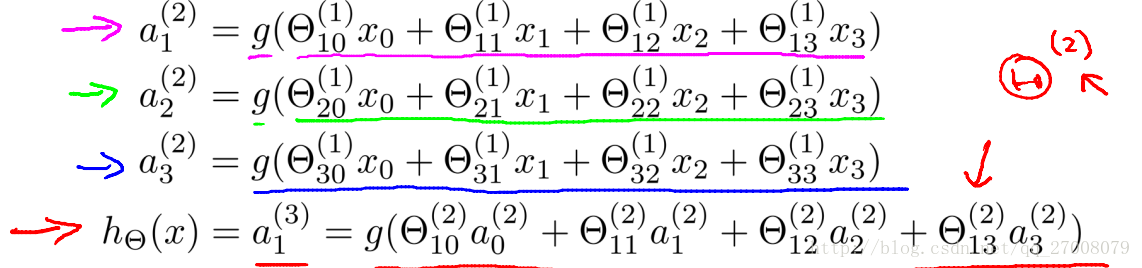Stanford coursera Andrew Ng 机器学习课程第四周总结(附Exercise 3)
Introduction
Neural NetWork的由来
先考虑一个非线性分类,当特征数很少时,逻辑回归就可以完成了,但是当特征数变大时,高阶项将呈指数性增长,复杂度可想而知。如下图:对房屋进行高低档的分类,当特征值只有x1,x2,x3时,我们可以对它进行处理,分类。但是当特征数增长为x1,x2....x100时,分类器的效率就会很低了。
Neural NetWork模型
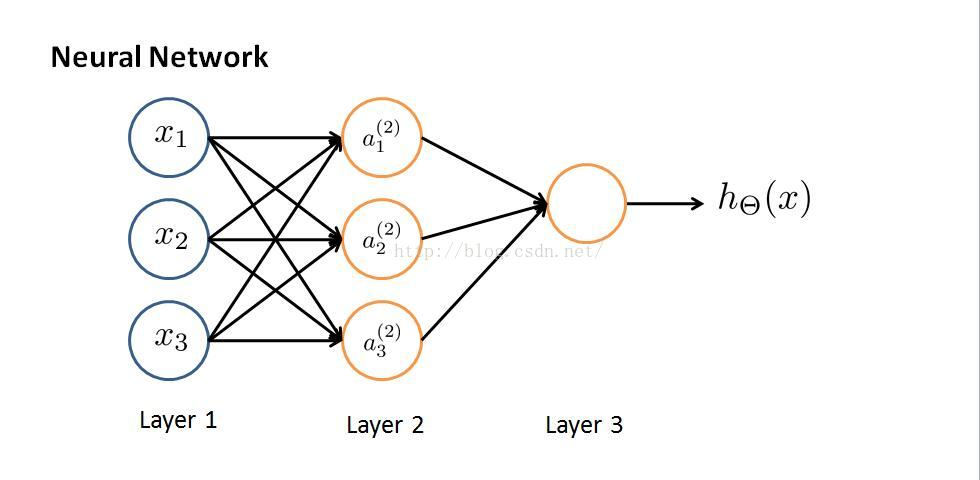
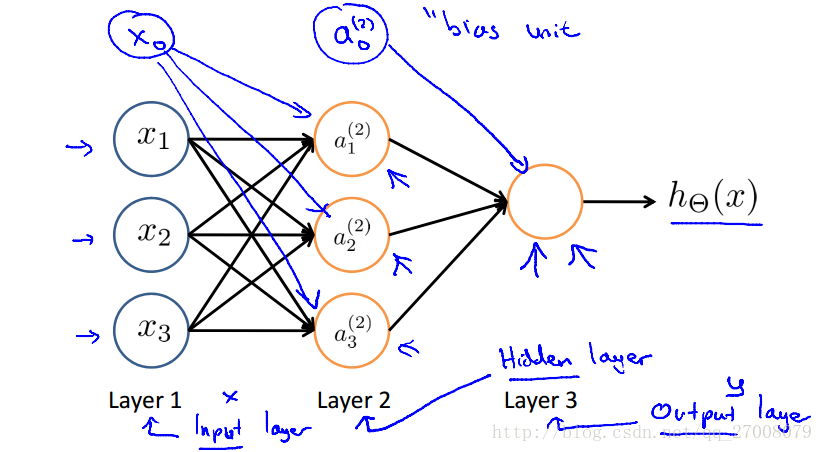
该图是最简单的神经网络,共有3层,输入层Layer1;隐藏层Layer2;输出层Layer3,每层都有多个激励函数ai(j).通过层与层之间的传递参数Θ得到最终的假设函数hΘ(x)。我们的目的是通过大量的输入样本x(作为第一层),训练层与层之间的传递参数(经常称为权重),使得假设函数尽可能的与实际输出值接近h(x)≈y(代价函数J尽可能的小)。
逻辑回归模型
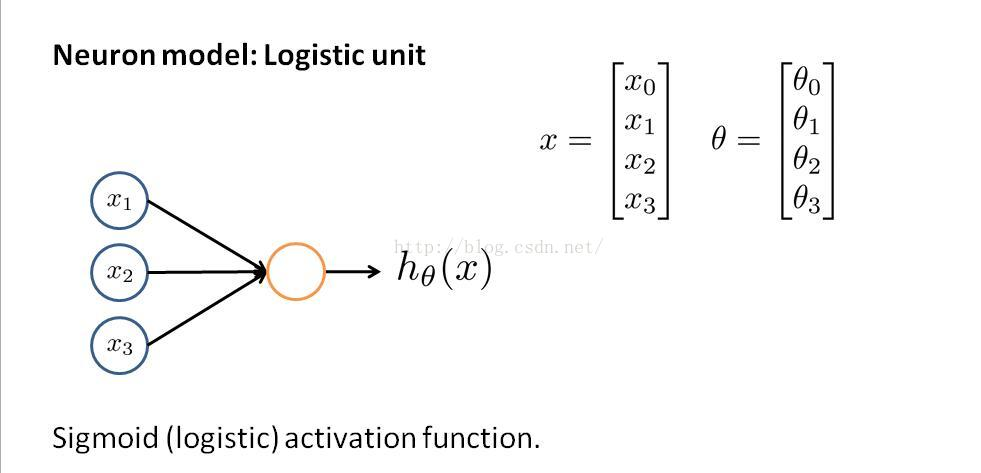
很容易看出,逻辑回归是没有隐藏层的神经网络,层与层之间的传递函数就是θ。
Neural NetWork
神经网络模型---正向传播
Cost function(代价函数)
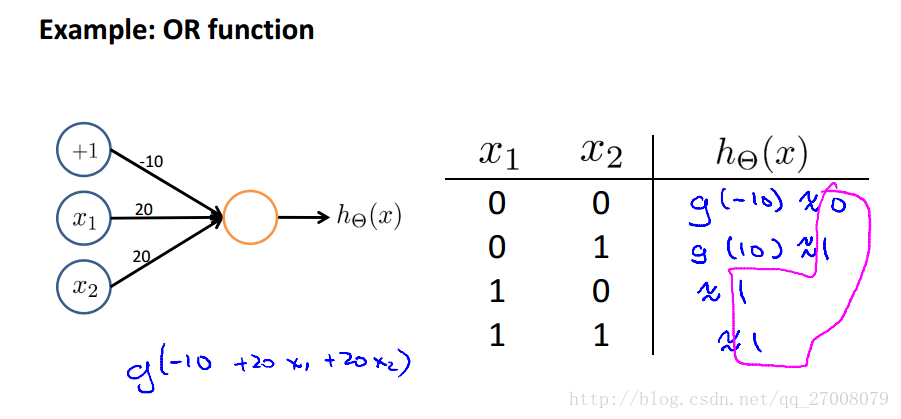
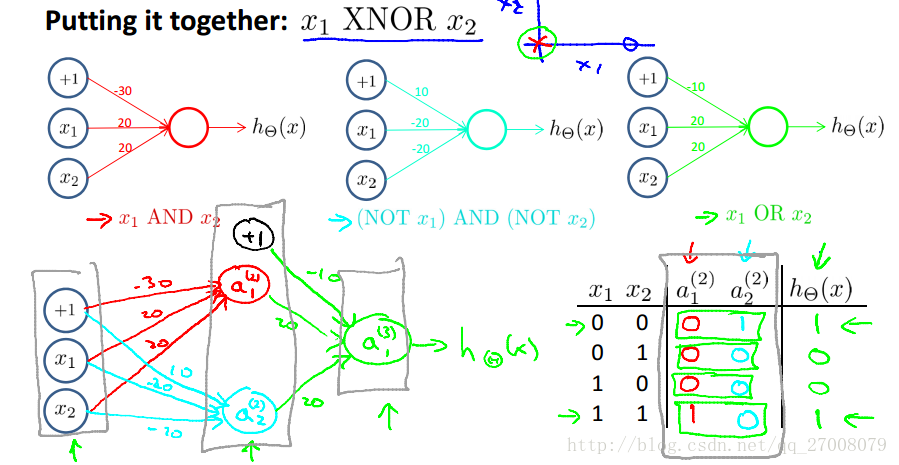
Examples and intuitions
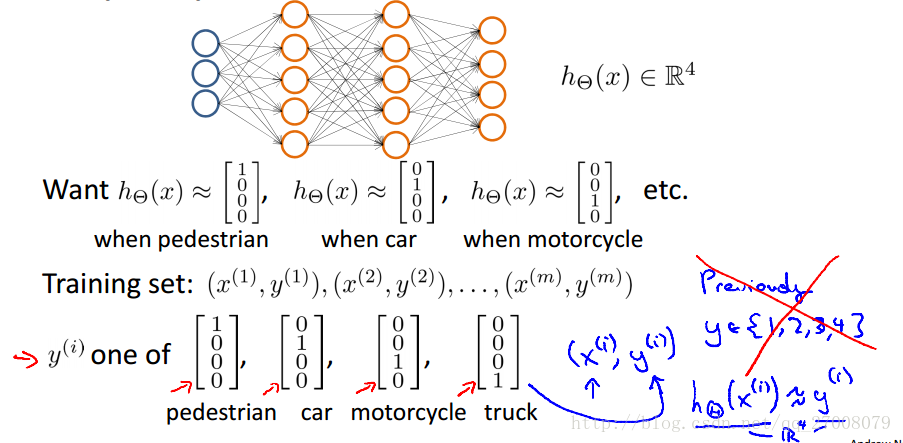
Multi-class classification
对于多分类问题,我们可以通过设置多个输出值来实现。
编程作业就是一个多分类问题——手写数字识别
输入的是手写的照片(数字0-9),5000组样本、每个像素点用20×20的点阵表示成一行,输入向量为5000×400的矩阵X,经过神经网络传递后,输出一个假设函数(列向量),取最大值所在的行号即为假设值(0-9中的一个)。也就是输出值y = 1,2,3,4,5.....10又有可能,为了方便数值运算,我们用10×1的列向量表示,譬如 y = 5,有
Exercises
这次的作业是用逻辑回归和神经网络来实现手写数字识别,比较下两者的准确性。
Logistic Regression
lrCostFunction.m
function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda)
%LRCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with
%regularization
% J = LRCOSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Hint: The computation of the cost function and gradients can be
% efficiently vectorized. For example, consider the computation
%
% sigmoid(X * theta)
%
% Each row of the resulting matrix will contain the value of the
% prediction for that example. You can make use of this to vectorize
% the cost function and gradient computations.
%
% Hint: When computing the gradient of the regularized cost function,
% there're many possible vectorized solutions, but one solution
% looks like:
% grad = (unregularized gradient for logistic regression)
% temp = theta;
% temp(1) = 0; % because we don't add anything for j = 0
% grad = grad + YOUR_CODE_HERE (using the temp variable)
%
theta_reg=[0;theta(2:size(theta))]; J = (-y'*log(sigmoid(X*theta))-(1-y)'*log(1-sigmoid(X*theta)))/m + lambda/(2*m)*(theta_reg')*theta_reg; grad = X'*(sigmoid(X*theta)-y)/m + lambda/m*theta_reg; % ============================================================= grad = grad(:); end
oneVsAll.m
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda)
%ONEVSALL trains multiple logistic regression classifiers and returns all
%the classifiers in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta
%corresponds to the classifier for label i
% [all_theta] = ONEVSALL(X, y, num_labels, lambda) trains num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers and returns each of these classifiers
% in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta corresponds
% to the classifier for label i % Some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
n = size(X, 2); % You need to return the following variables correctly
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1); % Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X]; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should complete the following code to train num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers with regularization
% parameter lambda.
%
% Hint: theta(:) will return a column vector.
%
% Hint: You can use y == c to obtain a vector of 1's and 0's that tell you
% whether the ground truth is true/false for this class.
%
% Note: For this assignment, we recommend using fmincg to optimize the cost
% function. It is okay to use a for-loop (for c = 1:num_labels) to
% loop over the different classes.
%
% fmincg works similarly to fminunc, but is more efficient when we
% are dealing with large number of parameters.
%
% Example Code for fmincg:
%
% % Set Initial theta
% initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
%
% % Set options for fminunc
% options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
%
% % Run fmincg to obtain the optimal theta
% % This function will return theta and the cost
% [theta] = ...
% fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), ...
% initial_theta, options);
% initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1); options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50); for c = 1:num_labels
all_theta(c,:) = fmincg (@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), initial_theta, options);
end % ========================================================================= end
predictOneVsAll.m
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label for a trained one-vs-all classifier. The labels
%are in the range 1..K, where K = size(all_theta, 1).
% p = PREDICTONEVSALL(all_theta, X) will return a vector of predictions
% for each example in the matrix X. Note that X contains the examples in
% rows. all_theta is a matrix where the i-th row is a trained logistic
% regression theta vector for the i-th class. You should set p to a vector
% of values from 1..K (e.g., p = [1; 3; 1; 2] predicts classes 1, 3, 1, 2
% for 4 examples) m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(all_theta, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); % Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X]; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters (one-vs-all).
% You should set p to a vector of predictions (from 1 to
% num_labels).
%
% Hint: This code can be done all vectorized using the max function.
% In particular, the max function can also return the index of the
% max element, for more information see 'help max'. If your examples
% are in rows, then, you can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max
% for each row.
% [maxx, p]=max(X*all_theta',[],2); % ========================================================================= end
Training Set Accuracy: 95.100000
下面是以三层bp神经网络处理的手写数字识别,其中权重矩阵已给出。
predict.m
function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label of an input given a trained neural network
% p = PREDICT(Theta1, Theta2, X) outputs the predicted label of X given the
% trained weights of a neural network (Theta1, Theta2) % Useful values
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned neural network. You should set p to a
% vector containing labels between 1 to num_labels.
%
% Hint: The max function might come in useful. In particular, the max
% function can also return the index of the max element, for more
% information see 'help max'. If your examples are in rows, then, you
% can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max for each row.
%
X = [ones(m, 1) X]; temp=sigmoid(X*Theta1'); temp = [ones(m, 1) temp]; temp2=sigmoid(temp*Theta2'); [maxx, p]=max(temp2, [], 2); % ========================================================================= end
Training Set Accuracy: 97.520000
注意事项
1.X = [ones(m, 1) X];是确保矩阵维度一致。X0就是一行1
2.正则化时theta0要用0替代,处理如theta_reg=[0;theta(2:size(theta))];
Stanford coursera Andrew Ng 机器学习课程第四周总结(附Exercise 3)的更多相关文章
- Stanford coursera Andrew Ng 机器学习课程编程作业(Exercise 2)及总结
Exercise 1:Linear Regression---实现一个线性回归 关于如何实现一个线性回归,请参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/hapjin/p/6079012.htm ...
- Stanford coursera Andrew Ng 机器学习课程第二周总结(附Exercise 1)
Exercise 1:Linear Regression---实现一个线性回归 重要公式 1.h(θ)函数 2.J(θ)函数 思考一下,在matlab里面怎么表达?如下: 原理如下:(如果你懂了这道作 ...
- Stanford coursera Andrew Ng 机器学习课程编程作业(Exercise 1)
Exercise 1:Linear Regression---实现一个线性回归 在本次练习中,需要实现一个单变量的线性回归.假设有一组历史数据<城市人口,开店利润>,现需要预测在哪个城市中 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 15—Anomaly Detection异常检测
Lecture 15 Anomaly Detection 异常检测 15.1 异常检测问题的动机 Problem Motivation 异常检测(Anomaly detection)问题是机器学习算法 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 1_Introduction and Basic Concepts 介绍和基本概念
目录 1.1 欢迎1.2 机器学习是什么 1.2.1 机器学习定义 1.2.2 机器学习算法 - Supervised learning 监督学习 - Unsupervised learning 无 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 17—Large Scale Machine Learning 大规模机器学习
Lecture17 Large Scale Machine Learning大规模机器学习 17.1 大型数据集的学习 Learning With Large Datasets 如果有一个低方差的模型 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 16—Recommender Systems 推荐系统
Lecture 16 Recommender Systems 推荐系统 16.1 问题形式化 Problem Formulation 在机器学习领域,对于一些问题存在一些算法, 能试图自动地替你学习到 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 14—Dimensionality Reduction 降维
Lecture 14 Dimensionality Reduction 降维 14.1 降维的动机一:数据压缩 Data Compression 现在讨论第二种无监督学习问题:降维. 降维的一个作用是 ...
- 【原】Coursera—Andrew Ng机器学习—课程笔记 Lecture 12—Support Vector Machines 支持向量机
Lecture 12 支持向量机 Support Vector Machines 12.1 优化目标 Optimization Objective 支持向量机(Support Vector Machi ...
随机推荐
- 几种查看CentOS系统版本号和位数的方法
查看系统版本号: cat /etc/redhat-release cat /proc/version uname -a cat /etc/issue 查看64位还是32位: getconf LONG_ ...
- Deferred Rendering(二)G-Buffer的组织
先来看一张网上广为流传的<杀戮地带2>典型的Deferred Shading的G-Buffer组织: 这里补充解释下几个点: 不存Position,而由depth和屏幕像素坐标反推出来.參 ...
- 【bzoj4538】[Hnoi2016]网络
我们考虑树剖,线段树上维护一个堆,保存不经过该段区间的路径的权值. 对于一条路径我们将对于线段树中的区间提取出来,在对于线段树中进行修改.也就是在堆中插入或删除. 对于一次询问,只要找到包含该点的线段 ...
- Binary safe
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary-safe A binary-safe function is one that treats its input as a r ...
- LeetCode——Regular Expression Matching
Implement regular expression matching with support for '.' and '*'. '.' Matches any single character ...
- regulator_get 调用过程【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/u012719256/article/details/52083961 Touch panel DTS 分析(MSM8994平台,Atmel 芯片 ...
- 关于redis、memcache、mongoDB的对比
从以下几个维度,对 Redis.memcache.MongoDB 做了对比.1.性能都比较高,性能对我们来说应该都不是瓶颈.总体来讲,TPS 方面 redis 和 memcache 差不多,要大于 m ...
- 两个ajax写在一起报错
这样做完导致的结果是:在谷歌浏览器页面正常显示,在火狐浏览器会不定期出现系统异常错误提示!最后分析原因是: 从异步请求的执行原理来看,我们知道当一个异步请求发送时,浏览器不会处于锁死.等待的状态,从一 ...
- cmd 高级用法
1. 查看服务(service)信息 查看所有启动的服务信息: C:\Users\hasee>net start 根据启动的服务名,进一步对其启动和关闭: C:\Users\hasee>n ...
- IJ:工程配置Tomcat
ylbtech-IJ:工程配置Tomcat 1.返回顶部 1. 1.2. 1.3. 1.4. 2. 2.返回顶部 1. 2. 3.返回顶部 1. 2. 4.返回顶部 0.修改文件位置 D:\work- ...