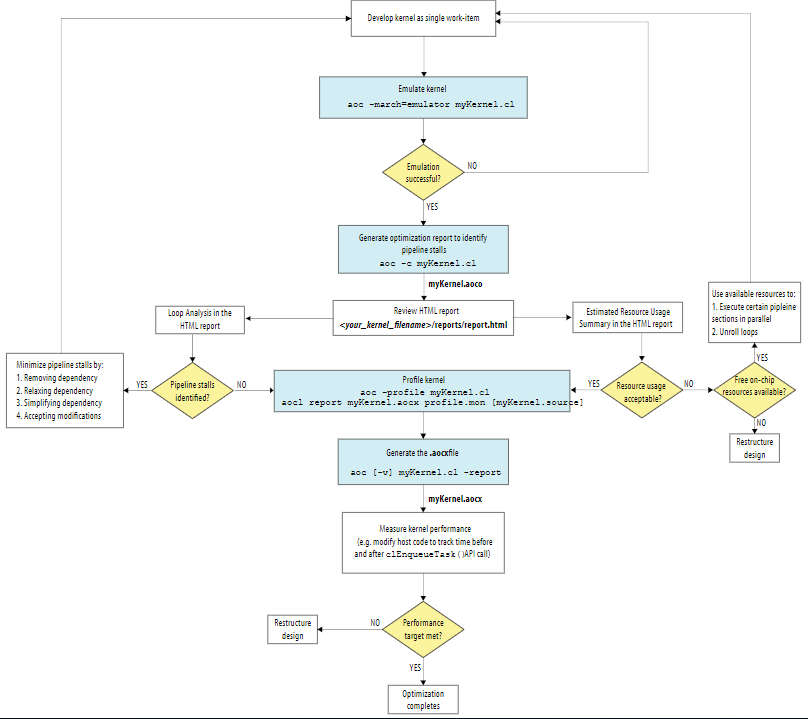
OpenCL 增强单work-item kernel性能策略
1、基于反馈的Optimization Report解决单个Work-item的Kernel相关性
在许多情况下,将OpenCL™应用程序设计为单个工作项内核就足以在不执行其他优化步骤的情况下最大化性能。
建议采用以下优化单个work-item kernel的选项来按照实用性顺序解决单个work-item kernel循环携带的依赖性:
removal,relaxation,simplification,transfer to local memory。
(1) Removing Loop-Carried Dependency
根据优化报告的反馈,可以通过实现更简单的内存访问的方式来消除循环携带的依赖关系。
优化前:
#define N 128 __kernel void unoptimized (__global int * restrict A,
__global int * restrict B,
__global int* restrict result)
{
int sum = ; for (unsigned i = ; i < N; i++) {
for (unsigned j = ; j < N; j++) {
sum += A[i*N+j];
}
sum += B[i];
} * result = sum;
}
优化后:
#define N 128 __kernel void optimized (__global int * restrict A,
__global int * restrict B,
__global int * restrict result)
{
int sum = ; for (unsigned i = ; i < N; i++) {
// Step 1: Definition
int sum2 = ; // Step 2: Accumulation of array A values for one outer loop iteration
for (unsigned j = ; j < N; j++) {
sum2 += A[i*N+j];
} // Step 3: Addition of array B value for an outer loop iteration
sum += sum2;
sum += B[i];
} * result = sum;
}
(2) Relaxing Loop-Carried Dependency
根据优化报告的反馈,可以通过增加依赖距离的方式来relax缓解循环携带的依赖关系。
优化前:
#define N 128 __kernel void unoptimized (__global float * restrict A,
__global float * restrict result)
{
float mul = 1.0f; for (unsigned i = ; i < N; i++)
mul *= A[i]; * result = mul;
}
优化后:
#define N 128
#define M 8 __kernel void optimized (__global float * restrict A,
__global float * restrict result)
{
float mul = 1.0f; // Step 1: Declare multiple copies of variable mul
float mul_copies[M]; // Step 2: Initialize all copies
for (unsigned i = ; i < M; i++)
mul_copies[i] = 1.0f; for (unsigned i = ; i < N; i++) {
// Step 3: Perform multiplication on the last copy
float cur = mul_copies[M-] * A[i]; // Step 4a: Shift copies
#pragma unroll
for (unsigned j = M-; j > ; j--)
mul_copies[j] = mul_copies[j-]; // Step 4b: Insert updated copy at the beginning
mul_copies[] = cur;
} // Step 5: Perform reduction on copies
#pragma unroll
for (unsigned i = ; i < M; i++)
mul *= mul_copies[i]; * result = mul;
}
(3) Transferring Loop-Carried Dependency to Local Memory
对于不能消除的循环携带的依赖关系,可以通过将具有循环依赖的数组从全局内存global memory移动到local memory的方式来改进循环的启动间隔(initiation interval, II)。
优化前:
#define N 128 __kernel void unoptimized( __global int* restrict A )
{
for (unsigned i = ; i < N; i++)
A[N-i] = A[i];
}
优化后:
#define N 128 __kernel void optimized( __global int* restrict A )
{
int B[N]; for (unsigned i = ; i < N; i++)
B[i] = A[i]; for (unsigned i = ; i < N; i++)
B[N-i] = B[i]; for (unsigned i = ; i < N; i++)
A[i] = B[i];
}
(4) Relaxing Loop-Carried Dependency by Inferring Shift Registers
为了使SDK能够有效地处理执行双精度浮点运算的单个work-item kernels,可以通过推断移位寄存器的方式移除循环携带的依赖性。
优化前:
__kernel void double_add_1 (__global double *arr,
int N,
__global double *result)
{
double temp_sum = ; for (int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
temp_sum += arr[i];
} *result = temp_sum;
}
优化后:
//Shift register size must be statically determinable
#define II_CYCLES 12 __kernel void double_add_2 (__global double *arr,
int N,
__global double *result)
{
//Create shift register with II_CYCLE+1 elements
double shift_reg[II_CYCLES+]; //Initialize all elements of the register to 0
for (int i = ; i < II_CYCLES + ; i++)
{
shift_reg[i] = ;
} //Iterate through every element of input array
for(int i = ; i < N; ++i)
{
//Load ith element into end of shift register
//if N > II_CYCLE, add to shift_reg[0] to preserve values
shift_reg[II_CYCLES] = shift_reg[] + arr[i]; #pragma unroll
//Shift every element of shift register
for(int j = ; j < II_CYCLES; ++j)
{
shift_reg[j] = shift_reg[j + ];
}
} //Sum every element of shift register
double temp_sum = ; #pragma unroll
for(int i = ; i < II_CYCLES; ++i)
{
temp_sum += shift_reg[i];
} *result = temp_sum;
}
(5) Removing Loop-Carried Dependencies Cause by Accesses to Memory Arrays
在单个work-item的kernel中包含ivdep pragma以保证堆内存array的访问不会导致循环携带的依赖性。
如果对循环中的内存阵列的所有访问都不会导致循环携带的依赖性,在内核代码中的循环之前添加#pragma ivdep。
// no loop-carried dependencies for A and B array accesses
#pragma ivdep
for (int i = ; i < N; i++) {
A[i] = A[i - X[i]];
B[i] = B[i - Y[i]];
}
要指定对循环内特定内存数组的访问不会导致循环携带的依赖关系,在内核代码中的循环之前添加#pragma ivdep arrayarray_name)。
ivdep pragma指定的数组必须是local / private内存数组,或者是指向global/local/private内存存储的指针变量。 如果指定的数组是指针,则ivdep pragma也适用于所有可能带有指定指针别名的数组。
ivdep pragma指示指定的数组也可以是struct的数组或指针成员。
// No loop-carried dependencies for A array accesses
// The offline compiler will insert hardware that reinforces dependency constraints for B
#pragma ivdep array(A)
for (int i = ; i < N; i++) {
A[i] = A[i - X[i]];
B[i] = B[i - Y[i]];
} // No loop-carried dependencies for array A inside struct
#pragma ivdep array(S.A)
for (int i = ; i < N; i++) {
S.A[i] = S.A[i - X[i]];
} // No loop-carried dependencies for array A inside the struct pointed by S
#pragma ivdep array(S->X[2][3].A)
for (int i = ; i < N; i++) {
S->X[][].A[i] = S.A[i - X[i]];
} // No loop-carried dependencies for A and B because ptr aliases
// with both arrays
int *ptr = select ? A : B;
#pragma ivdep array(ptr)
for (int i = ; i < N; i++) {
A[i] = A[i - X[i]];
B[i] = B[i - Y[i]];
} // No loop-carried dependencies for A because ptr only aliases with A
int *ptr = &A[];
#pragma ivdep array(ptr)
for (int i = ; i < N; i++) {
A[i] = A[i - X[i]];
B[i] = B[i - Y[i]];
}
2、Single work-item kernel的设计技巧
避免指针混淆。使用restrict关键词。
创建格式正确的循环。退出条件与整数进行比较,且每次迭代的增量为1。格式正确的嵌套循环也对最大化kernel性能有帮助。
最小化loop-carried循环携带依赖遵循以下原则:
避免使用指针算数;
声明简单的数组索引;
尽可能在kernel中使用恒定边界的循环。
避免复杂的循环退出条件;
将嵌套循环转换为单循环;
避免条件循环; 避免if else中包含循环,尽量转换为在循环中包含if else。
在尽可能深的范围内声明变量。
OpenCL 增强单work-item kernel性能策略的更多相关文章
- NGUI ScrollView 循环 Item 实现性能优化
今天来说说一直都让我在项目中头疼的其中一个问题,NGUI 的scrollView 列表性能问题,实现循环使用item减少性能上的开销. 希望能够给其他同学们使用和提供一个我个人的思路,这个写的不是太完 ...
- GIS性能策略
当一个地理平台上线运行,我们经常会遇到这些问题:1.系统刚上线时速度较快,一段时间后访问较慢?2.在地理平台目前的配置下,发布多少个服务才合理?一个服务配置多少个实例数才合适?这些问题,都涉及整个地理 ...
- 推广TrustAI可信分析:通过提升数据质量来增强在ERNIE模型下性能
项目链接:https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/projectdetail/4622139?contributionType=1 fork一下,由于内容过多这里就不全 ...
- CUDA ---- Kernel性能调节
Exposing Parallelism 这部分主要介绍并行分析,涉及掌握nvprof的几个metric参数,具体的这些调节为什么会影响性能会在后续博文解释. 代码准备 下面是我们的kernel函数s ...
- oop的三种设计模式(单例、工厂、策略)
参考网站 单例模式: 废话不多说,我们直接上代码: <?php /** 三私一公 *私有的静态属性:保存类的单例 *私有的__construct():阻止在类的外部实例化 *私有的__clone ...
- virtualbox linux客户机中安装增强功能包缺少kernel头文件问题解决
linux客户机中安装增强功能包总会提示缺少kernel头文件 根据发行版的不同,用命令行软件包管理命令安装dkms build-essential linux-headers-$(uname -r) ...
- Hibernate学习笔记(三)Hibernate生成表单ID主键生成策略
一. Xml方式 <id>标签必须配置在<class>标签内第一个位置.由一个字段构成主键,如果是复杂主键<composite-id>标签 被映射的类必须定义对应数 ...
- OpenCL Kernel设计优化
使用Intel® FPGA SDK for OpenCL™ 离线编译器,不需要调整kernel代码便可以将其最佳的适应于固定的硬件设备,而是离线编译器会根据kernel的要求自适应调整硬件的结构. 通 ...
- OpenCL 第10课:kernel,work_item和workgroup
转载自:http://www.cmnsoft.com/wordpress/?p=1429 前几节我们一起学习了几个用OPENCL完成任务的简单例子,从这节起我们将更详细的对OPENCL进行一些“理论” ...
随机推荐
- Oracle 对表的基本CURD操作
Oracle对表的基本Curd操作: 样式表: 接下来对这张(表明:Stud)表进行Curd操作(请看面SQL代码) 增加新的字段列:alter table Stud add(heigh ...
- shell专题(十一):企业真实面试题(重点)
11.1 京东 问题1:使用Linux命令查询file1中空行所在的行号 答案: [atguigu@hadoop102 datas]$ awk '/^$/{print NR}' sed.txt 问题2 ...
- Django框架03 /视图相关
Django框架03 /视图相关 目录 Django框架03 /视图相关 1. 请求相关 2.响应相关 3.FBV和CBV 视图(视图函数和视图类) 3.1 类视图 CBV 3.2 视图函数 FBV ...
- Python 实现邮件发送功能(初级)
在我们日常项目中,会经常使用到邮件的发送功能,如何利用Python发送邮件也是一项必备的技能.本文主要讲述利用Python来发送邮件的一些基本操作. 本章主要包含知识点: 邮件发送原理简述即常用smt ...
- .NET Core ResponseCache【缓存篇(一)】
一.前言 源码 1.最近一直在看项目性能优化方式,俗话说的好项目优化第一步那当然是添加缓存,我们的项目之所以卡的和鬼一样,要么就是你的代码循环查询数据库(这个之前在我们的项目中经常出现,现在慢慢在 ...
- echarts 踩坑 : id必须不同
我们可能用react前端框架开发项目. 也就是组件化开发. 一个页面里可能有很多组件. 而echarts是寻找特定ID的DOM去渲染的. 也就是说,如果整个页面.包括所有页面组件,有id相同的DOM, ...
- less : 解决升级后报错的问题
vue2项目. 上版本. { "name": "xxx", "version": "1.0.0", "desc ...
- 关于 iframe 的小问题若干
我们知道,iframe在传统的MVC项目里是个很常用的东西. 但这玩意用起来有时会有点烦人. 比如说:我有个一个页面套了一个iframe,iframe里面的页面通过a标签来切换.怎么做? <li ...
- 47 张图带你 MySQL 进阶!!!
我们在 MySQL 入门篇主要介绍了基本的 SQL 命令.数据类型和函数,在局部以上知识后,你就可以进行 MySQL 的开发工作了,但是如果要成为一个合格的开发人员,你还要具备一些更高级的技能,下面我 ...
- 一张PDF了解JDK11 GC调优秘籍-附PDF下载
目录 简介 废弃的VM选项 Source-File Mode Code Heap状态分析 AppCDS 总结 简介 JDK11相比JDK10,添加了一个新的Source-File Mode,可以直接通 ...
