【C++ Primer | 10】泛型算法
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std; void elimDups(vector<string> &words)
{
sort(words.begin(), words.end());
auto unique_end = unique(words.begin(), words.end());
words.erase(unique_end, words.end());
} void display(vector<string> &words)
{
for (auto c : words)
cout << c << " ";
cout << endl;
} int main()
{
ifstream in("test.txt");
if (!in)
{
cout << "打开文件失败" << endl;
exit();
} vector<string> words;
string str;
while (in >> str)
words.push_back(str);
elimDups(words);
display(words);
return ;
}

输出结果:

定制操作
示例代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std; void elimDups(vector<string> &words)
{
sort(words.begin(), words.end());
auto unique_end = unique(words.begin(), words.end());
words.erase(unique_end, words.end());
} void biggies(vector<string> &words, vector<string>::size_type sz)
{
elimDups(words); //将单词按字典排序,删除重复单词
stable_sort(words.begin(), words.end(), [](const string &a, const string &b) { return a.size() < b.size(); });
auto wc = find_if(words.begin(), words.end(), [sz](const string &a) { return a.size() >= sz; });
auto count = words.end() - wc;
for_each(wc, words.end(), [](const string &s) { cout << s << " "; });
cout << endl;
} int main()
{
ifstream in("test.txt");
if (!in)
{
cout << "打开文件失败" << endl;
exit();
} vector<string> words;
string str;
while (in >> str)
words.push_back(str);
auto sz = ;
biggies(words, sz);
return ;
}
输出结果:

再探迭代器
3. 反向迭代器
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<iterator>
using namespace std; int main()
{
vector<int> vec = { , , , , , , , , , };
for (auto r_iter = vec.crbegin(); r_iter != vec.crend(); ++r_iter)
cout << *r_iter << " ";
cout << endl;
return ;
}
输出结果:

#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std; void print(int elem)
{
cout << elem << ' ';
} int main()
{
deque<int> coll;
for (int i = ; i <= ; ++i)
coll.push_back(i); deque<int>::iterator pos1;
pos1 = find(coll.begin(), coll.end(), ); deque<int>::iterator pos2;
pos2 = find(coll.begin(), coll.end(), );
for_each(pos1, pos2, print);
cout << endl; deque<int>::reverse_iterator rpos1(pos1);
deque<int>::reverse_iterator rpos2(pos2);
for_each(rpos2, rpos1, print);
cout << endl;
return ;
}
输出结果:

【分析】
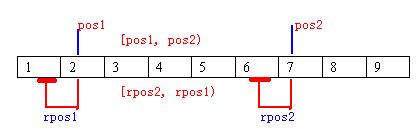
代码首先在一个deque中插入1到9,然后查找元素值为2和7的位置,分别赋值给迭代器pos1和pos2,然后输出,由于STL中的操作总是左开右闭的区间,即[2,7),所以输出2 3 4 5 6,7不会输出。
接下来将迭代器转换成逆向迭代器,再次输出,对于反向迭代器,由于是反向,所以按逻辑来说它是左开右闭的(这里我尝试了rpos2为iterator.end(),rpos1为iterator.begin(),此时输出全部),即(7,2](事实上还是左闭右开,只不过此时的左和iterator顺序一样)。所以输出6 5 4 3 2,下面的图片解释的很清楚。
【C++ Primer | 10】泛型算法的更多相关文章
- c++ primer 11 泛型算法
使用泛型算法必须包含头文件#inlucde <algorithm> 标准库还定义一组泛化的算术算法,其命名习惯与泛型算法相同,包含头文件#include <numeric> f ...
- C++ Primer 5th 第10章 泛型算法
练习10.1:头文件algorithm中定义了一个名为count的函数,它类似find,接受一对迭代器和一个值作为参数.count返回给定值在序列中出现的次数.编写程序,读取int序列存入vector ...
- [C++ Primer] : 第10章: 泛型算法
概述 泛型算法: 称它们为"算法", 是因为它们实现了一些经典算法的公共接口, 如搜索和排序; 称它们是"泛型的", 是因为它们可以用于不同类型的元素和多种容器 ...
- C++ Primer : 第十章 : 泛型算法 之 只读、写和排序算法
大多数算法都定义在<algorithm>头文件里,而标准库还在头文件<numeric>里定义了一组数值泛型算法,比如accumulate. ● find算法,算法接受一对迭代 ...
- 【足迹C++primer】30、概要(泛型算法)
概要(泛型算法) 大多数算法的头文件中定义algorithm在. 标准库也是第一个文件numeric它定义了一套通用算法. #include<iostream> #include<n ...
- C++ Primer笔记6_STL之泛型算法
1.泛型算法: 大多数算法定义在头文件algorithm中.标准库还在头文件numeric中定义了一组数值泛型算法 仅仅读算法: 举例: find函数用于找出容器中一个特定的值,有三个參数 int v ...
- 【c++ Prime 学习笔记】第10章 泛型算法
标准库未给容器添加大量功能,而是提供一组独立于容器的泛型算法 算法:它们实现了一些经典算法的公共接口 泛型:它们可用于不同类型的容器和不同类型的元素 利用这些算法可实现容器基本操作很难做到的事,例如查 ...
- C++ Primer 读书笔记:第11章 泛型算法
第11章 泛型算法 1.概述 泛型算法依赖于迭代器,而不是依赖容器,需要指定作用的区间,即[开始,结束),表示的区间,如上所示 此外还需要元素是可比的,如果元素本身是不可比的,那么可以自己定义比较函数 ...
- C++ Primer 学习笔记_45_STL实践与分析(19)--泛型算法的结构
STL实践与分析 --泛型算法的结构 引言: 正如全部的容器都建立在一致的设计模式上一样,算法也具有共同的设计基础. 算法最主要的性质是须要使用的迭代器种类.全部算法都指定了它的每一个迭代器形參可使用 ...
- C++ 泛型算法
<C++ Primer 4th>读书笔记 标准容器(the standard container)定义了很少的操作.标准库并没有为每种容器类型都定义实现这些操作的成员函数,而是定义了一组泛 ...
随机推荐
- MySQL数据库的锁详解【转】
当然在我们的数据库中也有锁用来控制资源的并发访问,这也是数据库和文件系统的区别之一. 为什么要懂数据库锁? 通常来说对于一般的开发人员,在使用数据库的时候一般懂点 DQL(select),DML(in ...
- VB获取CAD属性值
Dim myAcadApp As AutoCAD.AcadApplication, activeDoc As AutoCAD.AcadDocument, acMS As AutoCAD.AcadMod ...
- 设计模式C++学习笔记之十七(Chain of Responsibility责任链模式)
17.1.解释 概念:使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接收者之间的耦合关系.将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止. main(),客户 IWom ...
- 【翻译】Chemkin - Chapter 1
[这段文字是2013年3月翻译的,整理老文档时发现就拿出来,提醒我们:任何试图翻译英文手册的尝试都是徒劳的] 第一章 介绍 Chemkin理论手册提供了一个对关系和公式的宽泛的概览,这些关系和公式 ...
- Linq与Lambda常用查询语法
1.查询全部 2.按条件查询全部 3.去除重复 4.连接查询 between and 5.排序 6.分组
- Centos 6.5 freeswitch 编译mod_shout
1. yum install -y patch 2. yum install -y libshout-devel lame-devel libmpg123-devel 3. make install ...
- ebs 12.1.1 单节点多用户安装
本次测试环境:操作系统 oracle linux 6.9 oracle ebs 12.1.1 192.168.20.210 erpapp1.hthorizon.com erpapp1 yum ...
- linux /proc目录
1. /proc目录Linux 内核提供了一种通过 /proc 文件系统,在运行时访问内核内部数据结构.改变内核设置的机制.proc文件系统是一个伪文件系统,它只存在内存当中,而不占用外存空间.它以文 ...
- mysql:赋予用户权限、查看及修改端口号
一.mysql 赋给用户权限 grant all privileges on *.* to joe@localhost identified by '1'; flush privileges; 即用u ...
- Webapi 跨域 解决解决错误No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource 问题
首先是web端(http://localhost:53784) 请求 api(http://localhost:81/api/)时出现错误信息: 查看控制台会发现错误:XMLHttpRequest c ...
