[LeetCode] 505. The Maze II 迷宫之二
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ball's start position, the destination and the maze, find the shortest distance for the ball to stop at the destination. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the destination (included). If the ball cannot stop at the destination, return -1.
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The start and destination coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
Example 1
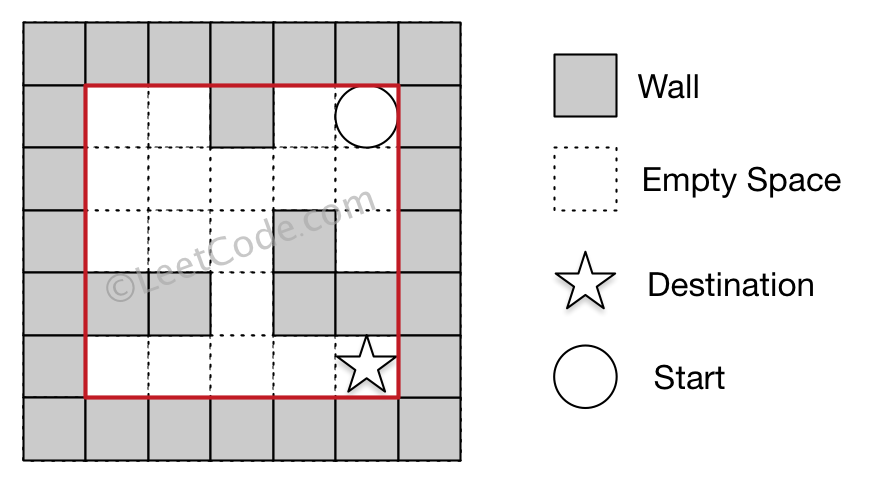
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (4, 4) Output: 12
Explanation: One shortest way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right.
The total distance is 1 + 1 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12.
Example 2
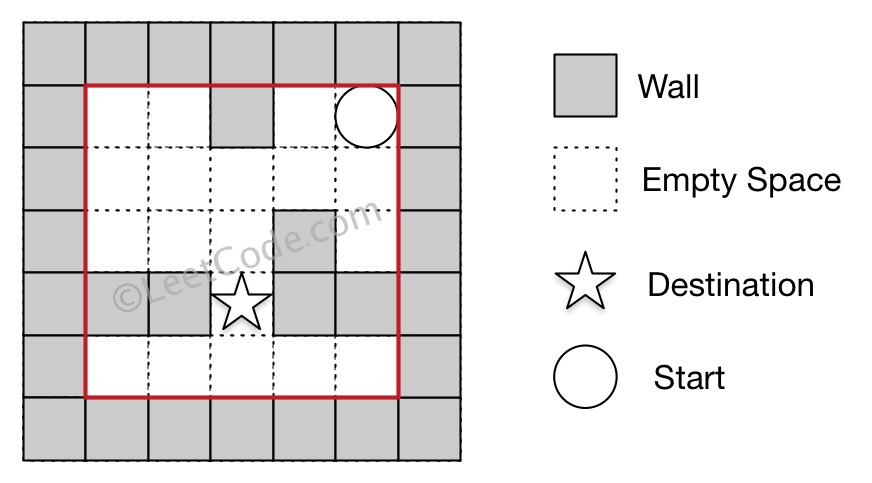
Input 1: a maze represented by a 2D array 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 Input 2: start coordinate (rowStart, colStart) = (0, 4)
Input 3: destination coordinate (rowDest, colDest) = (3, 2) Output: -1
Explanation: There is no way for the ball to stop at the destination.
Note:
- There is only one ball and one destination in the maze.
- Both the ball and the destination exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
- The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and both the width and height of the maze won't exceed 100.
这道题是之前那道 The Maze 的拓展,那道题只让我们判断能不能在终点位置停下,而这道题让求出到达终点的最少步数。其实本质都是一样的,难点还是在于对于一滚到底的实现方法,唯一不同的是,这里用一个二位数组 dists,其中 dists[i][j] 表示到达 (i,j) 这个位置时需要的最小步数,都初始化为整型最大值,在后在遍历的过程中不断用较小值来更新每个位置的步数值,最后来看终点位置的步数值,如果还是整型最大值的话,说明没法在终点处停下来,返回 -1,否则就返回步数值。注意在压入栈的时候,对x和y进行了判断,只有当其不是终点的时候才压入栈,这样是做了优化,因为如果小球已经滚到终点了,就不要让它再滚了,就不把终点位置压入栈,免得它还滚,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[].size();
vector<vector<int>> dists(m, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX));
vector<vector<int>> dirs{{,-},{-,},{,},{,}};
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({start[], start[]});
dists[start[]][start[]] = ;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
for (auto d : dirs) {
int x = t.first, y = t.second, dist = dists[t.first][t.second];
while (x >= && x < m && y >= && y < n && maze[x][y] == ) {
x += d[];
y += d[];
++dist;
}
x -= d[];
y -= d[];
--dist;
if (dists[x][y] > dist) {
dists[x][y] = dist;
if (x != destination[] || y != destination[]) q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
int res = dists[destination[]][destination[]];
return (res == INT_MAX) ? - : res;
}
};
上面这种解法的 DFS 形式之前是可以通过 OJ 的,但是现在被卡时间过不了了,代码可以参见评论区第二十三楼。我们还可以使用迪杰斯特拉算法 Dijkstra Algorithm 来做,LeetCode 中能使用到此类高级算法的时候并不多,Network Delay Time 就是一次。该算法是主要是在有向权重图中计算单源最短路径,即单个点到任意点到最短路径。因为这里起点只有一个,所以适用,然后迷宫中的每个格子都可以看作是图中的一个结点,权重可以都看成是1,那么就可以当作是有向权重图来处理。Dijkstra 算法的核心是松弛操作 Relaxtion,当有对边 (u, v) 是结点u到结点v,如果 dist(v) > dist(u) + w(u, v),那么 dist(v) 就可以被更新,这是所有这些的算法的核心操作。Dijkstra 算法是以起点为中心,向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。那么看到这里,你可能会有个疑问,到底 Dijkstra 算法和 BFS 算法究竟有啥区别。这是个好问题,二者在求最短路径的时候很相似,但却还是有些区别的。首先 Dijkstra 算法是求单源点的最短路径,图需要有权重,而且权重值不能为负,这道题中两点之间的距离可以看作权重,而且不会为负,满足要求。而 BFS 算法是从某点出发按广度优先原则依次访问连通的结点,图可以无权重。另外一点区别就是,BFS 算法是将未访问的邻居压入队列,然后再将未访问邻居的未访问过的邻居入队列再依次访问,而 Dijkstra 算法是在剩余的为访问过的结点中找出权重最小的并访问,这就是为什么要用一个优先队列(最小堆)来代替普通的 queue,这样就能尽量先更新离起点近的位置的 dp 值,优先队列里同时也存了该点到起点的距离,这个距离不一定是最短距离,可能还能松弛。但是如果其 dp 值已经小于优先队列中保存的距离,那么就不必更新其周围位置的距离了,因为优先队列中保存的这个距离值不是最短的,使用它来更新周围的 dp 值没有意义。这相当于利用了松弛操作来进行剪枝,大大提高了运算效率,之后就是类似于之前的 BFS 的操作了,遍历其周围的四个位置,尝试去更新其 dp 值。最后还是跟之前一样,如果遍历到了终点,就不要再排入队列了,因为已经得到需要的结果了,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
int shortestDistance(vector<vector<int>>& maze, vector<int>& start, vector<int>& destination) {
int m = maze.size(), n = maze[].size();
vector<vector<int>> dists(m, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX));
vector<vector<int>> dirs{{,-},{-,},{,},{,}};
auto cmp = [](vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) {
return a[] > b[];
};
priority_queue<vector<int>, vector<vector<int>>, decltype(cmp) > pq(cmp);
pq.push({start[], start[], });
dists[start[]][start[]] = ;
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto t = pq.top(); pq.pop();for (auto dir : dirs) {
int x = t[], y = t[], dist = dists[t[]][t[]];
while (x >= && x < m && y >= && y < n && maze[x][y] == ) {
x += dir[];
y += dir[];
++dist;
}
x -= dir[];
y -= dir[];
--dist;
if (dists[x][y] > dist) {
dists[x][y] = dist;
if (x != destination[] || y != destination[]) pq.push({x, y, dist});
}
}
}
int res = dists[destination[]][destination[]];
return (res == INT_MAX) ? - : res;
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/505
类似题目:
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/the-maze-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/the-maze-ii/discuss/98401/java-accepted-dfs
https://leetcode.com/problems/the-maze-ii/discuss/98456/simple-c-bfs-solution
LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)
[LeetCode] 505. The Maze II 迷宫之二的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] 505. The Maze II 迷宫 II
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolli ...
- [LeetCode] The Maze II 迷宫之二
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolli ...
- LeetCode 505. The Maze II
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/the-maze-ii/ 题目: There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces a ...
- [LeetCode] 499. The Maze III 迷宫 III
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolli ...
- 【LeetCode】505. The Maze II 解题报告(C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客:http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 BFS 日期 题目地址:https://leetcod ...
- 505. The Maze II
原题链接:https://leetcode.com/articles/the-maze-ii/ 我的思路 在做完了第一道迷宫问题 http://www.cnblogs.com/optor/p/8533 ...
- [LeetCode] 253. Meeting Rooms II 会议室之二
Given an array of meeting time intervals consisting of start and end times [[s1,e1],[s2,e2],...] (si ...
- [LeetCode] 213. House Robber II 打家劫舍之二
You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each house has a certain amount ...
- [LC] 505. The Maze II
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolli ...
随机推荐
- telnet: Unable to connect to remote host: No route to host
用iptables -F这个命令来关闭防火墙,但是使用这个命令前,千万记得用iptables -L查看一下你的系统中所有链的默认target,iptables -F这个命令只是清除所有规则,只不会真正 ...
- Linux 网络通信 API详解【转载】
TCP/IP分层模型 OSI协议参考模型,它是基于国际标准化组织(ISO)的建议发展起来的, 它分为7个层次:应用层.表示层.会话层.传输层.网络层.数据链路层及物理层. 这个7层的协议模型虽然规定得 ...
- mybatis的参数传递
mybatis的参数传递分为两种:1.单参数传递 2.多参数传递 单参数 mybatis会直接取出参数值给Mapper文件赋值 例子如下: 1.Mapper文件内容如下: public void d ...
- 七、Spring之深入理解AOP源码
Spring之深入理解AOP源码 在上一篇博文中,我们对AOP有了初步的了解,那么接下来我们就对AOP的实现原理进行深入的分析. 在之前写的那个AOP示例代码当中有这样一个注解:@Enable ...
- Oracle 11g 服务端的安装步骤
Ø 简介 本文主要介绍 Oracle 11g 服务端的安装步骤,在介绍之前说明以下几点: 1. 所安装的服务器是本机的虚拟机,操作系统为 Windows Server 2019: 2. 以下 ...
- ASP.NET web.config 配置里部分参数详细说明
Session配置 <!-- <identity impersonate = "false" [true|false] userName = "" ...
- Yapi接口管理平台 本地部署 windows环境 -
YApi 是高效.易用.功能强大的 api 管理平台,旨在为开发.产品.测试人员提供更优雅的接口管理服务.可以帮助开发者轻松创建.发布.维护 API,YApi 还为用户提供了优秀的交互体验,开发人员只 ...
- 初识Android App自动化测试框架--Unittest
1.为什么需要使用框架实现自动化测试 作为测试工程师,可能在代码能力上相比开发工程师要弱一点,所以我们在写脚本的时候就会相对容易的碰到更多的问题,如果有一个成熟的框架供给我们使用的话,可以帮助我们避免 ...
- Linux文件查找与打包
一.文件查找 locate与find是经常使用的Linux 命令,刚接触Linux时对这两个命令的使用傻傻的分不清.现在我们来对比一下两个命令到底有哪些区别. 1.1 locate locate让使用 ...
- i春秋暑期训练营丨渗透测试工程师开课啦
每个人的夏天 都有专属的解锁方式 或来一次难忘的旅行 或躺在家里吹着空调吃西瓜 又或者是和小伙伴参加暑期训练营 i春秋暑期渗透测试工程师 报名通道已全部开启 为了保证课程质量,采取小班教学,每班仅限3 ...
