Hdu 5444 Elven Postman dfs
Elven Postman
Time Limit: 1 Sec
Memory Limit: 256 MB
题目连接
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444
Description
Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long time and their magical prowess are not something to be taken lightly. Also, they live on trees. However, there is something about them you may not know. Although delivering stuffs through magical teleportation is extremely convenient (much like emails). They still sometimes prefer other more “traditional” methods.
So, as a elven postman, it is crucial to understand how to deliver the mail to the correct room of the tree. The elven tree always branches into no more than two paths upon intersection, either in the east direction or the west. It coincidentally looks awfully like a binary tree we human computer scientist know. Not only that, when numbering the rooms, they always number the room number from the east-most position to the west. For rooms in the east are usually more preferable and more expensive due to they having the privilege to see the sunrise, which matters a lot in elven culture.
Anyways, the elves usually wrote down all the rooms in a sequence at the root of the tree so that the postman may know how to deliver the mail. The sequence is written as follows, it will go straight to visit the east-most room and write down every room it encountered along the way. After the first room is reached, it will then go to the next unvisited east-most room, writing down every unvisited room on the way as well until all rooms are visited.
Your task is to determine how to reach a certain room given the sequence written on the root.
For instance, the sequence 2, 1, 4, 3 would be written on the root of the following tree.
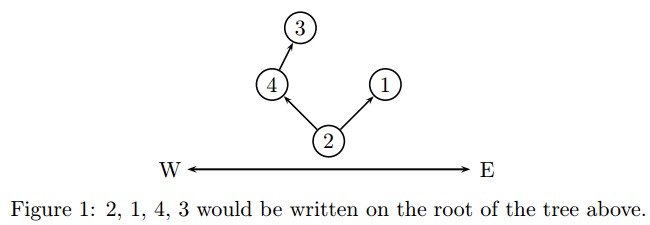
Input
First you are given an integer T(T≤10) indicating the number of test cases.
For each test case, there is a number n(n≤1000) on a line representing the number of rooms in this tree. n integers representing the sequence written at the root follow, respectively a1,...,an where a1,...,an∈{1,...,n}.
On the next line, there is a number q representing the number of mails to be sent. After that, there will be q integers x1,...,xq indicating the destination room number of each mail.
Output
For each query, output a sequence of move (E or W) the postman needs to make to deliver the mail. For that E means that the postman should move up the eastern branch and W the western one. If the destination is on the root, just output a blank line would suffice.
Note that for simplicity, we assume the postman always starts from the root regardless of the room he had just visited.
Sample Input
2
4
2 1 4 3
3
1 2 3
6
6 5 4 3 2 1
1
1
Sample Output
E
WE
EEEEE
HINT
题意
建树;编号是这棵树从右往左进行编号的,越往右边的编号越小
给你一个数组,然后问你走到一些点,究竟该怎么走
题解:
注意,树的形态是唯一的
我们可以处理每个节点能够放的点的大小的范围,然后就可以求出这棵树的样子了
回答就可以顺便再DFS建树的过程中处理出来
赛后听人说,这是先序遍历/中序遍历?
非计算机专业完全不懂= =
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <ctime>
#include <list>
#include <bitset>
typedef unsigned char byte;
#define pb push_back
#define input_fast std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);std::cin.tie(0)
#define local freopen("in.txt","r",stdin)
#define pi acos(-1) using namespace std;
struct node
{
int L , R ;
string str;
}; const int maxn = 1e3 + ;
int n , p[maxn] , q , ctt = ;
vector<int>qq;
node c[maxn]; bool dfs(int u)
{
/* cout << "u is " << u << endl;
cout << "ctt is " << ctt << endl;
getch();*/
if(ctt == n + ) return true;
while()
{
if(c[u].L <= p[ctt] && p[ctt] <= c[u].R)
{
int x = p[ctt];
int y = u;
if(x < y)
{
c[x].str = c[u].str + 'E';
c[x].R = y;
c[x].L = c[u].L;
}
else
{
c[x].str = c[u].str + 'W';
c[x].L = y;
c[x].R = c[u].R;
}
ctt++;
if(ctt == n + ) return true;
if(dfs(x)) return true;
}
else
return false;
if(ctt == n + ) return true;
}
} void initiation()
{
qq.clear();
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = ; i <= n ; ++ i) scanf("%d",p + i);
scanf("%d",&q);
for(int i = ; i <= q; ++ i)
{
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
qq.push_back(x);
}
for(int i = ; i <= n ; ++ i)
{
c[i].str = "";
c[i].L = - , c[i].R = ;
}
ctt = ;
dfs(p[]);
} void solve()
{
for(int i = ; i < q ;++ i) cout << c[qq[i]].str << endl;
} int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
int Case;
scanf("%d",&Case);
while(Case--)
{
initiation();
solve();
}
return ;
}
Hdu 5444 Elven Postman dfs的更多相关文章
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman
题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444 Elven Postman Description Elves are very peculia ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(长春网路赛——平衡二叉树遍历)
题目链接:pid=5444http://">http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444 Elven Postman Time Limi ...
- 2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online HDU 5444 Elven Postman【二叉排序树的建树和遍历查找】
Elven Postman Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)T ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman 二叉树
Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others) Problem Descrip ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(二叉树)——2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online
Problem Description Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long ...
- HDU 5444 Elven Postman (2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online)
Elven Postman Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long time ...
- HDU 5444 Elven Postman 二叉排序树
HDU 5444 题意:给你一棵树的先序遍历,中序遍历默认是1...n,然后q个查询,问根节点到该点的路径(题意挺难懂,还是我太傻逼) 思路:这他妈又是个大水题,可是我还是太傻逼.1000个点的树,居 ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(根据先序遍历和中序遍历求后序遍历)2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online
很坑的一道题,读了半天才读懂题,手忙脚乱的写完(套上模板+修改模板),然后RE到死…… 题意: 题面上告诉了我们这是一棵二叉树,然后告诉了我们它的先序遍历,然后,没了……没了! 反复读题,终于在偶然间 ...
- HDU 5444 Elven Postman (二叉树,暴力搜索)
题意:给出一颗二叉树的先序遍历,默认的中序遍历是1..2.……n.给出q个询问,询问从根节点出发到某个点的路径. 析:本来以为是要建树的,一想,原来不用,其实它给的数是按顺序给的,只要搜结点就行,从根 ...
随机推荐
- poj1286Necklace of Beads(ploya定理)
链接 这个东东是新知识 let's 从头学起吧 这篇文库讲的不错 至少把各种概念学了一遍 然后再看此题 共有两种类型的置换 一种是旋转之后相同算一种 一种是翻转之后相同算一种 对于旋转 共有N次置换 ...
- freemarker 如何获得list的索引值
<#list toplist as toplists> ${toplists_index} </#list> 相当方便
- 宏FSP_SEG_INODES_PER_PAGE
#define FSP_SEG_INODES_PER_PAGE(zip_size) \ (((zip_size ? zip_size : UNIV_PAGE_SIZE) \ - FSEG_ARR_OF ...
- poj3281
非常非常经典的构图 有二分图学习基础的话,很容易想到这是一个“三分图”的匹配问题 我们将牛,food,drink作为点 为了方便,我们将牛放在中间,每头牛的出边指向drink种类,入边由food指入 ...
- 高性能PHP支持静态类型
PHP+QB是一个可选的PHP虚拟机,它声称在性能上提供了数量级的提升.而负面影响就是它需要所有的内容都必须是静态类型,同时也对数组做了一些限制. 静态 类型声明 是通过PHPDoc语法的一个扩展添加 ...
- [swustoj 1091] 土豪我们做朋友吧
土豪我们做朋友吧(1091) 问题描述: 人都有缺钱的时候,缺钱的时候要是有个朋友肯帮助你,那将是一件非常幸福的事情.有N个人(编号为1到N),一开始他们互相都不认识,后来发生了M件事情,事情分为2个 ...
- 【转】android 最新 NDK r8 在window下开发环境搭建 安装配置与使用 详细图文讲解,完整实际配置过程记录(原创)
原文网址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zdz8207/archive/2012/11/27/android-ndk-install.html android 最新 NDK r8 在w ...
- jquery滚动条
查看demo: 下载Demo
- HDU 1736 美观化文字
美观化文字 Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
- e2e 自动化集成测试 架构 实例 WebStorm Node.js Mocha WebDriverIO Selenium Step by step (四) Q 反回调
上一篇文章“e2e 自动化集成测试 架构 京东 商品搜索 实例 WebStorm Node.js Mocha WebDriverIO Selenium Step by step (三) SqlServ ...
