C语言命令行处理
一、简介
getopt()函数是一个标准库调用,可允许您使用直接的 while/switch 语句方便地逐个处理命令行参数和检测选项(带或不带附加的参数)。与其类似的getopt_long()允许在几乎不进行额外工作的情况下处理更具描述性的长选项,这非常受开发人员的欢迎。
二、示例
1、getopt()
函数原型
getopt(int argc,char *const argv[],const char *optstring)
参数说明
argc和argv一般就将main函数的那两个参数原样传入。
optstring是一段自己规定的选项串,“:”表示该选项必须带有额外的参数,全域变量optarg会指向此额外参数,“::”标识该额外的参数可选(带的额外参数必须紧挨着该选项,有些Uinx可能不支持“::”)
全域变量optind指示下一个要读取的参数在argv中的位置。如果getopt()找不到符合的参数则会印出错信息,并将全域变量optopt设为“?”字符。如果不希望getopt()印出错信息,则只要将全域变量opterr设为0即可。
使用示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int ch;
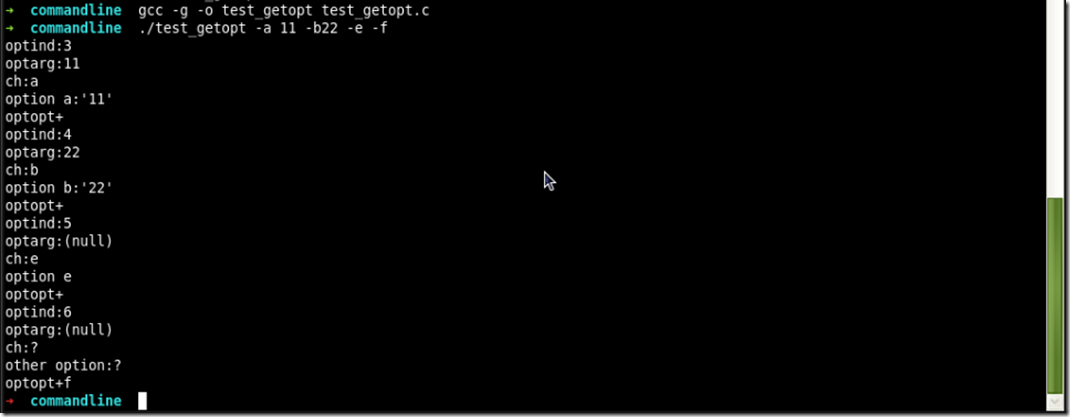
opterr=0; while((ch=getopt(argc,argv,"a:b::cde"))!=-1)
{
printf("optind:%d\n",optind);
printf("optarg:%s\n",optarg);
printf("ch:%c\n",ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 'a':
printf("option a:'%s'\n",optarg);
break;
case 'b':
printf("option b:'%s'\n",optarg);
break;
case 'c':
printf("option c\n");
break;
case 'd':
printf("option d\n");
break;
case 'e':
printf("option e\n");
break;
default:
printf("other option:%c\n",ch);
}
printf("optopt+%c\n",optopt);
}
}
运行
2、getopt_long()
函数原型
int getopt_long(int argc, char * const argv[], const char *optstring, const struct option *longopts, int *longindex)
参数说明
函数中的argc和argv通常直接从main()的两个参数传递而来。optsting是选项参数组成的字符串:
字符串optstring可以下列元素:
1.单个字符,表示选项,
2.单个字符后接一个冒号:表示该选项后必须跟一个参数。参数紧跟在选项后或者以空格隔开。该参数的指针赋给optarg。
3.单个字符后跟两个冒号,表示该选项后可以有参数也可以没有参数。如果有参数,参数必须紧跟在选项后不能以空格隔开。该参数的指针赋给optarg。(这个特性是GNU的扩张)。
参数longopts,其实是一个结构的实例:
struct option
{
const char *name;//name表示的是长参数名
int has_arg; //has_arg有3个值,no_argument(或者是0),表示该参数后面不跟参数值
// required_argument(或者是1),表示该参数后面一定要跟个参数值
// optional_argument(或者是2),表示该参数后面可以跟,也可以不跟参数值
int *flag; //用来决定,getopt_long()的返回值到底是什么。如果flag是null(通常情况),则函数会返回与该项option匹配的val值;
//如果flag不是NULL,则将val值赋予flag所指向的内存,并且返回值设置为0
int val; //和flag联合决定返回值
} 参数longindex,表示当前长参数在longopts中的索引值
使用示例
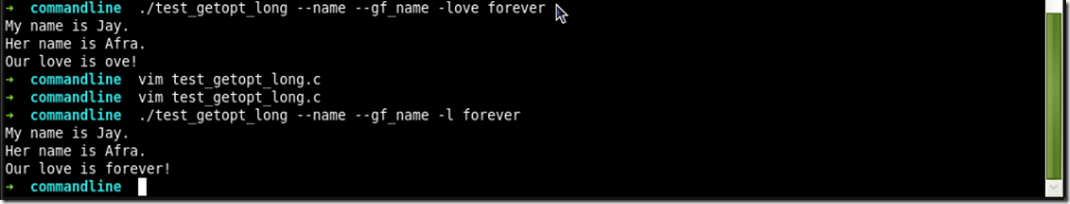
#include <stdio.h>
#include <getopt.h> int do_name, do_gf_name;
char *l_opt_arg; struct option longopts[] =
{
{ "name", no_argument, NULL, 'n'},
{ "gf_name", no_argument, NULL, 'g'},
{ "love", required_argument, NULL, 'l'},
{ 0, 0, 0, 0},
}; int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int c; while((c = getopt_long(argc, argv, ":l:", longopts, NULL)) != -1)
{
switch (c)
{
case 'n':
printf("My name is Jay.\n");
break;
case 'g':
printf("Her name is Afra.\n");
break;
case 'l':
l_opt_arg = optarg;
printf("Our love is %s!\n", l_opt_arg);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
运行
3、使用 gperf实现高效的C/C++ 命令行处理
三、Apache 命令行处理分析
Apache通过apr_getopt_init函数对命令行结构opt进行初始化
apr_getopt_init(&opt, pcommands, process->argc, process->argv);
apr_getopt_init函数实现在文件:srclib\apr\misc\unix\getopt.c,代码如下:
APR_DECLARE(apr_status_t) apr_getopt_init(apr_getopt_t **os, apr_pool_t *cont, int argc, const char *const *argv)
{
void *argv_buff; *os = apr_palloc(cont, sizeof(apr_getopt_t));
(*os)->cont = cont;
(*os)->reset = 0;
(*os)->errfn = (apr_getopt_err_fn_t*)(fprintf);
(*os)->errarg = (void*)(stderr); (*os)->place = EMSG;
(*os)->argc = argc; /* The argv parameter must be compatible with main()'s argv, since
that's the primary purpose of this function. But people might
want to use this function with arrays other than the main argv,
and we shouldn't touch the caller's data. So we copy. */
argv_buff = apr_palloc(cont, (argc + 1) * sizeof(const char *));
memcpy(argv_buff, argv, argc * sizeof(const char *));
(*os)->argv = argv_buff;
(*os)->argv[argc] = NULL; (*os)->interleave = 0;
(*os)->ind = 1;
(*os)->skip_start = 1;
(*os)->skip_end = 1; return APR_SUCCESS;
}
而后调用apr_getopt(opt, AP_SERVER_BASEARGS, &c, &optarg)进行命令行解析处理,代码如下
while ((rv = apr_getopt(opt, AP_SERVER_BASEARGS, &c, &optarg)) == APR_SUCCESS)
{
char **new;
switch (c) {
case 'c':
new = (char **)apr_array_push(ap_server_post_read_config);
*new = apr_pstrdup(pcommands, optarg);
break;
case 'C':
new = (char **)apr_array_push(ap_server_pre_read_config);
*new = apr_pstrdup(pcommands, optarg);
break;
case 'd':
def_server_root = optarg;
break;
case 'D':
new = (char **)apr_array_push(ap_server_config_defines);
*new = apr_pstrdup(pcommands, optarg);
/* Setting -D DUMP_VHOSTS is equivalent to setting -S */
if (strcmp(optarg, "DUMP_VHOSTS") == 0)
configtestonly = 1;
/* Setting -D DUMP_MODULES is equivalent to setting -M */
if (strcmp(optarg, "DUMP_MODULES") == 0)
configtestonly = 1;
break;
case 'e':
if (strcasecmp(optarg, "emerg") == 0) {
ap_default_loglevel = APLOG_EMERG;
}
else if (strcasecmp(optarg, "alert") == 0) {
ap_default_loglevel = APLOG_ALERT;
}
else if (strcasecmp(optarg, "crit") == 0) {
ap_default_loglevel = APLOG_CRIT;
}
else if (strncasecmp(optarg, "err", 3) == 0) {
ap_default_loglevel = APLOG_ERR;
}
else if (strncasecmp(optarg, "warn", 4) == 0) {
ap_default_loglevel = APLOG_WARNING;
}
else if (strcasecmp(optarg, "notice") == 0) {
ap_default_loglevel = APLOG_NOTICE;
}
else if (strcasecmp(optarg, "info") == 0) {
ap_default_loglevel = APLOG_INFO;
}
else if (strcasecmp(optarg, "debug") == 0) {
ap_default_loglevel = APLOG_DEBUG;
}
else {
usage(process);
}
break;
case 'E':
temp_error_log = apr_pstrdup(process->pool, optarg);
break;
case 'X':
new = (char **)apr_array_push(ap_server_config_defines);
*new = "DEBUG";
break;
case 'f':
confname = optarg;
break;
case 'v':
printf("Server version: %s\n", ap_get_server_description());
printf("Server built: %s\n", ap_get_server_built());
destroy_and_exit_process(process, 0);
case 'V':
show_compile_settings();
destroy_and_exit_process(process, 0);
case 'l':
ap_show_modules();
destroy_and_exit_process(process, 0);
case 'L':
ap_show_directives();
destroy_and_exit_process(process, 0);
case 't':
configtestonly = 1;
break;
case 'S':
configtestonly = 1;
new = (char **)apr_array_push(ap_server_config_defines);
*new = "DUMP_VHOSTS";
break;
case 'M':
configtestonly = 1;
new = (char **)apr_array_push(ap_server_config_defines);
*new = "DUMP_MODULES";
break;
case 'h':
case '?':
usage(process);
}
}
/* bad cmdline option? then we die */
if (rv != APR_EOF || opt->ind < opt->argc) {
usage(process);
}
apr_getopt函数实现在文件:srclib\apr\misc\unix\getopt.c,逻辑如下:
1、进行(os->reset || !*os->place)判断,作用未知
2、通过strchr(opts, os->opt)判断选项(os->opt)是否合法
3、若选项合法,则通过(*++oli != ':')判断该选项是否需要额外参数
4、若需要额外参数,则通过optch、optarg返回解析结果
APR_DECLARE(apr_status_t) apr_getopt(apr_getopt_t *os, const char *opts, char *optch, const char **optarg)
{
const char *oli; /* option letter list index */ if (os->reset || !*os->place) { /* update scanning pointer */
os->reset = 0;
if (os->ind >= os->argc || *(os->place = os->argv[os->ind]) != '-') {
os->place = EMSG;
*optch = os->opt;
return (APR_EOF);
}
if (os->place[1] && *++os->place == '-') { /* found "--" */
++os->ind;
os->place = EMSG;
*optch = os->opt;
return (APR_EOF);
}
} /* option letter okay? */
if ((os->opt = (int) *os->place++) == (int) ':' ||
!(oli = strchr(opts, os->opt))) {
/*
* if the user didn't specify '-' as an option,
* assume it means -1.
*/
if (os->opt == (int) '-') {
*optch = os->opt;
return (APR_EOF);
}
if (!*os->place)
++os->ind;
if (os->errfn && *opts != ':') {
(os->errfn)(os->errarg, "%s: illegal option -- %c\n",
apr_filepath_name_get(*os->argv), os->opt);
}
*optch = os->opt;
return (APR_BADCH);
}
if (*++oli != ':') { /* don't need argument */
*optarg = NULL;
if (!*os->place)
++os->ind;
}
else { /* need an argument */
if (*os->place) /* no white space */
*optarg = os->place;
else if (os->argc <= ++os->ind) { /* no arg */
os->place = EMSG;
if (*opts == ':') {
*optch = os->opt;
return (APR_BADARG);
}
if (os->errfn) {
(os->errfn)(os->errarg,
"%s: option requires an argument -- %c\n",
apr_filepath_name_get(*os->argv), os->opt);
}
*optch = os->opt;
return (APR_BADCH);
}
else /* white space */
*optarg = os->argv[os->ind];
os->place = EMSG;
++os->ind;
}
*optch = os->opt;
return APR_SUCCESS;
}
C语言命令行处理的更多相关文章
- 【嵌入式开发】C语言 命令行参数 函数指针 gdb调试
. 作者 : 万境绝尘 转载请注明出处 : http://blog.csdn.net/shulianghan/article/details/21551397 | http://www.hanshul ...
- C语言 命令行参数 函数指针 gdb调试
. 作者 : 万境绝尘 转载请注明出处 : http://blog.csdn.net/shulianghan/article/details/21551397 | http://www.hanshul ...
- Go语言命令行操作命令详细介绍
转自:http://www.jb51.net/article/56781.htm Go 命令 Go语言自带有一套完整的命令操作工具,你可以通过在命令行中执行go来查看它们: 图 Go命令显示详细的信息 ...
- c语言命令行参数
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { ..... } argc: 代表启动程序时,命令行参数的个数.C和C++语言规定,可执行程序程序本身的文件名,也算是一个命令行参 ...
- Go语言 命令行解析(一)
命令行启动服务的方式,在后端使用非常广泛,如果有写过C语言的同学相信不难理解这一点!在C语言中,我们可以根据argc和argv来获取和解析命令行的参数,从而通过不同的参数调取不同的方法,同时也可以用U ...
- C语言命令行解析函数:getopt/getopt_long
命令行工具下的参数选项有两种,长选项和短选项.短选项以-开头,后面跟单个字母:长选项以--开头,后面可跟多个字母. 一. getopt() 1.功能:解析命令行短选项参数 2.函数原型: #inclu ...
- 关于C语言命令行参数问题
1 int main(int argc,char** argv) 参数: argc:命令行参数的个数 argv:保存命令行参数:argv[0]保存本程序自己的名称 现在自己只知道这些以后再有学习继续补 ...
- R 语言命令行参数处理
在unix.windows外部需要调用R脚本执行,然后又需要输入不同的参数,类似shell脚本的命令行参数输入,可以使用Rcript命令实现. 命令格式:Rscript [options] [-e e ...
- R语言命令行参数
批量画图任务中,需要在R中传入若干参数,之前对做法是在perl中每一个任务建立一个Rscript,这种方式超级不cool,在群里学习到R的@ARGV调用方式,差不多能够达到批量任务的要求: a ...
随机推荐
- jenkins配置email
# 系统设置 # Jenkins Location # 邮件通知 # 高级 # Failed to send out e-mail 勾选“使用SSL协议” SMTP端口改为465 密码使用授权码,不能 ...
- JProfiler 8(一个很好的java性能监控工具) 下载和注册码
windows x64 zip下载地址:http://download-aws.ej-technologies.com/jprofiler/jprofiler_windows-x64_8_0_1.zi ...
- create index 与 alter table add index 区别
众所周知,MySQL创建索引有两种语法,即:ALTER TABLE HeadOfState ADD INDEX (LastName, FirstName);CREATE INDEX index_nam ...
- laravel中生成支付宝 二维码 扫码支付
文档教程模拟: http://www.023xs.cn/Article/37/laravel5%E9%9B%86%E6%88%90%E6%94%AF%E4%BB%98%E5%AE%9Dalipay%E ...
- A Newbie’s Install of Keras & Tensorflow on Windows 10 with R
This weekend, I decided it was time: I was going to update my Python environment and get Keras and T ...
- host is not allowed to connect to this mysql解决方案
报错:1130-host ... is not allowed to connect to this MySql server 解决方法: 1. 改表法. 可能是你的帐号不允许从远程登陆,只能在l ...
- poj 1930 Dead Fraction(循环小数化分数)
Dead Fraction Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 30000K Total Submissions: 3478 Accepted: 1162 Des ...
- ehcache配置:使用Spring+SpringMVC+Mybatis或者有shiro
SSM框架的搭建就不在叙述了 本文主要是讲解在SSM基础上再加上ehcache 1:首先:pom.xml需要的jar <dependency> <groupId>org.myb ...
- CentOS 6.7 编译PHP7 make时出现错误:undefined reference to `libiconv_close’
编辑Makefile文件,找到变量EXTRA_LIBS,并在末尾添上-liconv EXTRA_LIBS = -lcrypt -lz -lexslt -lcrypt -lrt -lmcrypt -ll ...
- python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
python manage.py runserver 这种命令行,可以在服务器端输入IP:8000直接访问 在 python manage.py runserver 127.0.01:8000 在服务 ...
