TIJ——Chapter Eleven:Holding Your Objects
Java Provides a number of ways to hold objects:
- An array associates numerical indexes to objects. It holds objects of a known type so that you don't have to cast the result when you're looking up an object. It can be multidimensional, and it can hold primitives. However, its size cannot be changed once you create it.
- A Collection holds signle elements, and a Map holds associated pairs. With Java generics, you specify the type of objec to be held in the containers, so you can't put the wrong type into a container and you don't have to cast elements when you fetch them out of a container. Both Collections and Maps automatically resize themselves as you add more elements. A container won't hold primitives, but autoboxing takes care of translating primitives back and forth to the wrapper types held in the container.
- Like an array, a List also associates numerical indexed to objects—thus, arrays and Lists are ordered containers.
- Use an ArrayList if you're doing a lot of random accesses, but a LinkedList if you will be doing a lot of insertions and removals in the middle of the list.
- The behavior of Queue and Stack is provided via the LinkedList.
- A Map is a way to associate not integral values, but objects with other objects. HashMap are designed for rapid access, whereas a TreeMap keeps its keys in sorted order, and thus is not as fast as a HashMap. A LinkedHashMap keeps its elements in insertion order, but provides rapid access with hashing.
- A set only accepts one of each type of object. HashSet provide maximally fast lookups, whereas TreeSet keep the elements in sorted order. LinkedHashSet keep elements in insertion order.
- There's no need to use the legacy classes Vector, Hashtable, and Stack in new code.
It's helpful to look at a simplified diagram of the Java containers(without the abstract classes or legacy components). This only includes the interfaces and classes that you will encounter on a regular basis.
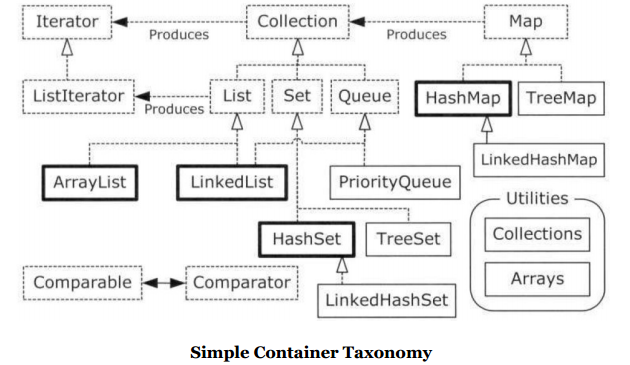
图中,用粗黑线框包围的容器(HashMap、ArrayList、LinkedList、HashSet)是我们在开发过程中要频繁使用的;虚线框表示接口,实线框表示具体的实现类;空心箭头表示某一个类实现了所指向的接口,实心箭头表示一个类(或实现某个接口的类)能生成一个指向类的对象。
- 对于容器而言,使用泛型与不使用泛型的几个重要的区别是:当往容器中放元素的时候,如果使用泛型,那么对于类型不兼容的对象,会在编译期报错;而且从容器中取出元素的时候,使用泛型则不需要类型转换,而不使用泛型则必须进行类型转换。可以看出,使用泛型可以使我们的代码更精简、健壮,同时不必记忆放入容器中元素的类型。
- The Java container library takes the idea of "holding your object" and divides it into two distinct concepts, expressed as the basic interfaces of the library:Lists promise to maintain elements in a particular sequence. The List interface adds a number of methods to Collection that allow insertion and removal of elements in the middle of a List. There are two types of List:
- Collection: a sequence of individual elements with one or more rules applied to them. A List must hold the elements in the way that they were inserted, a Set cannot have duplicate elements.
- Map: a group of key-value object pairs, allowing you to look up a value using a key. An ArrayList allows you to look up an object using a number, so in a sense it associates number to objects. A map allows you to look up an object using another object. It's also called an associative array, because it associates objects with another objects, or a dictionary, because you look up a value object using a key object just like you look up a definition using a word. Maps are powerful programming tools.
- Lists promise to maintain elements in a particular sequence. The List Interface adds a number of methods to Collection that allow insertion and removal of elements in the middle of a List. There are two types of List:
- The basic ArrayList, which excels at randomly accessing elements, but is slower when inserting and removing elements in the middle of a List.
- The LinkedList, which provides optimal sequential access, with inexpensive insertions and deletions from the middle of the List. A LinkedList is relatively slow for random access, but it has a larger feature set than the ArrayList.
- The Java Iterator can move in only one direction, There's not much you can do with an Iterator except(With an Iterator, you don't need to worry about the number of elements in the container. That's taken care of for you by hasNext() and next()):
- Ask a Collection to hand you an Iterator using a method called iterator(). That Iterator will be ready to return the first element in the sequence.
- Get the next object in the sequence with next().
- See if there are more object in the sequence with hasNext().
- Remove the last element returned by the iterator with remove().
- HashSet uses hashing for speed. The Order maintained by a HashSet is different from a TreeSet or a LinkedHashSet, since each implementation has a different way of storing elements. TreeSet keeps elements sorted into a red-black tree data structure, whereas HashSet uses the hashing fuction. LinkedHashSet also uses hashing for lookup speed, but appears to maintain elements in insertion order using a linked list.
- A foreach statement works with an array or anything Iterable, but that doesn't mean that an array is automatically an Iterable, nor is there any autoboxing that takes place:
public class ArrayIsNotIterable
{
static <T> void test(Iterable<T> ib)
{
for(T t : ib)
{
System.out.print(t + " ");
}
} public static void main(String[] args)
{
test(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
String[] strings = {"A", "B", "C"}; // An array works in foreach, but it's not Iterable:
// !test(strings);
// You must explicitly convert it to Iterable:
test(Arrays.asList(strings));
}
}
/*
Output:
1 2 3 A B C
*/
TIJ——Chapter Eleven:Holding Your Objects的更多相关文章
- TIJ——Chapter One:Introduction to Objects
///:~容我对这个系列美其名曰"读书笔记",其实shi在练习英文哈:-) Introduction to Objects Object-oriented programming( ...
- TIJ——Chapter Two:Everything Is an Object
If we spoke a different language, we would perceive a somewhat different world. Ludwig Wittgenstein( ...
- TIJ——Chapter Twelve:Error Handling with Exception
Exception guidelines Use exceptions to: Handle problems at the appropriate level.(Avoid catching exc ...
- TIJ——Chapter Eight:Polymorphism
The twist |_Method-call binding Connecting a method call to a method body is called binding. When bi ...
- TIJ——Chapter Seven:Reusing Classes
Reusing Classes 有两种常用方式实现类的重用,组件(在新类中创建存在类的对象)和继承. Composition syntax Every non-primitive object has ...
- TIJ——Chapter Five:Initialization & Cleanup
Method overloading |_Distinguishing overloaded methods If the methods hava the same name, how can Ja ...
- Think Python - Chapter 15 - Classes and objects
15.1 User-defined typesWe have used many of Python’s built-in types; now we are going to define a ne ...
- Chapter 3 Introduction to Objects and Input/Output
与声明一个primitive variable不同,声明一个对象的时候,并不创建用来存储一个对象的内存空间,而是创建了一个存储该对象所在内存空间的地址. 在java里,new是一个操作符,它让系统分配 ...
- TIJ——Chapter Thirteen:Strings
String 对象是不可修改的,对于被String 重载的'+' 和'+=' 运算符来说,当你用它们来连接两个String 对象的时候,它在底层并不会对于每一次连接均生成一个String 对象,取而代 ...
随机推荐
- activity 、window与view的关系 (上)
我在研究任玉刚老师的<android开发艺术探索>的关于windowmanager那一章时,我发现自己对于acitivity.window和view之间的概念还是比较模糊. 然后查了一下a ...
- BZOJ2471 : Count
考虑KMP,设$f[i][j][S]$表示还剩最低$i$位没有确定,目前KMP匹配到了$j$这个位置,前缀匹配情况是$S$,最终会匹配到哪里,中途匹配成功几次. 其中$S[i]$是一个pair< ...
- 不想说作用域scope,因为是scopeTree,
ps:本文前面大部分是错的,后边大部分也是错的,搞混了不要怪我................... 这篇文章讲述了一个悲伤的故事,从一个似似而非的概念一步一步到错误的理解,最后勉强正确的过程 其实我 ...
- log4j mongoDB配置
log4j.rootCategory=INFO, stdout log4j.appender.stdout=org.springframework.data.document.mongodb.log4 ...
- 给备战NOIP 2014 的战友们的10条建议
应老胡要求,要写10条建议= = begin 1. 注意文件关联 比如 halt 前要close(input); close(output); 还有就是一定要打这两句话= = 2. 快排,大家都懂得. ...
- 自动爬取ZiMuZu的内容发布到Wordpress
先说一下大致的步骤. 首先需要模拟浏览器登录网站才能看到相应电影信息, 然后通过正则表达式从网页源代码中筛选出所需要的电影, 最后通过python-wordpress-xmlrpc将信息逐条发布到Wo ...
- javascript:cors跨域postMessage、xhr2和xmldomain
一.h5 postMessage node http-server配置服务器 有关配置:请参考我的http://www.cnblogs.com/leee/p/5502727.html 我把文件夹a配置 ...
- java jdbc
1.java 的jdbc类包括,DriverManager,Connection Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:odb ...
- 关于thinkphp开发的几种规范(仅限个人)
一.只要设计到where查询语句,无论是增删改查 $cn['username'] = session('member.username'); $cn['itemid'] = $itemid; $ite ...
- php_cz
post.php <?php require_once 'config.php'; $ddh=trim(htmlspecialchars($_POST['ddh'])); //支付宝交易号 $m ...
