Android五大布局详解——LinearLayout(线性布局)
Android五大布局
本篇开始介绍Android的五大布局的知识,一个丰富的界面显示总是要有众多的控件来组成的,那么怎样才能让这些控件能够按你的想法进行摆放,从而自定义你所想要的用户界面呢?这就牵涉到本章将要学习的知识————五大布局。本篇将依次对LinearLayout(线性布局)、RelativeLayout(相对布局)、TableLayout(表格布局)、FrameLayout(帧布局)、GridLayout(网格布局)进行介绍。
LinearLayout(线性布局)
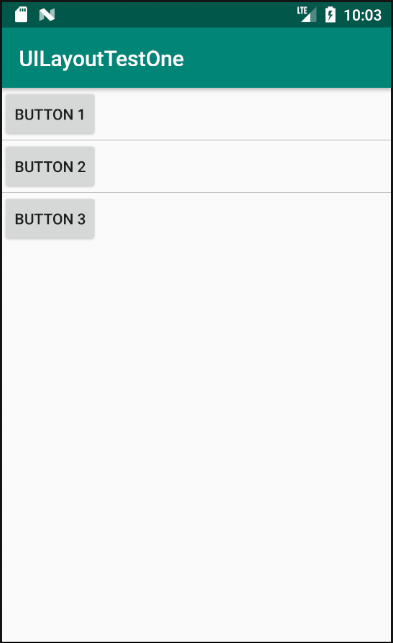
这是一个非常常用的布局,它会将其中的控件在线性方向上依次排列,通过android:orientation属性指定其控件的排列方向,有vertical(垂直方向)以及horizontal(水平方向)排列。新建UILayoutTsetOne项目,其他设置保持默认。修改activity_main.xml中的代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 2" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 3" />
</LinearLayout>
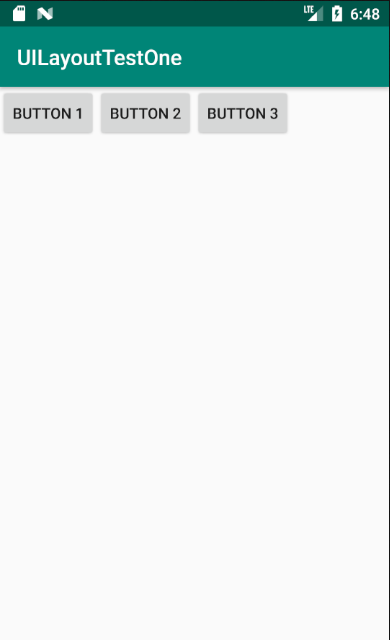
模拟器中运行结果如下图所示,从图中可以看出,定义的三个button控件按照vertical依次排列。

接下来将vertical参数改变为horizontal参数。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 2" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 3" />
</LinearLayout>
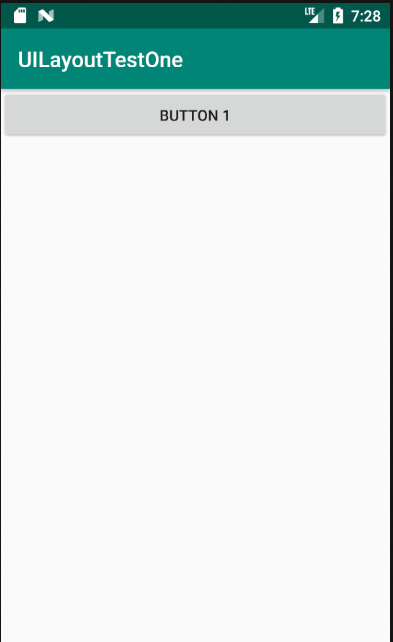
运行程序,效果如下,从图中可以看出,定义的三个button组件按照horizontal依次排列。
attention!
倘若LinearLayout的排列方向指定为horizontal,则内部的控件就绝对不能将宽度指定为match_parent,因为如果这样设置,单独的控件将会将整个水平方向占满,其他控件将没有放置的位置了。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 2" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 3" />
</LinearLayout>
效果如图:
同样,倘若LinearLayout的排列方向指定为vertical,则内部的控件就绝对不能将高度指定为match_parent。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="Button 1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 2" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 3" />
</LinearLayout>
效果如图:

下面来看两个长得很像的属性:android:gravity属性和android:layout_gravity属性。
- android:gravity属性:用于指定文字在控件中的对齐方式。可以选择的值有:top、bottom、left、right、center等,还可以用“|”来同时指定多个值,其中center值将相当于center_vertical|center_horizontal,表示文字在垂直和水平方向都居中对齐。
- android:layout_gravity属性:用于指定控件在布局中的对齐方式。其可选值和android:gravity属性差不多,需要注意的是,当LinearLayout的排列方向是horizontal时只有垂直方向上的对齐方式才会生效,因为此时水平方向上的长度是不固定的,每添加一个控件,水平方向上的长度都会改变,因而无法指定该方向上的对齐方式。同样,当LinearLayout的排列方向是vertical时,只有水平方向上的对齐方式才会生效。修改activity_main.xml中的代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="top"
android:text="Button 1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:text="Button 2" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:text="Button 3" />
</LinearLayout>
运行效果如图:
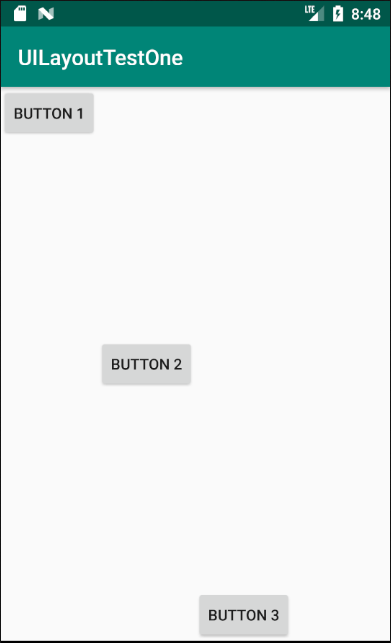
接下来,我们学习另一个重要属性:android:layout_weight,它允许我们使用比例的方式来指定控件的大小,在手机的适配性方面可以起到非常重要的作用。这里通过编写一个消息发送界面来做演示。所用到的控件有:一个文本编辑框和一个发送按钮。
修改activity_main.xml中的代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/input_msg"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:hint="Type in Some words" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/send_button"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="send_msg" />
</LinearLayout>
运行程序,效果如图:
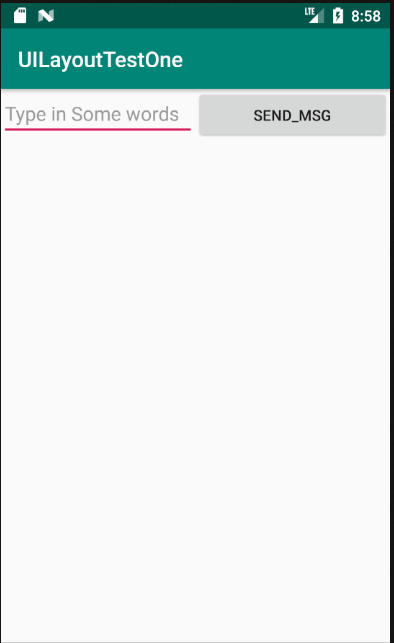
这里你会发现EditText和Button的宽度都被指定为了0dp,你可能会担心这样这两个控件还能正常的显示出来吗?不用担心,因为这里,使用了android:layout_weight属性,此时控件的宽度就不由android:layout_width来决定了,这里写成了0dp是一种比较标准的写法。另外,dp是Android中用于指定控件大小、间距等属性的单位。可以看到这里通过android:layout_weight属性将值指定为了1,这表示两个控件在水平方向上平分宽度。原理:系统会将所有控件指定的layout_weight值相加,得到一个总值,然后每个控件所占大小的比例就是用该控件指定的layout_weight值除以刚才算出的总值。因此如果想让EditText占据屏幕宽度的3/5,Button占据屏幕宽度的2/5,只需要将EditText的layout_weight改成3,Button的layout_weight改成2就可以了。重新运行程序,效果如图:
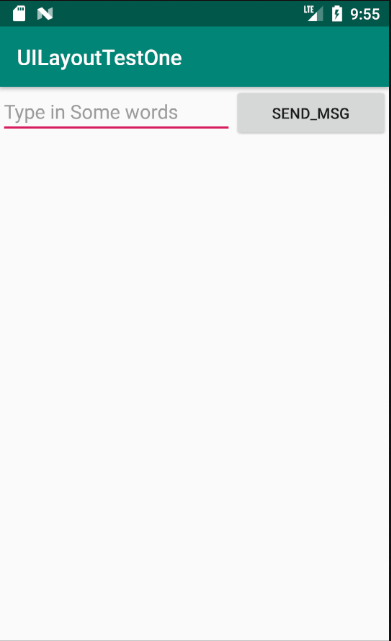
接着再来看一下如何实现在两个控件之间用分割线进行分割,效果如图:
实现这种效果有两种方式:
- 1.直接在布局中添加一个view,这个view的作用仅仅是显示出一条线,实现如下:
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1px"
android:background="#000000" />
实现代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button 1" />
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1px"
android:background="#000000" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button 2" />
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="1px"
android:background="#000000" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button 3" />
</LinearLayout>
- 2.使用LinearLayout的一个divider属性,直接为LinearLayout设置分割线,这里需要准备一张线的图片 1)android:divider设置作为分割线的图片 2)android:showDividers设置分割线的位置,none(无),beginning(开始),end(结束),middle(每两个组件间) 3)dividerPadding设置分割线的Padding
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/LinearLayout1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:divider="@drawable/thread"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:showDividers="middle"
android:dividerPadding="10dp"
tools:context="com.example.uilayouttestone.MainActivity" >
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 2" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 3" />
</LinearLayout>
Android五大布局详解——LinearLayout(线性布局)的更多相关文章
- Android 布局详解 -三表格布局(TableLayout)以及重要属性
TableLayout跟TableRow 是一组搭配应用的布局,TableLayout置底,TableRow在TableLayout的上方,而Button.TextView等控件就 ...
- Html5移动端页面自适应布局详解(阿里rem布局)
在移动设备上进行网页的重构或开发,首先得搞明白的就是移动设备上的viewport,通读网上的各种对于viewport的解释之后 大概viewport可以理解为三种 1.layout viewport ...
- Android 布局详解
Android 布局详解 1.重用布局 当一个布局文件被多处使用时,最好<include>标签来重用布局. 例如:workspace_screen.xml的布局文件,在另一个布局文件中被重 ...
- 2.2.1 LinearLayout(线性布局)
本节引言 本节开始讲Android中的布局,Android中有六大布局,分别是: LinearLayout(线性布局), RelativeLayout(相对布局), TableLayout(表格布局) ...
- Grid 网格布局详解
Grid网格布局详解: Grid布局与Flex布局有着一定的相似性,Grid布局是将容器划分成行和列,产生单元格,可以看做是二维布局. 基本概念: 采用网格布局的区域,称为"容器" ...
- Android布局管理详解(1)—— LinearLayout 线性布局
Android的布局方式共有6种,分别是LinearLayout(线性布局).TableLayout(表格布局).FrameLayout(帧布局).RelativeLayout(相对布局).GridL ...
- [置顶] Android系统五大布局详解Layout
我们知道Android系统应用程序一般是由多个Activity组成,而这些Activity以视图的形式展现在我们面前,视图都是由一个一个的组件构成的.组件就是我们常见的Button.TextEdit等 ...
- Android系统五大布局详解Layout
我们知道Android系统应用程序一般是由多个Activity组成,而这些Activity以视图的形式展现在我们面前, 视图都是由一个一个的组件构成的.组件就是我们常见的Button.TextEdit ...
- Android开发之详解五大布局
http://bbs.chinaunix.net/thread-3654213-1-1.html 为了适应各式各样的界面风格,Android系统提供了5种布局,这5种布局分别是: LinearLayo ...
随机推荐
- 调用rest api杀死yarn上的应用
调用rest api杀死yarn上的应用 调用yarn reat api,通过app name 获取application id public static String getApplication ...
- Windows安装MSYS2_切换zsh_整合cmder
MSYS2是什么 MSYS2 (Minimal SYStem 2) 是一个MSYS的独立改写版本,主要用于 shell 命令行开发环境.同时它也是一个在Cygwin (POSIX 兼容性层) 和 Mi ...
- redis(5)--redis集群之哨兵机制
哨兵机制 在前面讲的master/slave模式,在一个典型的一主多从的系统中,slave在整个体系中起到了数据冗余备份和读写分离的作用.当master遇到异常终端后,需要从slave中选举一个新的m ...
- 一篇文章搞明白Integer、new Integer() 和 int 的概念与区别
基本概念的区分 1.Integer 是 int 的包装类,int 则是 java 的一种基本数据类型 2.Integer 变量必须实例化后才能使用,而int变量不需要 3.Integer 实际是对象的 ...
- Python连载58-http协议简介
一.http协议实战 1.URL(Uniform Resource Located) (1)使用FFTP的URL,例如:ftp://rtfm.mit.edu (2)使用HTTP的URL,例如:http ...
- webpack构建原理和实现简单webpack
webpack打包原理分析 基础配置,webpack会读取配置 (找到入口模块) 如:读取webpack.config.js配置文件: const path = require("path& ...
- JVM CPU Profiler技术原理及源码深度解析
研发人员在遇到线上报警或需要优化系统性能时,常常需要分析程序运行行为和性能瓶颈.Profiling技术是一种在应用运行时收集程序相关信息的动态分析手段,常用的JVM Profiler可以从多个方面对程 ...
- highreport报表工具功能介绍
目前国产报表工具大部分都是Java版本,例如润乾和帆软,而C#写的报表工具国内还没有,介绍一款VS2010(C#)写的国产报表工具(highreport),采用类Excel设计,零代码实现复杂报表展示 ...
- Android框架式编程之架构方案
目前移动端应用市场已经是百花齐放,很多独角兽公司都是通过App创业发展起来的,现在App类型更加丰富,功能越来越完善,基本上涵盖了各个行业的每个角落.为了开发出更加有竞争力的App,不仅需要功能上有创 ...
- Windows系统下解决PhPStudy MySQL启动失败
报错 Apache\Nginx服务正常启动了,但是MySQL却一直启动失败. 解决流程 查看端口是否被占用 打开系统自带的资源管理器,查看监听端口3306是不是被占用,下图中3306端口被mysqld ...
