Spring Boot(五)启动流程分析
学习过springboot的都知道,在Springboot的main入口函数中调用SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class,args)函数便可以启用SpringBoot应用程序,跟踪一下SpringApplication源码可以发现,最终还是调用了SpringApplication的动态run函数。
下面以SpringBoot2.0.3.RELEASE为例简单分析一下运行过程。
SpringApplicatiton部分源码:
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources,
String[] args) {
//创建springapplication对象,调用函数run(args)
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
上面的源码可以发现还是先创建SpringApplication实例,再调用run方法
第一步 分析 SpringApplication构造函数
SpringApplication构造函数代码如下:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//1:判断web环境
this.webApplicationType = deduceWebApplicationType();
//2:加载classpath下META-INF/spring.factories中配置的ApplicationContextInitializer
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//3:加载classpath下META-INF/spring.factories中配置的ApplicationListener
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//4:推断main方法所在的类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
具体逻辑分析:
- deduceWebApplicationType(), SpringApplication构造函数中首先初始化应用类型,根据加载相关类路径判断应用类型,具体逻辑如下:
private static final String REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS = "org.springframework."
+ "web.reactive.DispatcherHandler"; 4 private static final String MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS = "org.springframework."
+ "web.servlet.DispatcherServlet"; private static final String[] WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" }; private WebApplicationType deduceWebApplicationType() {
//当类路径中存在REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS并且不存在MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS时
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(REACTIVE_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(MVC_WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
//当加载的类路径中不包含WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES中定义的任何一个类时,返回标准应用()
for (String className : WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
//加载的类路径中包含了WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES中定义的所有类型则判断为servlet的web应用
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
2. setInitializers初始化属性initializers,加载classpath下META-INF/spring.factories中配置的ApplicationContextInitializer,此处getSpringFactoriesInstances方法入参type=ApplicationContextInitializer.class
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()方法将会从calssptah下的META-INF/spring.factories中读取key为//org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的值,并以集合形式返回
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
//根据返回names集合逐个实例化,也就是初始化各种ApplicationContextInitializer,这些Initializer实际是在Spring上下文ApplicationContext执行refresh前调用
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances); //对instance排序
return instances;
13 }
以我的demo为例,实际debug时得到的initializers如下,其中数据来源于spring-boot,spring-boot-autoconfiguration和spring-boot-devtolls三个jar包下的classpath中,ApplicationContextInitializer接口是Spring框架提供地的,其主要作用是在Spring容器初始化过程中调用refresh()方法之前回调,具体可参考:Spring Boot(七)扩展分析
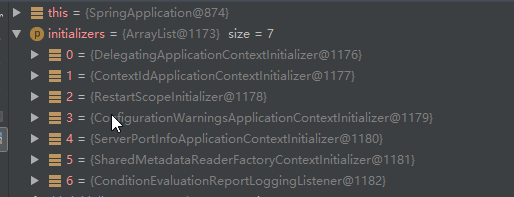
3. setListeners 初始化属性listeners,加载classpath下META-INF/spring.factories中配置的ApplicationListener,此处入参为getSpringFactoriesInstances方法入参type= ApplicationListener.class
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()方法将会从calssptah下的META-INF/spring.factories中读取key为//org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener的值,并以集合形式返回
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
//根据配置,初始化各种ApplicationListener,作用是用来监听ApplicationEvent
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
第二步 分析 SpringApplication中 run方法
SpringApplication的run方法代码如下:
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//设置系统变量java.awt.headless
configureHeadlessProperty();
//1:获取监听器:加载classpath下面的META-INF/spring.factories配置的监听器SpringApplicationRunListener
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//2:启动监听器:执行所有runlistener的starting方法,实际上发布一个【ApplicationStartingEvent】事件
listeners.starting();
try {
//3:实例化ApplicationArguments对象
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
//4: 准备应用上下文环境Environment (web环境 or 标准环境)+配置Environment,主要是把run方法的参数配置到Environment 发布【ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent】事件
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印banner,SpringBoot启动时,控制台输出的一个歪歪扭扭的很不清楚的Spring几个大字母,也可以自定义
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//5: 根据不同environment实例化上下文 context
context = createApplicationContext();
// 异常处理,实例化一个SpringBootExceptionReporter.class 用于处理启动过程中的错误
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//6: 上下文相关预处理 发布【ApplicationPreparedEvent】事件
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
//7: 【刷新应用上线文】执行spring容器(context)的refresh方法,并且调用context的registerShutdownHook方法
refreshContext(context);
//8:空方法,用于扩展
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//9:执行所有runlisteners的started方法,发布【ApplicationStartedEvent】事件
listeners.started(context);
//10: 遍历执行CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner
//如果需要在SpringBoot应用启动后运行一些特殊的逻辑,可以通过实现ApplicationRunner或CommandLineRunner接口中的run方法,该自定义类的run方法会在此处统一调用
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
具体分析:
1. 获取监听器:getRunListeners(args) 加载各种SpringApplicationRunListener实例,内部实现也还是通过SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader))实现,加载META-INF/spring.factories中key为org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener的值,生成对应实例,SpringBoot实际加载了一个EventPublishingRunListener监听器,该监听器继承SpringApplicationRunListener接口,SpringApplicationRunListener规定了SpringBoot的生命周期,在各个生命周期广播相应的事件,调用实际的ApplicationListener类。
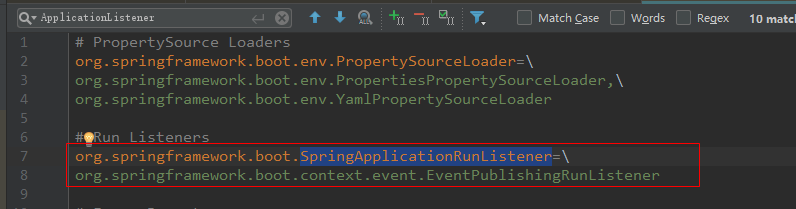
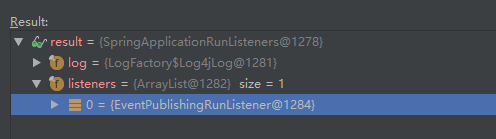
2. 启动监听器: listeners.starting() 执行所有SpringApplicationRunListener的stating方法,发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件,该事件被ApplicationListener类型的listener监听
3. 实例化ApplicationArguments对象
4 . 准备应用上下文环境 并发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//根据properties和profiles配置环境
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 执行EventPublishingRunListener发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,将会被ApplicationListener监听到
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
10 //
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.NONE) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment);
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
备注:实际上载spring-boot-2.0.3.RELEASE.jar包中,可以发现spring.factories中只配置了一个RunListener: org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
截取EventPublishingRunListener.java部分代码:
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered {
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
//将SpringApplication实例中的ApplicationListener类型的listeners添加到initialMulticaster,后续执行监听
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
// 发布一个ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
//所有被添加到initialMulticaster中的listener都将监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
this.application, this.args, environment));
}
}
4.1 根据properties和profiles配置环境:configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
以下假设指定配文件application-dev.properties,跟踪一下源码,可以发现:
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
String[] args) {
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
configureEnvironment方法内部比较简洁,直接调用两个方法完事,
configurePropertySources(environment, args)方法的作用是将args封装成了SimpleCommandLinePropertySource并加入到了environment中,其中arg中含有启动参数:--spring.profiles.active=dev
configureProfiles(environment, args)作用是将启动参数中指定的配置文件激活。
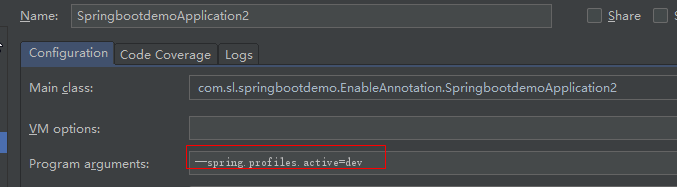
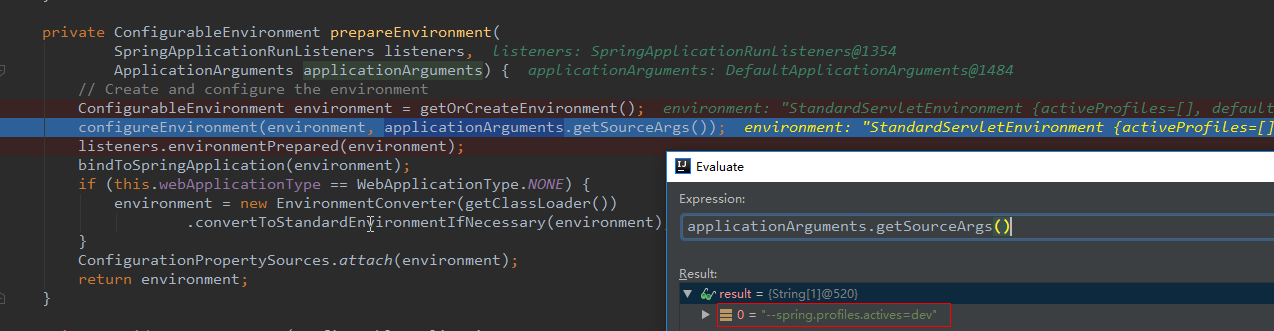
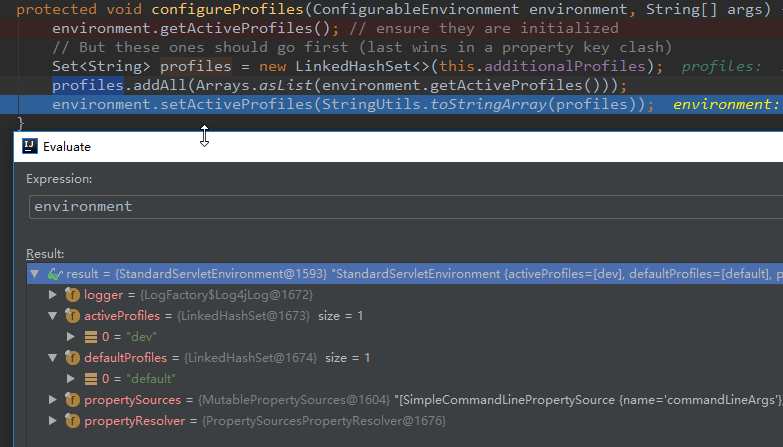
configureProfiles中执行enviroment.getActiveProfiles():强制读取启动命令中指定的配置文件
protected Set<String> doGetActiveProfiles() {
synchronized (this.activeProfiles) {
if (this.activeProfiles.isEmpty()) {
String profiles = getProperty(ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profiles)) {
setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(profiles)));
}
}
return this.activeProfiles;
}
}
5. 根据environment类型创建ApplicationContext
6. 上下文相关处理:
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//配置beanNameGenerator和资源加载器
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//回调所有的ApplicationContextInitializer
applyInitializers(context);
//执行所有SpringApplicationRunListener的contextPrepared方法,触发事件,实际上EventPublishingRunListener中contextPrepared是一个空方法,什么都没执行
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
} //向Spring容器注入springApplicationArguments和springBootBanner
// Add boot specific singleton beans
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
} // Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
//执行所有SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded方法,下面是EventPublishingRunListener中的contextLoaded
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
EventPublishingRunListener.java中contextLoaded方法具体实现
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.application.getListeners()) {
if (listener instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) listener).setApplicationContext(context);
}
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
//触发ApplicationPreparedEvent事件,ApplicationListener负责监听
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(
new ApplicationPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
}
7. 执行context的refresh,并且调用context的registerShutdownHook方法,refresh方法的具体逻辑分析可以参考:
Spring源码解析 – AnnotationConfigApplicationContext容器创建过程
8. afterRefresh空方法
9. 执行所有runlisteners的started方法,发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件
10. 遍历执行CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner
以上。
Spring Boot(五)启动流程分析的更多相关文章
- spring boot应用启动原理分析
spring boot quick start 在spring boot里,很吸引人的一个特性是可以直接把应用打包成为一个jar/war,然后这个jar/war是可以直接启动的,不需要另外配置一个We ...
- Spring Boot应用启动原理分析(转)
在spring boot里,很吸引人的一个特性是可以直接把应用打包成为一个jar/war,然后这个jar/war是可以直接启动的,不需要另外配置一个Web Server. 如果之前没有使用过sprin ...
- 头秃了,二十三张图带你从源码了解Spring Boot 的启动流程~
持续原创输出,点击上方蓝字关注我 目录 前言 源码版本 从哪入手? 源码如何切分? 如何创建SpringApplication? 设置应用类型 设置初始化器(Initializer) 设置监听器(Li ...
- Spring MVC启动流程分析
本文是Spring MVC系列博客的第一篇,后续会汇总成贴子. Spring MVC是Spring系列框架中使用频率最高的部分.不管是Spring Boot还是传统的Spring项目,只要是Web项目 ...
- spring boot容器启动详解
目录 一.前言 二.容器启动 三.总结 =======正文分割线====== 一.前言 spring cloud大行其道的当下,如果不了解基本原理那么是很纠结的(看见的都是约定大于配置,但是原理呢?为 ...
- Spring Boot启动流程分析
引言 早在15年的时候就开始用spring boot进行开发了,然而一直就只是用用,并没有深入去了解spring boot是以什么原理怎样工作的,说来也惭愧.今天让我们从spring boot启动开始 ...
- Spring Boot 应用程序启动流程分析
SpringBoot 有两个关键元素: @SpringBootApplicationSpringApplication 以及 run() 方法 SpringApplication 这个类应该算是 Sp ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(五):SpringBoot自动装配原理实现
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- Spring源码解析02:Spring IOC容器之XmlBeanFactory启动流程分析和源码解析
一. 前言 Spring容器主要分为两类BeanFactory和ApplicationContext,后者是基于前者的功能扩展,也就是一个基础容器和一个高级容器的区别.本篇就以BeanFactory基 ...
- Spring源码解析 | 第二篇:Spring IOC容器之XmlBeanFactory启动流程分析和源码解析
一. 前言 Spring容器主要分为两类BeanFactory和ApplicationContext,后者是基于前者的功能扩展,也就是一个基础容器和一个高级容器的区别.本篇就以BeanFactory基 ...
随机推荐
- python教程(二)·条件语句
条件语句一般用来判断给定的条件是否成立,根据结果来执行不同的代码,也就是说,有了条件语句,才可以根据不同的情况做不同的事,从而控制程序的流程. 布尔类型 前面说到数据类型的时候,其中有一种叫 &quo ...
- 使用bison和yacc制作脚本语言(2)
我们先来想一下语法 一般脚本语言不需要定义类型直接在赋值的时候确定 我们主要考虑一下变量的类型 a = 1; b = 1.1; c = "str"; 一般来讲,我们使用这三种类型, ...
- C# 获取UTC 转换时间戳为C#时间
获取UTC /// <summary> /// 获取时间戳 /// </summary> /// <returns>UTC</returns> publ ...
- Java设计模式(2)——创建型模式之工厂方法模式(Factory Method)
一.概述 上一节[简单工厂模式]介绍了通过工厂创建对象以及简单的利弊分析:这一节来看看工厂方法模式对类的创建 工厂方法模式: 工厂方法与简单工厂的不同,主要体现在简单工厂的缺点的改进: 工厂类不再负责 ...
- 【POJ1733】Parity game
[POJ1733]Parity game 题面 vjudge 题解 比较简单的分类并查集 将一个查询操作看作前缀和\(s_r-s_{l-1}\)的奇偶性 将每个点拆成一奇一偶然后分别连边即可 如果一个 ...
- 通过反编译看Java String及intern内幕--费元星站长
通过反编译看Java String及intern内幕 一.字符串问题 字符串在我们平时的编码工作中其实用的非常多,并且用起来也比较简单,所以很少有人对其做特别深入的研究.倒是面试或者笔试的时候,往 ...
- android 学习十四 探索安全性和权限
1.部署安全性:应用程序必须使用数字证书才能安装到设备上. 2.执行期间的安全性: 2.1 使用独立进程 2.2 使用固定唯一用户ID 2.3 申明性权限模型 3数字证书 ...
- Python 列表下标操作
Python 列表下标操作 引用网址: https://www.jianshu.com/p/a98e935e4d46
- web自动化原理揭秘
做过两年自动化测试的小伙伴说web自动化测试真的不难,无非就是一些浏览器操作,页面元素操作,常规的情况很容易处理,再学一学特殊元素的处理,基本就能应付项目的测试了. 这个话倒没错,但是真正要学好自动化 ...
- Consul 简介
Consul包含很多组件,总体来数,Consul是一种服务发现和配置工具. 服务发现:一个客户端提供自己的服务,例如api服务,或者mysql服务,另一个客户端就可以利用Consul通过DNS或者ht ...
