Hessian的使用以及理解
官网
http://hessian.caucho.com/
Hessian的使用以及理解
Hessian版本:3.1.5
将包括如下的内容:
Hessian的基本使用
Hessian的原理
Hessian和Spring 的结合使用
扩展
简单说来,Hessian是一个轻量级的RPC框架(RPC是什么?请参考这里https://www.zhihu.com/question/25536695)。
它基于HTTP协议传输,使用Hessian二进制序列化,对于数据包比较大的情况比较友好。
但是它的参数和返回值都需要实现Serializable接口。
简单实现一个Hessian的例子:
创建接口和实现类
public interface Basic {
String sayHello(String name);
}
public class BasicImpl implements Basic{
public String sayHello(String name) {
return "This is Hello words from HESSIAN Server. " + name;
}
}
配置HessianServlet, web.xml中:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HessianServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>service-class</param-name>
<param-value>example.impl.BasicImpl</param-value>
</init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>HessianServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hessian</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
我们将会把Servlet部署在Tomcat上,端口8080。
编写客户端代码:
public class BasicClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String url = "http://localhost:8080/hessian";
HessianProxyFactory factory = new HessianProxyFactory();
factory.setOverloadEnabled(true);
Basic basic = (Basic) factory.create(Basic.class, url);
System.out.println(basic.sayHello("SW"));
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
创建HessianProxyFactory对象,创建Basic “对象”,然后调用sayHello()方法。
整个过程感觉很简单,并没有什么配置。
启动Tomcat,运行Client。
输出如下:
This is Hello words from HESSIAN Server. SW
可见是调用成功了。
等等,这个过程到底发生了些什么?
我们先从服务端说起,主要是有这几个步骤:
编写接口和实现类
在web.xml中声明HessianServlet,并且将上一步的实现类设置为Servlet的[service-class]属性值
将Servlet部署在Tomcat容器中
可见我们所有的工作都围绕在HessianServlet在展开。该Servlet中有两个比较重要的方法:init()、service();
init方法初始化服务和服务对象,主要分为3步:
通过home-class或者service-class创建服务端的实现类实例;
if (_homeImpl != null) {
}
else if (getInitParameter("home-class") != null) {
String className = getInitParameter("home-class");
Class homeClass = loadClass(className);
_homeImpl = homeClass.newInstance();
init(_homeImpl);
}
else if (getInitParameter("service-class") != null) {
String className = getInitParameter("service-class");
Class homeClass = loadClass(className);
_homeImpl = homeClass.newInstance();
init(_homeImpl);
}
else {
if (getClass().equals(HessianServlet.class))
throw new ServletException("server must extend HessianServlet");
_homeImpl = this;
}
通过home-api或者api-class加载实现类的接口对象;
if (_homeAPI != null) {
}
else if (getInitParameter("home-api") != null) {
String className = getInitParameter("home-api");
_homeAPI = loadClass(className);
}
else if (getInitParameter("api-class") != null) {
String className = getInitParameter("api-class");
_homeAPI = loadClass(className);
}
else if (_homeImpl != null)
_homeAPI = _homeImpl.getClass();
init方法还会创建HessianSkeleton对象,这是Hessian服务端的核心功能部分。
HessianSkeleton继承自AbstractSkeleton,其构造方法,将会从实现类中抽取方法和方法的Method对象,并且存储到_methodMap中。
对于一个Servlet来说其service方法是对外提供服务的方法:
/**
* Execute a request. The path-info of the request selects the bean.
* Once the bean's selected, it will be applied.
*/
public void service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException
{
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request;
HttpServletResponse res = (HttpServletResponse) response; if (! req.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
res.setStatus(500, "Hessian Requires POST");
PrintWriter out = res.getWriter(); res.setContentType("text/html");
out.println("<h1>Hessian Requires POST</h1>"); return;
} String serviceId = req.getPathInfo();
String objectId = req.getParameter("id");
if (objectId == null)
objectId = req.getParameter("ejbid"); ServiceContext.begin(req, serviceId, objectId); try {
InputStream is = request.getInputStream();
OutputStream os = response.getOutputStream(); HessianInput in = new HessianInput(is);
HessianOutput out = new HessianOutput(os); if (objectId != null)
_objectSkeleton.invoke(in, out);
else
_homeSkeleton.invoke(in, out);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (ServletException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new ServletException(e);
} finally {
ServiceContext.end();
}
}
最主要的是调用HessianSkeleton对象的invoke方法。注意,Servlet实例中有两个HessianSkeleton变量,分别是:_objectSkeleton和 _homeSkeleton,调用谁,是由objectid决定的。此处还有不明白的地方。
invoke方法:
首先从HessianInput对象中获取到Method信息,获取到真正的service对象。
根据反射机制,调用service对象的invoke方法,获取到返回值。
最后调用HessianOutput对象将结果写回到调用方。
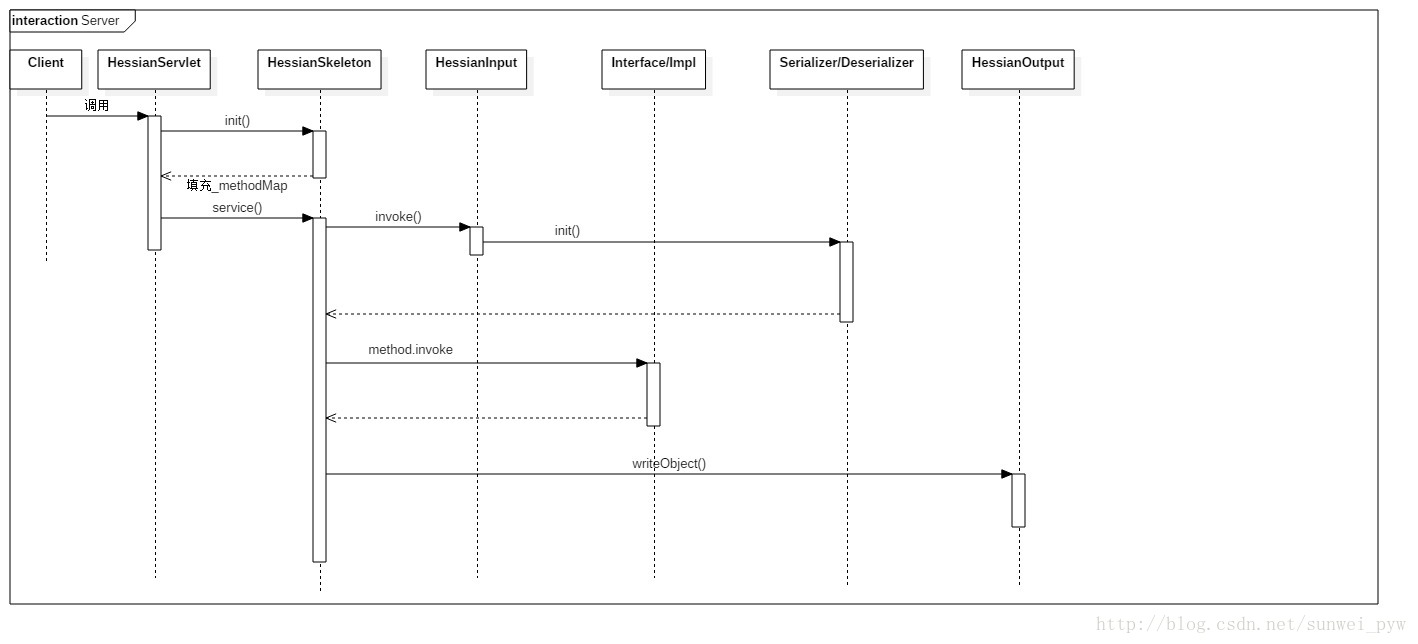
客户端代码
Hessian原生API编写客户端HessianClient:
public class BasicClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
String url = "http://localhost:8080/hessian";
HessianProxyFactory factory = new HessianProxyFactory();
factory.setOverloadEnabled(true);
Basic basic = (Basic) factory.create(Basic.class, url);
System.out.println(basic.sayHello("SW"));
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
创建HessianProxyFacotry,创建接口Basic的代理对象,然后调用sayHello()方法。
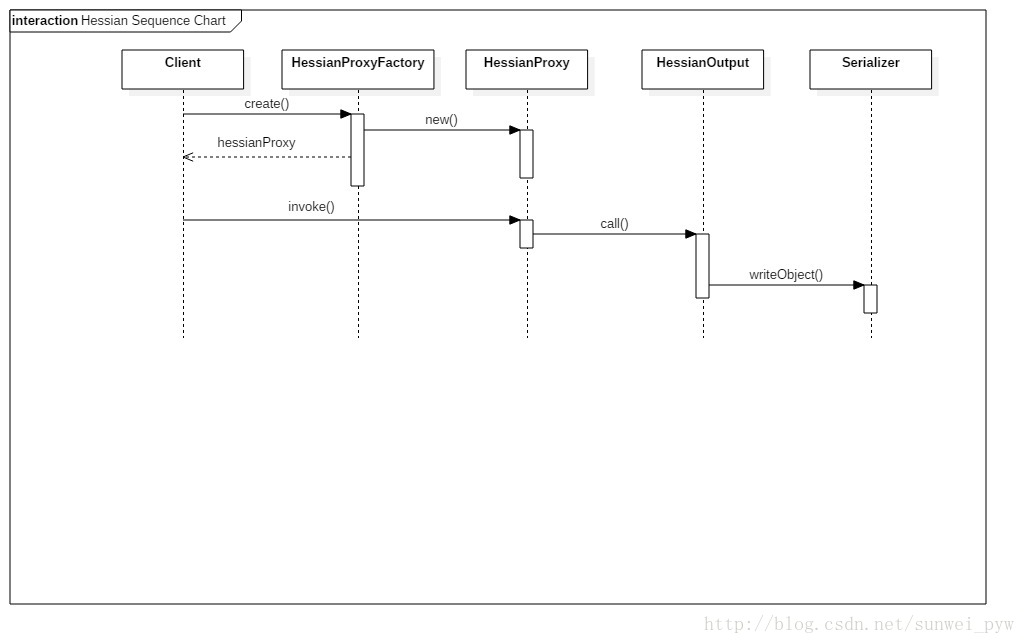
那么重点就在于创建代理对象,首先创建HessianProxyFacotry对象,构造方法中创建了一个HessianProxyResolver对象,这个对象的lookup方法将用来查找远程服务。此外HessianProxyFacotry还有包括权限验证方面的支持。
创建了factory之后,接下来就是通过Class对象和远程服务的URL创建代理对象了。
HessianProxyFactory使用HessianProxy对象作为代理的Handler,也就是说,我们对代理对象的所有操作,都会由这个handler来处理。handler的invoke方法,在进行一些方法名和参数的确认之后,创建HttpURLConnection对象,调用sendRequest方法,将方法名和参数用HessianOutput对象(设置序列化的方式)的call方法,写入到服务端。
主要代码如下:
protected URLConnection sendRequest(String methodName, Object []args)
throws IOException
{
URLConnection conn = null; conn = _factory.openConnection(_url); // Used chunked mode when available, i.e. JDK 1.5.
if (_factory.isChunkedPost() && conn instanceof HttpURLConnection) {
try {
HttpURLConnection httpConn = (HttpURLConnection) conn; httpConn.setChunkedStreamingMode(8 * 1024);
} catch (Throwable e) {
}
} addRequestHeaders(conn); OutputStream os = null; try {
os = conn.getOutputStream();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new HessianRuntimeException(e);
} try {
if (log.isLoggable(Level.FINEST)) {
PrintWriter dbg = new PrintWriter(new LogWriter(log));
os = new HessianDebugOutputStream(os, dbg);
} AbstractHessianOutput out = _factory.getHessianOutput(os); out.call(methodName, args);
out.flush(); return conn;
} catch (IOException e) {
if (conn instanceof HttpURLConnection)
((HttpURLConnection) conn).disconnect(); throw e;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (conn instanceof HttpURLConnection)
((HttpURLConnection) conn).disconnect(); throw e;
}
}
服务端拿到请求,进行反序列化,然后将方法调用,再将结果序列化之后写回到connection。所以,客户端在sendRequest之后,所要做的就是将返回的结果进行解析,看返回的code是不是200:
conn = sendRequest(mangleName, args);
if (conn instanceof HttpURLConnection) {
httpConn = (HttpURLConnection) conn;
int code = 500;
try {
code = httpConn.getResponseCode();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
parseResponseHeaders(conn);
if (code != 200) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
int ch;
.....
AbstractHessianInput in = _factory.getHessianInput(is);
in.startReply();
Object value = in.readObject(method.getReturnType());
if (value instanceof InputStream) {
value = new ResultInputStream(httpConn, is, in, (InputStream) value);
is = null;
httpConn = null;
}
else
in.completeReply();
return value;
解析HessianInput对象,并且从中读取到结果返回。
至此,服务端和客户端的交互过程已经简单地介绍完毕。
Spring也为Hessian提供了很友好的支持,通过使用spring-remoting包,我们可以很方便地发布和调用服务。
这部分提供一个简单的实现例子:
在web.xml中,我们配置SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet> <servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>SpringMVC</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/remote/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd"
default-lazy-init="true"> <bean id = "basicService" class="example.impl.BasicImpl"/> <bean name="/basicHessianService" class="org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianServiceExporter">
<property name="service" ref="basicService"/>
<property name="serviceInterface" value="example.Basic"/>
</bean>
</beans>
这里,我们使用了org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianServiceExporter来发布服务。将程序部署在tomcat中。
客户端,使用org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianProxyFactoryBean来代理请求:
client.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd"
default-lazy-init="true"> <bean id="basicService" class="org.springframework.remoting.caucho.HessianProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="serviceUrl" value="http://localhost:8080/remote/basicHessianService"/>
<property name="serviceInterface" value="example.Basic"/>
</bean>
</beans>
编写客户端:
public class SpringClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"classpath:client.xml"});
Basic basic = (Basic)context.getBean("basicService");
System.out.println(basic.sayHello("SUNWEI"));
}
}
这样,服务端/客户端的代码都已经编写完成。
最原始的实现,我们的服务是通过Servlet来绑定的,而Spring的实现,我们使用了SpringMVC的加载时机,将配置文件加载。HessianServiceExporter
public class HessianServiceExporter extends RemoteExporter implements HttpRequestHandler, InitializingBean {
....
这个类实现了InitializingBean接口,这是spring-beans包中很重要的一个扩展接口。
这个接口的说明如下:
Interface to be implemented by beans that need to react once all their
properties have been set by a BeanFactory: for example, to perform custom
initialization, or merely to check that all mandatory properties have been set.
也就是说,它会随着Spring容器(此处为Spring MVC容器)的启动而被加载。看看HessianServiceExporter的实现:
public void prepare() {
HessianSkeleton skeleton = null;
try {
try {
Constructor ctor = (class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton == null?(class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton = class$("com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianSkeleton")):class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton).getConstructor(new Class[]{class$java$lang$Object == null?(class$java$lang$Object = class$("java.lang.Object")):class$java$lang$Object, class$java$lang$Class == null?(class$java$lang$Class = class$("java.lang.Class")):class$java$lang$Class});
this.checkService();
this.checkServiceInterface();
skeleton = (HessianSkeleton)ctor.newInstance(new Object[]{this.getProxyForService(), this.getServiceInterface()});
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var4) {
Constructor ctor = (class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton == null?(class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton = class$("com.caucho.hessian.server.HessianSkeleton")):class$com$caucho$hessian$server$HessianSkeleton).getConstructor(new Class[]{class$java$lang$Object == null?(class$java$lang$Object = class$("java.lang.Object")):class$java$lang$Object});
skeleton = (HessianSkeleton)ctor.newInstance(new Object[]{this.getProxyForService()});
}
} catch (Throwable var5) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Hessian skeleton initialization failed", var5);
}
if(hessian2Available) {
this.skeletonInvoker = new Hessian2SkeletonInvoker(skeleton, this.serializerFactory);
} else {
this.skeletonInvoker = new Hessian1SkeletonInvoker(skeleton, this.serializerFactory);
}
}
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Assert.notNull(this.skeletonInvoker, "HessianServiceExporter has not been initialized");
if(!"POST".equals(request.getMethod())) {
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException("POST", "HessianServiceExporter only supports POST requests");
} else {
try {
this.skeletonInvoker.invoke(request.getInputStream(), response.getOutputStream());
} catch (Throwable var4) {
throw new NestedServletException("Hessian skeleton invocation failed", var4);
}
}
}
在prepare方法中,获取service和serviceInterface的配置,创建HessianSkeleton对象。
同时,还实现了HttpRequestHandler,spring-web中的接口。
又因为实现了HttpRequestHandler接口,所以在handleRequest方法中,可以像HessianServlet的service方法一样,调用Hessian2SkeletonInvoker的invoke方法进行实际的方法调用。
最后一点尾巴
定义一个自己的HttpRequestHandler对象,配置在applicationContext.xml中,然后通过页面访问:
public class MyHandler implements HttpRequestHandler, InitializingBean {
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("初始化 MyHandler");
}
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("执行 MyHandler");
}
}
配置在applicationContext.xml中:
<bean id = "/myHandler" class="client.MyHandler"/>
通过Spring MVC的上下文加载该Handler,启动Tomcat的时候,可以看到控制台输出:
初始化 MyHandler
在浏览器中访问:http://localhost:8080/remote/myHandler
将触发执行:执行 MyHandler
Hessian的使用以及理解的更多相关文章
- Xml,Json,Hessian,Protocol Buffers序列化对比
简介 这篇博客主要对Xml,Json,Hessian,Protocol Buffers的序列化和反序列化性能进行对比,Xml和Json的基本概念就不说了. Hessian:Hessian是一个轻量级的 ...
- Deep learning:四十三(用Hessian Free方法训练Deep Network)
目前,深度网络(Deep Nets)权值训练的主流方法还是梯度下降法(结合BP算法),当然在此之前可以用无监督的方法(比如说RBM,Autoencoder)来预训练参数的权值,而梯度下降法应用在深度网 ...
- 深入理解图优化与g2o:图优化篇
前言 本节我们将深入介绍视觉slam中的主流优化方法——图优化(graph-based optimization).下一节中,介绍一下非常流行的图优化库:g2o. 关于g2o,我13年写过一个文档,然 ...
- RMI、Hessian、Burlap、Httpinvoker、WebService的比较
RMI.Hessian.Burlap.Httpinvoker.WebService的比较 2(转) [2]Java远程调用方法性能比较 [IT168技术]现在,Java远程调用方法很多,各种方 ...
- Kryo 为什么比 Hessian 快
Kryo 是一个快速高效的Java对象图形序列化框架,它原生支持java,且在java的序列化上甚至优于google著名的序列化框架protobuf.由于 protobuf需要编写Schema文件(. ...
- 理解本真的REST架构风格
http://kb.cnblogs.com/page/186516/ 引子 在移动互联网.云计算迅猛发展的今天,作为一名Web开发者,如果您还没听说过“REST”这个buzzword,显然已经落 ...
- Hessian源码分析--总体架构
Hessian是一个轻量级的remoting onhttp工具,使用简单的方法提供了RMI的功能. 相比WebService,Hessian更简单.快捷.采用的是二进制RPC协议,因为采用的是二进制协 ...
- Jacobian矩阵、Hessian矩阵和Newton's method
在寻找极大极小值的过程中,有一个经典的算法叫做Newton's method,在学习Newton's method的过程中,会引入两个矩阵,使得理解的难度增大,下面就对这个问题进行描述. 1, Jac ...
- 【转载】理解本真的REST架构风格
本文将带您领略REST架构的起源.与Web的关系.REST架构的本质及特性,以及REST架构与其他架构风格之间的比较. 引子 在移动互联网.云计算迅猛发展的今天,作为一名Web开发者,如果您还没听说过 ...
随机推荐
- 1005:Number Sequence(hdu,数学规律题)
Problem Description A number sequence is defined as follows: f(1) = 1, f(2) = 1, f(n) = (A * f(n - 1 ...
- LeetCode(82):删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
Medium! 题目描述: 给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 的数字. 示例 1: 输入: 1->2->3->3->4->4- ...
- 制作linux下的.run安装包
前言 之前往linux上安装一个软件,都是以压缩包或者压缩包+shell的方法,这每次安装,都是先scp到某个目录, 解压,安装......稍微厉害的,会写个shell脚本.但是还是达不到真正的快速方 ...
- 80端口被占用 导致apach无法启动问题
1.查找是哪个程序占用了80端口 netstat -ano 列出所有进程 观察 “本地地址” 列 找到对应的PID 我这里是4 简单的办法,打开任务管理器,查看PID是4的 是哪个进程. 发现是Sys ...
- asp.net core 图片验证码,后台验证
验证方法: public static string VerificationCodeCacheFormat="vcode_cache_{0}"; public IActionRe ...
- OS模块常用方法
#OS模块 #os模块就是对操作系统进行操作,使用该模块必须先导入模块: import os #getcwd() 获取当前工作目录(当前工作目录默认都是当前文件所在的文件夹) result = os. ...
- 现在k8s新版里,如何在每个node上运行一个带privileged的daemonset
以前,我们会在kubelet上加--allow-prividged启动参数来实现. 而现在,更推荐的是用pod secureity policy来实现.前面的那种方式以后会被废弃. https://k ...
- mybatis_generator_逆向工程的使用笔记
1:解压mybatis_generator_1.3.1.zip文件. 2:把features,pougins文件夹copy到D:\java\eclipse\eclipse目录下(D:\java\ecl ...
- LeetCode高频148错题记录
3. Max Points on a Line 共线点个数3种解法 思路一:思考如何确定一条直线,两点法,确定斜率后带入一点.有三种情况,1. 两点重合,2. 斜率不存在,3. 正常算,依次以每个点为 ...
- kudu的分区方式
为了提供可扩展性,Kudu 表被划分为称为 tablets 的单元,并分布在许多 tablet servers 上.行总是属于单个 tablet .将行分配给 tablet 的方法由在表创建期间设置的 ...
