PAT 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree
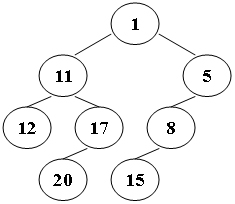
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in "zigzagging order" -- that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
8
12 11 20 17 1 15 8 5
12 20 17 11 15 8 5 1
Sample Output:
1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15
#include<iostream>//根据中,后序建树,再层级遍历
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int n;
vector<int> post(30, 0), in(30, 0);
struct node{
int val;
node* left=NULL;
node* right=NULL;
node(int v):val(v), left(NULL), right(NULL){
}
};
node* buildtree(node* root, int inl, int inr, int postl, int postr){
if(inl>inr) return NULL;
root=new node(post[postr]);
int i=inl;
while(i<=inr&&in[i]!=post[postr]) i++;
int cnt=i-inl;
root->left=buildtree(root->left, inl, i-1, postl, postl+cnt-1);
root->right=buildtree(root->right, i+1, inr, postl+cnt, postr-1);
return root;
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>in[i];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>post[i];
node* root=NULL;
root=buildtree(root, 0, n-1, 0, n-1);
queue<node*> q;
int flag=0, k=0, level=0;
q.push(root);
cout<<root->val;
while(!q.empty()){
vector<node*> v;
while(!q.empty()){
node *t=q.front();
q.pop();
if(t->left) v.push_back(t->left);
if(t->right) v.push_back(t->right);
}
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
q.push(v[i]);
if(level % 2 == 0)
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
printf(" %d", v[i]->val);
else
for(int i = v.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
printf(" %d", v[i]->val);
level ++;
}
return 0;
}
PAT 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree的更多相关文章
- PAT 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree[难]
1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分) Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive in ...
- PAT甲级1127. ZigZagging on a Tree
PAT甲级1127. ZigZagging on a Tree 题意: 假设二叉树中的所有键都是不同的正整数.一个唯一的二叉树可以通过给定的一对后序和顺序遍历序列来确定.这是一个简单的标准程序,可以按 ...
- PAT甲级 1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)
1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- pat 甲级 1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)
1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)
1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分) Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive in ...
- PAT 甲级 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree
https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805349394006016 Suppose that all the k ...
- PAT Advanced 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30) [中序后序建树,层序遍历]
题目 Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree c ...
- PAT甲题题解-1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)-中序、后序建树
根据中序遍历和前序遍历确定一棵二叉树,然后按“层次遍历”序列输出.输出规则:除根节点外,接下来每层的节点输出顺序是:先从左到右,再从右到左,交替输出 #include <iostream> ...
- PAT A1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)——二叉树,建树,层序遍历
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can ...
随机推荐
- .NET Runtime version 2.0.50727.8762 - 执行引擎错误(7969097A) (80131506)
VS2010调试IIS发布的web工程提示:无法连接到 Visual Studio 开发服务器 .NET Runtime version 2.0.50727.8762 - 执行引擎错误(7969097 ...
- E20170603-ts
sanitize vt. 净化; 进行消毒; 使清洁; 审查; omission n. 遗漏; 疏忽; 省略,删节; [法] 不履行法律责任; separator n. 分离器,分离装置; 防胀 ...
- XML消息解析_php
初识php——微信消息处理 <?php $test = new weixin(); $test->Message(); class weixin{ public function Mess ...
- bzoj 4756: [Usaco2017 Jan]Promotion Counting【dfs+树状数组】
思路还是挺好玩的 首先简单粗暴的想法是dfs然后用离散化权值树状数组维护,但是这样有个问题就是这个全局的权值树状数组里并不一定都是当前点子树里的 第一反应是改树状数组,但是显然不太现实,但是可以这样想 ...
- 题解报告:poj 3669 Meteor Shower(bfs)
Description Bessie hears that an extraordinary meteor shower is coming; reports say that these meteo ...
- SQL数据库,增加查询修改以及防sql写入攻击
SQL添加信息 SQL查询信息 SQL修改信息 SQL语句写入攻击: 普通语句添加信息 sql写入语句攻击: 解决方法:分开传送语句与参数关键:@
- 6.12mysql自己的数据库的作用
- 常见Z纯CSS小样式合集(三角形)
三角形 .sanjiao{ width:0px; height: 0px; overflow: hidden; border-width: 100px; border-color: transpare ...
- 01按照官方步骤编译NanoPiM1Plus的Android
01按照官方步骤编译NanoPiM1Plus的Android 大文实验室/大文哥 壹捌陆捌零陆捌捌陆捌贰 21504965 AT qq.com 完成时间:2017/12/6 10:58 版本:V1.0 ...
- MySql备份表数据
一:根据user表创建user_backup表 drop table if exists user_backup; create table user_backup like user; // lik ...
