Nacos服务注册原理分析
在分布式服务中,原来的单体服务会被拆分成一个个微服务,服务注册实例到注册中心,服务消费者通过注册中心获取实例列表,直接请求调用服务。
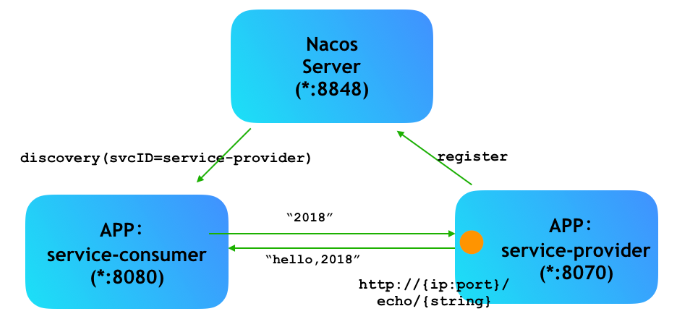
服务是如何注册到注册中心,服务如果挂了,服务是如何检测?带着这些问题,我们从源码上对服务注册进行简单的源码分析。
版本 2.1.1
Nacos Server:2.1.1spring-cloud-starter-alibaba:2.1.1.RELEASEspring-boot:2.1.1.RELEASE
方便统一版本,客户端和服务端版本号都为
2.1.1。
客户端
启动nacos服务注册和发现需要添加maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
<version>${latest.version}</version>
</dependency>
根据maven依赖找到对应的spring.factories文件:
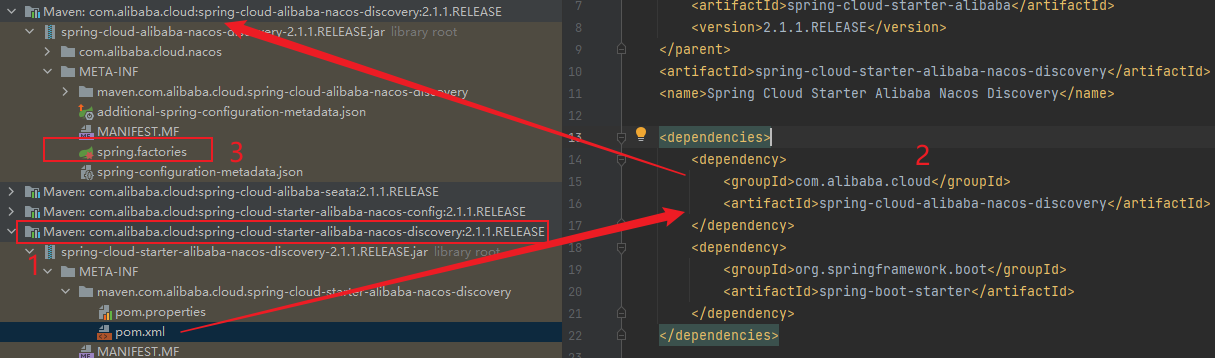
在spring.factories文件里找到启动配置类信息,SpringBoot服务启动时会将这些配置类信息注入到bean容器中。
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.NacosDiscoveryAutoConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.ribbon.RibbonNacosAutoConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.endpoint.NacosDiscoveryEndpointAutoConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.discovery.NacosDiscoveryClientAutoConfiguration,\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.discovery.configclient.NacosConfigServerAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.discovery.configclient.NacosDiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration
服务注册的核心配置类为:NacosDiscoveryAutoConfiguration,该类配置三个bean对象:
NacosServiceRegistryNacosRegistrationNacosAutoServiceRegistration
NacosAutoServiceRegistration
NacosAutoServiceRegistration继承了抽象类AbstractAutoServiceRegistration。AbstractAutoServiceRegistration抽象类又实现了ApplicationListener接口。
实现ApplicationListener接口的方法,会在Spring容器初始化完成之后调用onApplicationEvent方法:
public void onApplicationEvent(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
bind(event);
}
调用bind方法:
public void bind(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
ApplicationContext context = event.getApplicationContext();
if (context instanceof ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext) {
if ("management".equals(((ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext) context)
.getServerNamespace())) {
return;
}
}
this.port.compareAndSet(0, event.getWebServer().getPort());
// 调用 start 方法
this.start();
}
调用了start方法:
public void start() {
if (!isEnabled()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Discovery Lifecycle disabled. Not starting");
}
return;
}
if (!this.running.get()) {
this.context.publishEvent(
new InstancePreRegisteredEvent(this, getRegistration()));
register();
if (shouldRegisterManagement()) {
registerManagement();
}
this.context.publishEvent(
new InstanceRegisteredEvent<>(this, getConfiguration()));
this.running.compareAndSet(false, true);
}
}
调用了register方法,最终调用的是NacosServiceRegistry类的register方法。
NacosServiceRegistry
根据上文可知,服务器启动后调用NacosServiceRegistry类的register方法,该方法实现将实例注册到服务端:
public void register(Registration registration) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(registration.getServiceId())) {
log.warn("No service to register for nacos client...");
return;
}
String serviceId = registration.getServiceId();
String group = nacosDiscoveryProperties.getGroup();
// 创建实例
Instance instance = getNacosInstanceFromRegistration(registration);
try {
// 注册实例
namingService.registerInstance(serviceId, group, instance);
log.info("nacos registry, {} {} {}:{} register finished", group, serviceId,
instance.getIp(), instance.getPort());
}
catch (Exception e) {
log.error("nacos registry, {} register failed...{},", serviceId,
registration.toString(), e);
}
}
创建实例,然后通过namingService.registerInstance方法注册实例,然后查看registerInstance方法:
@Override
public void registerInstance(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
if (instance.isEphemeral()) {
// 封装心跳包
BeatInfo beatInfo = new BeatInfo();
beatInfo.setServiceName(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName));
beatInfo.setIp(instance.getIp());
beatInfo.setPort(instance.getPort());
beatInfo.setCluster(instance.getClusterName());
beatInfo.setWeight(instance.getWeight());
beatInfo.setMetadata(instance.getMetadata());
beatInfo.setScheduled(false);
long instanceInterval = instance.getInstanceHeartBeatInterval();
beatInfo.setPeriod(instanceInterval == 0 ? DEFAULT_HEART_BEAT_INTERVAL : instanceInterval);
// 发送心跳包
beatReactor.addBeatInfo(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName), beatInfo);
}
// 发送实例
serverProxy.registerService(NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName), groupName, instance);
}
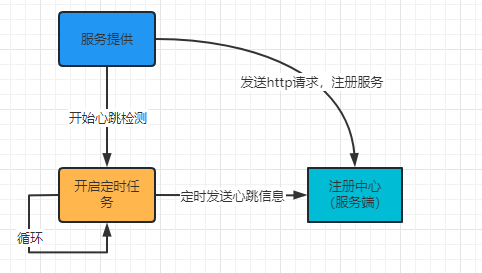
registerInstance主要做两件事:
- 发送心跳包
beatReactor.addBeatInfo使用定时服务,每隔5s向服务端发送一次心跳请求,通过http请求发送心跳信息,路径为/v1/ns/instance/beat。
心跳请求定时任务使用线程池ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.schedule(),而该方法只会调用一次,定时任务的实现是在每次请求任务只会再调用一次ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.schedule(),
简单说就是nacos在发送心跳的时候,会调用schedule方法,在schedule要执行的任务中,如果正常发送完心跳,会再次调用schedule方法。
那为什么不直接调用周期执行的线程池ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate()?可能是由于发送心跳服务发生异常后,定时任务还会继续执行,但是周期执行的线程池遇到报错后也不会重复调用执行的任务。
线程任务
BeatTask的run方法,,每次执行会先判断isStopped,如果是false,说明心跳停止,就不会触发下次执行任务。如果使用定时任务scheduleAtFixedRate,即使心跳停止还会继续执行任务,造成资源不必要浪费。
- 注册实例
registerService主要封装实例信息,比如ip、port、servicename,将这些信息通过http请求发送给服务端。路径为/v1/ns/instance。
根据上面流程,查看以下的流程图:
服务端
服务端就是注册中心,服务注册到注册中心,在https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/releases/tag/2.1.1下载源码部署到本地,方便调式和查看,部署方式详见我的另外一篇文章Nacos 源码环境搭建。
服务端主要接收两个信息:心跳包和实例信息。
心跳包
客户端向服务请求的路径为/v1/ns/instance/beat,对应的服务端为InstanceController类的beat方法:
@PutMapping("/beat")
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.WRITE)
public ObjectNode beat(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
ObjectNode result = JacksonUtils.createEmptyJsonNode();
result.put(SwitchEntry.CLIENT_BEAT_INTERVAL, switchDomain.getClientBeatInterval());
String beat = WebUtils.optional(request, "beat", StringUtils.EMPTY);
RsInfo clientBeat = null;
// 判断是否有心跳,存在心跳就转成RsInfo
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(beat)) {
clientBeat = JacksonUtils.toObj(beat, RsInfo.class);
}
String clusterName = WebUtils
.optional(request, CommonParams.CLUSTER_NAME, UtilsAndCommons.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_NAME);
String ip = WebUtils.optional(request, "ip", StringUtils.EMPTY);
int port = Integer.parseInt(WebUtils.optional(request, "port", "0"));
if (clientBeat != null) {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(clientBeat.getCluster())) {
clusterName = clientBeat.getCluster();
} else {
// fix #2533
clientBeat.setCluster(clusterName);
}
ip = clientBeat.getIp();
port = clientBeat.getPort();
}
String namespaceId = WebUtils.optional(request, CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, Constants.DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_ID);
String serviceName = WebUtils.required(request, CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME);
NamingUtils.checkServiceNameFormat(serviceName);
Loggers.SRV_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] full arguments: beat: {}, serviceName: {}, namespaceId: {}", clientBeat,
serviceName, namespaceId);
// 获取实例信息
BeatInfoInstanceBuilder builder = BeatInfoInstanceBuilder.newBuilder();
builder.setRequest(request);
int resultCode = getInstanceOperator()
.handleBeat(namespaceId, serviceName, ip, port, clusterName, clientBeat, builder);
result.put(CommonParams.CODE, resultCode);
// 下次发送心跳包间隔
result.put(SwitchEntry.CLIENT_BEAT_INTERVAL,
getInstanceOperator().getHeartBeatInterval(namespaceId, serviceName, ip, port, clusterName));
result.put(SwitchEntry.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED, switchDomain.isLightBeatEnabled());
return result;
}
在handleBeat方法中执行线程任务ClientBeatProcessorV2的run方法,延长lastHeartBeatTime时间。注册中心会定时查询实例,当前时间 - lastHeartBeatTime > 设置时间(默认15秒),就标记实例为不健康实例。如果心跳实例不健康,发送通知给订阅方,变更实例。
服务端在
15秒没有收到心跳包会将实例设置为不健康,在30秒没有收到心跳包会将临时实例移除掉。
实例注册
客户端请求的地址是/nacos/v1/ns/instance, 对应的是服务端是在InstanceController类。找到类上对应的post请求方法上。
注册流程:
InstanceController#register ——>InstanceOperatorClientImpl#registerInstance ——>ClientOperationServiceProxy#registerInstance ——>EphemeralClientOperationServiceImpl#registerInstance
创建 Service
服务注册后,将服务存储在一个双层map集合中:
private final Map<String, Map<String, Service>> serviceMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
通过是否存在ephemeral,true,走AP模式,否则走CP模式。
Nacos 默认就是采用的AP模式使用Distro协议实现。实现的接口是EphemeralConsistencyService对节点信息的持久化主要是调用put方法,
会先写入到DataStore中:
public void onPut(String key, Record value) {
if (KeyBuilder.matchEphemeralInstanceListKey(key)) {
Datum<Instances> datum = new Datum<>();
datum.value = (Instances) value;
datum.key = key;
datum.timestamp.incrementAndGet();
// 数据持久化到缓存中
dataStore.put(key, datum);
}
if (!listeners.containsKey(key)) {
return;
}
notifier.addTask(key, DataOperation.CHANGE);
}
总结
- 从依赖上找到需要启动的是要加载的服务注册类
NacosDiscoveryAutoConfiguration,主要配置三个对象NacosServiceRegistryNacosRegistrationNacosAutoServiceRegistration
NacosServiceRegistry类的register方法,封装实例和心跳信息- 通过
http请求,定时发送发送心跳包,默认时间间隔是5秒。 - 通过
http请求,发送实例信息。
- 通过
- 服务端
- 接收到心跳请求,更新心跳包最新时间。服务端在
15秒没有收到心跳包会将实例设为不健康,在30秒没有收到心跳包会将临时实例移除掉。 - 接收到服务注册接口,通过
ephemeral判断是否走AP还是走CP,AP模式使用Distro协议。通过调用EphemeralConsistencyService接口实现,持久化实例信息。
- 接收到心跳请求,更新心跳包最新时间。服务端在
参考
Nacos服务注册原理分析的更多相关文章
- Nacos 服务注册的原理
Nacos 服务注册需要具备的能力: 服务提供者把自己的协议地址注册到Nacos server 服务消费者需要从Nacos Server上去查询服务提供者的地址(根据服务名称) Nacos Serve ...
- 微服务架构 | *3.5 Nacos 服务注册与发现的源码分析
目录 前言 1. 客户端注册进 Nacos 注册中心(客户端视角) 1.1 Spring Cloud 提供的规范标准 1.2 Nacos 的自动配置类 1.3 监听服务初始化事件 AbstractAu ...
- nacos服务注册与发现原理解析
前言:nacos 玩过微服务的想必不会陌生,它是阿里对于springcloud孵化出来的产品,用来完成服务之间的注册发现和配置中心,其核心作用我就不废话了 大致流程:每个服务都会有一个nacos cl ...
- Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos 服务注册与发现功能实现!
Nacos 是 Spring Cloud Alibaba 中一个重要的组成部分,它提供了两个重要的功能:服务注册与发现和统一的配置中心功能. 服务注册与发现功能解决了微服务集群中,调用者和服务提供者连 ...
- Spring Cloud Alibaba | Nacos服务注册与发现
目录 Spring Cloud Alibaba | Nacos服务注册与发现 1. 服务提供者 1.1 pom.xml项目依赖 1.2 配置文件application.yml 1.3 启动类Produ ...
- Spring Cloud Alibaba(一) 如何使用nacos服务注册和发现
Nacos介绍 Nacos 致力于帮助您发现.配置和管理微服务.Nacos 提供了一组简单易用的特性集,帮助您快速实现动态服务发现.服务配置.服务元数据及流量管理. Nacos 帮助您更敏捷和容易地构 ...
- Alibaba Nacos 学习(三):Spring Cloud Nacos Discovery - FeignClient,Nacos 服务注册与发现
Alibaba Nacos 学习(一):Nacos介绍与安装 Alibaba Nacos 学习(二):Spring Cloud Nacos Config Alibaba Nacos 学习(三):Spr ...
- SpringCloud Alibaba Nacos 服务注册
业务服务接入Nacos服务治理中心 启动Nacos访问地址为:http://101.200.201.195:8848/nacos/ 创建bom工程用于管理依赖(下方附加源码地址) 准备工作完成后开始接 ...
- springcloudalibaba与nacos服务注册流程图
springboot + springcloud + springcloudalibaba + nacos 服务注册流程图: springboot ①WebApplicationContext ②st ...
- 实战二:nacos服务注册与发现,openfeign服务调用
一,参照上一篇创建好微服务结构后,按业务需求编写各微服务逻辑 二,服务注册 1,安装nacos:下载,解压,运行startup.cmd 2,访问 http://localhost:8848/nacos ...
随机推荐
- EBI、DDD及其演变架构史
一.引子 聊架构总离不开"领域驱动架构",大多能聊到DDD(Domain-Driven Design),实际上早期思想EBI架构 1992年就诞生了.核心价值点在于:关注核心业务领 ...
- vulnhub靶场之DOUBLETROUBLE: 1
准备: 攻击机:虚拟机kali.本机win10. 靶机:DOUBLETROUBLE: 1,网段地址我这里设置的桥接,所以与本机电脑在同一网段,下载地址:https://download.vulnhub ...
- K3S 安装及配置
K3S安装 curl -sfL https://rancher-mirror.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/k3s/k3s-install.sh | INSTALL_K3S_ ...
- [排序算法] 冒泡排序 (C++)
冒泡排序解释: 冒泡排序 BubbleSort 是一种最基础的交换排序.顾名思义,数组中的每一个元素就好像泡泡一样,根据自己的大小不同一点点的向一侧移动. 冒泡排序原理: 每一趟只能确定将一个数归位. ...
- python关于error: invalid command 'bdist_wheel报错的解决
看了很多解决办法,大部分在扯去下载一个 .whl 源文件然后在pip 安装,经过我亲自测试执行完这句即可解决! pip3 install wheel
- GitHub上的一个笔记相关小项目
就是一个笔记屑小项目, C++编写,有想一起开发的私信 AlgorithWeaver/V-note (github.com) 项目名V-note QVQ
- vue3 watch笔记
watchEffect 执行传入的一个函数,同时自动追踪函数中依赖到的数据,并在其依赖变更时重新运行该函数. 并且会在 组件挂载前 立即调用一次,(默认是挂载前,可通过修改 flush 属性改变,后边 ...
- 论文解读(PCL)《Probabilistic Contrastive Learning for Domain Adaptation》
论文信息 论文标题:Probabilistic Contrastive Learning for Domain Adaptation论文作者:Junjie Li, Yixin Zhang, Zilei ...
- C#从实习到搬砖
日常唠唠 没事就聊聊我在c#上踩过的那些坑,和一些笔记 少点比较,多些谦虚 会者不难 原博:轩先生大冒险 2022.4.19 datagridview 修改表头 dataGridView1.Colum ...
- maven 项目依赖自动导入失败(pom.xml 文件爆红),解决--手动导入
idea 报错信息提示:Dependency 'xxx' not found 解决方法:可以通过更换仓库的镜像配置解决,但是一般咱都在配置maven的时候,设置成阿里云仓库镜像了,更换成其他的,可能出 ...
