10":1},"8":{"11":1},"9":{"3":1,"6":1,"10":1},"10":{"7":1,"9":1,"11":1,"12":1},"11":{"8":1,"10":1},"12":{"10":1,"13":1,"17":1},"13":{"12":1,"14":1,"15":1},"14":{"13":1,"16":1},"15":{"13":1},"16":{"14":1},"17":{"12":1,"18":1},"18":{"17":1,"19":1,"20":1},"19":{"2":1,"18":1},"20":{"18":1}}
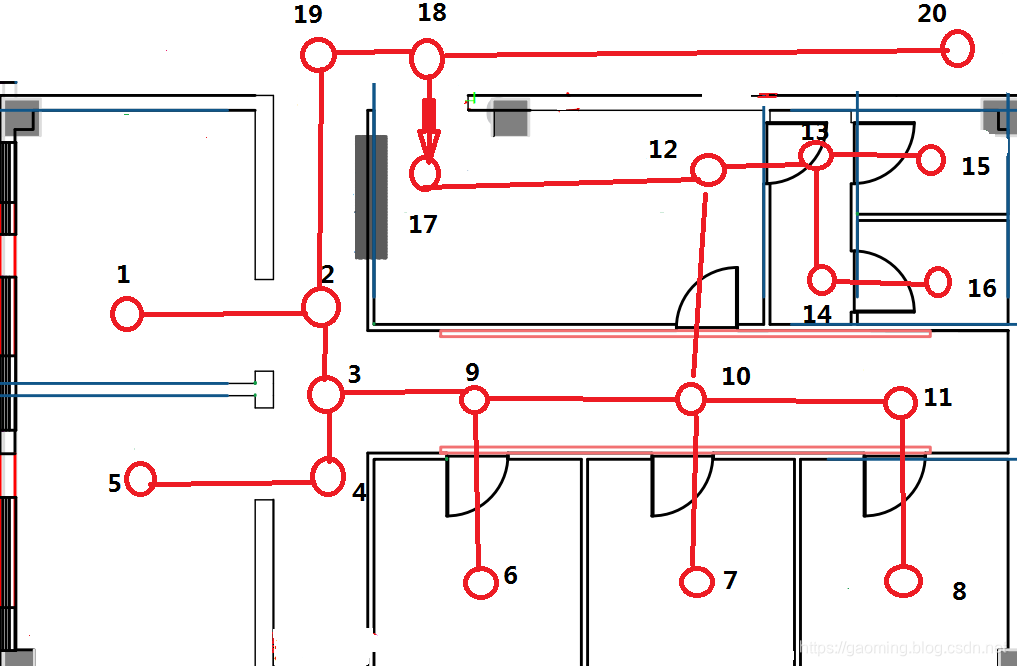
五、效果展示
-----------------从node12至node1的有效路径如下-----------------
[node12, node17, node18, node19, node2,node1]
[node12, node10, node9, node3, node2,node1]
Java 计算两点间的全部路径(二)的更多相关文章
- Java 计算两点间的全部路径(一)
算法要求: 在一个无向连通图中求出两个给定点之间的所有路径: 在所得路径上不能含有环路或重复的点: 算法思想描述: 整理节点间的关系,为每个节点建立一个集合,该集合中保存所有与该节点直接相连的节点(不 ...
- HDOJ2001计算两点间的距离
计算两点间的距离 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- hdu2001 计算两点间的距离【C++】
计算两点间的距离 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Su ...
- 计算两点间的距离,hdu-2001
计算两点间的距离 Problem Description 输入两点坐标(X1,Y1),(X2,Y2),计算并输出两点间的距离. Input 输入数据有多组,每组占一行,由4个实数组成,分别表示x1 ...
- TSQL 根据经纬度计算两点间的距离;返回米(m)
-- ============================================= -- Author:Forrest -- Create date: 2013-07-16 -- Des ...
- 转:Math: Math.atan() 与 Math.atan2() 计算两点间连线的夹角
我们可以使用正切操作将角度转变为斜率,那么怎样利用斜率来转换为角度呢?可以利用斜率的反正切函数将他转换为相应的角度.as中有两个函数可以计算反正切,我们来看一下. 1.Math.atan() Math ...
- 经纬度计算两点间的距离,根据距离排序SQL
#java的Utilspublic class DistanceUtil { // 地球平均半径 private static final double EARTH_RADIUS = 6378137; ...
- J - 计算两点间的距离
Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Description 输入两 ...
- 计算两点间的距离-hdu2001
Problem Description 输入两点坐标(X1,Y1),(X2,Y2),计算并输出两点间的距离. Input 输入数据有多组,每组占一行,由4个实数组成,分别表示x1,y1,x2,y2 ...
随机推荐
- CSS中 Padding和Margin两个属性的详细介绍和举例说明
代码示例: <!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF ...
- C++学习 之 初识C++
声明: 本人自学C++, 没有计算机基础,在学习的过程难免会出现理解错误,出现风马牛不相及的现象,甚至有可能会贻笑大方. 如果有幸C++大牛能够扫到本人的博客,诚心希望大牛能给予 ...
- 运维之思科篇——NAT基础配置
一. NAT(网络地址转换) 1. 作用:通过将内部网络的私有IP地址翻译成全球唯一的公网IP地址,使内部网络可以连接到互联网等外部网络上. 2. 优点: 节省公有合法IP地址 处理地址重叠 增强灵活 ...
- git重命名文件和文件夹
git mv -f oldfolder newfoldergit add -u newfolder (-u选项会更新已经追踪的文件和文件夹)git commit -m "changed th ...
- ModelAndView及页面转发
1.ModelAndView springMVC中返回值如果是ModelAndView,则其既包含模型数据信息,也包含视图信息. 在处理方法中可以使用ModelAndView对象的方法添加模型数据:a ...
- C#-WinForm跨线程修改UI界面
待解决的问题 在我做WinForm开发的过程中,经常会遇到耗时操作或阻塞操作.他们会引发软件的卡顿甚至假死,严重影响软件的使用. 因此,这类耗时或阻塞的操作一般都会使用异步的方式去执行,不影响主线程( ...
- golang可见性规则(公有与私有,访问权限)
Go语言没有像其它语言一样有public.protected.private等访问控制修饰符,它是通过字母大小写来控制可见性的,如果定义的常量.变量.类型.接口.结构.函数等的名称是大写字母开头 ...
- 【HANA系列】SAP HANA SQL查找字符串位置
公众号:SAP Technical 本文作者:matinal 原文出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/SAPmatinal/ 原文链接:[HANA系列]SAP HANA SQL查找字符 ...
- Pytorch1.0入门实战三:ResNet实现cifar-10分类,利用visdom可视化训练过程
人的理想志向往往和他的能力成正比. —— 约翰逊 最近一直在使用pytorch深度学习框架,很想用pytorch搞点事情出来,但是框架中一些基本的原理得懂!本次,利用pytorch实现ResNet神经 ...
- hue改下载行数
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/lingbo229/article/details/85991230 修改hue所在机器的默认配置后,重启hue即可 find / -name be ...
