安卓开发-Activity-多个Activity的开发方法。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38420342/article/details/84344496
一、切换Activity的5种方式
Intent intent = new Intent();
(1)intent.setClass(this,OtherActivity.class);
(2)intent.setClassName(this,"com.xiazdong.OtherActivity");
(3)intent.setClassName("com.xiazdong","com.xiazdong.OtherActivity");//此种方式用来激活不同应用的Activity,只需要指定第一个参数:包名 为另一个应用即可;
(4)
Component comp = new Component(this,OtherActivity.class);
intent.setComponent(comp);
(5)Intent intent = new Intent(this,OtherActivity.class);
————————————————
二、发送参数与接收参数方式
1、putExtra方式:
发送
intent.putExtra("name","xiazdong");
intent.putExtra("age",20);
接收
String name = intent.getStringExtra("name");
int age = intent.getIntExtra("age");
2、Bundle方式:
发送
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("name","xiazdong");
bundle.putInt("age",20);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
接收
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
String name = bundle.getString("name");
int age = bundle.getInt("age");
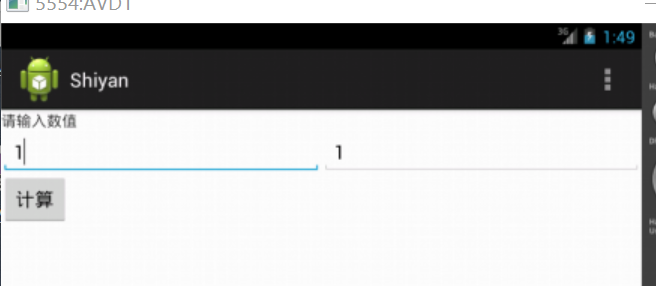
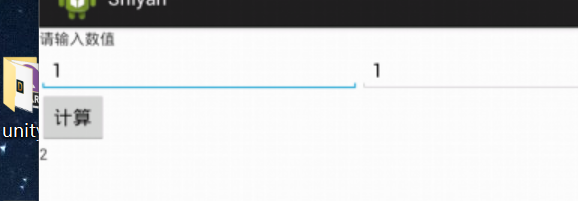
编写一个程序,可在第一个Activity中输入两个整数,单击“计算”按钮后,在第二个Activity负责求和计算,并将结果返回
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/tex"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="请输入数值" /> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" > <EditText
android:id="@+id/edt"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" /> <EditText
android:id="@+id/edt1"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout> <Button
android:id="@+id/but"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="计算" /> <TextView
android:id="@+id/tex1"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
/> </LinearLayout>
activity_mian.xml 程序
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView
android:id="@+id/e1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp"
/> <TextView
android:id="@+id/e2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/e3"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/b1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="回传" />
</LinearLayout>
activity_other.xml
package com.example.shiyan; import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView; public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private EditText edt;
private EditText edt1;
private TextView tex1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
edt=(EditText)this.findViewById(R.id.edt);
edt=(EditText)this.findViewById(R.id.edt1);
tex1=(TextView)this.findViewById(R.id.tex1);
Button but=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.but);
but.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
public void onClick(View v) {
String number = edt.getText().toString();
String number1 = edt.getText().toString();
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this,OtherActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("shu1",number);
intent.putExtra("shu2",number1);
MainActivity.this.startActivityForResult(intent,100);
}
}); } @Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if(requestCode==100&&resultCode==200){
String a=data.getStringExtra("sum");
tex1.setText(a); } } @Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
} }
MainActivity
package com.example.shiyan; import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView; public class OtherActivity extends Activity {
private TextView e1;
private TextView e2;
private TextView e3;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_other);
e1=(TextView)this.findViewById(R.id.e1);
e2=(TextView)this.findViewById(R.id.e2);
e3=(TextView)this.findViewById(R.id.e3);
Intent intent=getIntent();
String a=intent.getStringExtra("shu1");
String b=intent.getStringExtra("shu2");
int c=Integer.parseInt(a)+Integer.parseInt(b) ;
String str = String.valueOf(c);
e1.setText(a);
e2.setText(b);
e3.setText(str);
Button b1=(Button)this.findViewById(R.id.b1);
b1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent=getIntent();
String a=intent.getStringExtra("shu1");
String b=intent.getStringExtra("shu2");
int c=Integer.parseInt(a)+Integer.parseInt(b) ;
String str = String.valueOf(c);
intent.putExtra("sum",str);
setResult(200,intent);
OtherActivity.this.finish();
}
});
} @Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.other, menu);
return true;
} }
OtherActivity

安卓开发-Activity-多个Activity的开发方法。的更多相关文章
- 【Android Studio】安卓开发初体验2——Activity
Activity是什么 Activity用于提供可视化用户界面的组件,可以与用户进行交互来完成某项任务,一个应用程序中可以包含零个或多个活动 Activity的创建 首先将左侧的Active Tool ...
- 安卓开发笔记——重识Activity
Activity并不是什么新鲜的东西,老生常谈,这里只是随笔记录一些笔记. 每当说起Activity,感觉最关注的还是它的生命周期,因为要使我们的应用程序更加健壮,客户体验更加良好,如果对生命周期不熟 ...
- android开发中关于继承activity类中方法的调用
android开发中关于继承activity类中的函数,不能在其他类中调用其方法. MainActivity.java package com.example.testmain; import and ...
- Android开发之漫漫长途 Ⅱ——Activity的显示之Window和View(2)
该文章是一个系列文章,是本人在Android开发的漫漫长途上的一点感想和记录,我会尽量按照先易后难的顺序进行编写该系列.该系列引用了<Android开发艺术探索>以及<深入理解And ...
- Android开发之漫漫长途 Ⅱ——Activity的显示之Window和View(1)
该文章是一个系列文章,是本人在Android开发的漫漫长途上的一点感想和记录,我会尽量按照先易后难的顺序进行编写该系列.该系列引用了<Android开发艺术探索>以及<深入理解And ...
- Android开发学习之路--Activity之初体验
环境也搭建好了,android系统也基本了解了,那么接下来就可以开始学习android开发了,相信这么学下去肯定可以把android开发学习好的,再加上时而再温故下linux下的知识,看看androi ...
- Android开发——异步任务中Activity销毁时的问题
0. 前言 在Android开发中经常会发生Activity的销毁重建,比如用户长时间接听一个电话后回到APP.在Android开发--Fragment知识整理(二)中我们提到了使用Fragment ...
- Android开发之漫漫长途 Ⅲ——Activity的显示之Window和View(2)
该文章是一个系列文章,是本人在Android开发的漫漫长途上的一点感想和记录,我会尽量按照先易后难的顺序进行编写该系列.该系列引用了<Android开发艺术探索>以及<深入理解And ...
- Activity设置背景透明之开发坑
Activity设置背景透明的常规方法 方法一.在Manifest.xml中,直接在需要设置的Activity中添加主题样式: Android:theme="@android:style/T ...
- Android开发 旋转屏幕导致Activity重建解决方法(转)
文章来源:http://www.jb51.net/article/31833.htm Android开发文档上专门有一小节解释这个问题.简单来说,Activity是负责与用户交互的最主要机制,任何“ ...
随机推荐
- AD17无法复制原理图到Word的解决方法
标题: 解决AD17无法复制原理图到WORD 作者: 梦幻之心星 347369787@QQ.com 标签: [AD, Word, 原理图] 目录: 软件 日期: 2019-3-17 目录 前提说明: ...
- 「MoreThanJava」一文了解二进制和CPU工作原理
「MoreThanJava」 宣扬的是 「学习,不止 CODE」,本系列 Java 基础教程是自己在结合各方面的知识之后,对 Java 基础的一个总回顾,旨在 「帮助新朋友快速高质量的学习」. 当然 ...
- 搭建Prometheus平台,你必须考虑的6个因素
作者简介 Loris Degioanni,Sysdig的创始人和CTO,同时还是容器安全工具Falco的创建者. 原文链接 https://thenewstack.io/6-things-to-con ...
- 【asp.net core 系列】3 视图以及视图与控制器
0.前言 在之前的几篇中,我们大概介绍了如何创建一个asp.net core mvc项目以及http请求如何被路由转交给对应的执行单元.这一篇我们将介绍一下控制器与视图直接的关系. 1. 视图 这里的 ...
- [leetcode] 动态规划(Ⅰ)
这次按通过率从高到低刷题. 本文完成的题目:{338, 1025, 303, 121, 53, 392, 70, 746, 198} ,带有「面试」Tag 的题目:Interview - {1617, ...
- Java实现 LeetCode 678 有效的括号字符串(暴力+思路转换)
678. 有效的括号字符串 给定一个只包含三种字符的字符串:( ,) 和 *,写一个函数来检验这个字符串是否为有效字符串.有效字符串具有如下规则: 任何左括号 ( 必须有相应的右括号 ). 任何右括号 ...
- Java实现 LeetCode 676 实现一个魔法字典(暴力)
676. 实现一个魔法字典 实现一个带有buildDict, 以及 search方法的魔法字典. 对于buildDict方法,你将被给定一串不重复的单词来构建一个字典. 对于search方法,你将被给 ...
- Java实现 LeetCode 282 给表达式添加运算符
282. 给表达式添加运算符 给定一个仅包含数字 0-9 的字符串和一个目标值,在数字之间添加二元运算符(不是一元)+.- 或 * ,返回所有能够得到目标值的表达式. 示例 1: 输入: num = ...
- Java实现 LeetCode 213 打家劫舍 II(二)
213. 打家劫舍 II 你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋,每间房内都藏有一定的现金.这个地方所有的房屋都围成一圈,这意味着第一个房屋和最后一个房屋是紧挨着的.同时,相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗 ...
- Java实现 LeetCode 164 最大间距
164. 最大间距 给定一个无序的数组,找出数组在排序之后,相邻元素之间最大的差值. 如果数组元素个数小于 2,则返回 0. 示例 1: 输入: [3,6,9,1] 输出: 3 解释: 排序后的数组是 ...
