Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction读书笔记(3)--finite MDPs
> 目 录 <
- Agent–Environment Interface
- Goals and Rewards
- Returns and Episodes
- Policies and Value Functions
- Optimal Policies and Optimal Value Functions
> 笔 记 <
Agent–Environment Interface
MDPs are meant to be a straightforward framing of the problem of learning from interaction to achieve a goal. The learner and decision maker is called the agent. The thing it interacts with, comprising everything outside the agent, is called the environment. These interact continually, the agent selecting actions and the environment responding to these actions and presenting new situations to the agent.1 The environment also gives rise to rewards, special numerical values that the agent seeks to maximize over time through its choice of actions.
More specifcally, the agent and environment interact at each of a sequence of discrete time steps, t = 0,1,2,.... At each time step t, the agent receives some representation of the environment's state, $S_{t}\in S$, where $S$ is the set of possible states, and on that basis selects an action, $A_{t}\in A(S_{t})$, where $A(S_{t})$ is the set of actions available in state $S_{t}$. One time step later, in part as a consequence of its action, the agent receives a numerical reward, $R_{t+1}\in R \subset \mathbb{R}$, and finds itself in a new state, $S_{t+1}$.
At each time step, the agent implements a mapping from states to probabilities of selecting each possible action. This mapping is called the agent's policy and is denoted $\pi_{t}(a|s)$ is the probability that $A_{t}=a$ if $S_{t}=s$. Reinforcement learning methods specify how the agent changes its policy as a result of its experience. The agent's goal, roughly speaking, is to maximize the total amount of reward it receives over the long run.
the actions are the choices made by the agent; the states are the basis for making the choices; and the rewards are the basis for evaluating the choices.
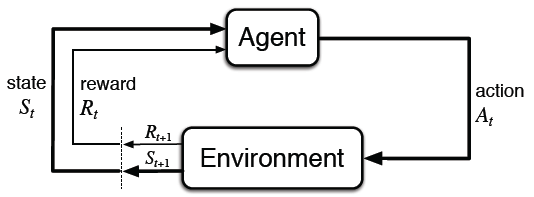
图1. agent-environment interaction in a MDP
马尔可夫性(Markov property): 如果state signal具有马尔科夫性,那么当前状态只跟上一状态有关,它包含了所有从过去经历中得到的信息。马尔可夫性对RL而言很重要,∵decisions和values通常都被认为是一个只跟当前state相关的函数。
MDP的动态性:$p(s',r|s,a)=Pr\left \{ S_{t}=s',R_{t}=r|S_{t-1}=s,A_{t-1}=a \right \}$,
where $ \underset{s'\in S \ r\in R}{\sum \sum}p(s',r|s,a)=1 $, for all $s\in S$, $a\in A(s)$.
基于the dynamics of the MDP, 我们可以很容易地得到状态转移概率(state-transition probabilities, $p(s'|s,a)$),state-action的期望回报(the expected rewards for state–action pairs, $r(s,a)$),以及state-action-next state的期望回报(the expected rewards for state–action-next state, $r(s,a,s')$)。
Goals and Rewards
agent的goal是以一个从environment传递给agent的reward signal的形式存在的。我们通过定义reward signal的值,可以实现跟agent的交流,告诉它what you want it to achieve, not how you want it achieved。
Agent的目标是最大化total reward。因此,最大化的不是immediate reward,而是cumulative reward in the long run。
Returns and Episodes
The return is the function of future rewards that the agent seeks to maximize (in expected value). return有多种形式,取决于task本身和是否希望对回报进行折扣。
Expected return: $G_{t}=R_{t+1}+R_{t+2}+...+R_{T}$, where T is a final time step。适合于episodic tasks。
Episodic tasks: each episode ends in the terminal state, followed by a reset to a standard starting state or a sample from a standard distribution of starting states.
Continuing tasks: the agent–environment interaction doesn’t break naturally into identifiable episodes, but goes on continually without limit.
Expected discounted return: $G_{t}=R_{t+1}+\gamma R_{t+2}+ \gamma ^{2}R_{t+3}+...=\sum_{k=0}^{\infty}\gamma ^{k}R_{t+k+1}$。其中,折扣率(discount rate, $\gamma$)决定了未来rewards的当前价值。适合于continuing tasks。
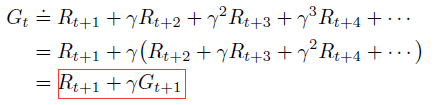
Policies and Value Functions
Value functions: functions of states (or state-action pairs) that estimate how good it is for the agent to be in a given state (or how good it is to perform a given action in a given state). The notion of “how good” here is defined in terms of future rewards that can be expected, or, in terms of the expected return from that state (or state-action pair).
Policy: a mapping from states to probabilities of selecting each possible action. If the agent is following policy $\pi$ at time t, then $\pi(a|s)$ is the probability that $A_{t} = a$ if $S_{t} = s$.
the value function of a state s under a policy $\pi$: (i.e. the expected return when starting in s and following $\pi$ thereafter)
We call the function $ v_{\pi}$ is the state-value function for policy $\pi$
the value of taking action a in state s under a policy $\pi$: (i.e. the expected return starting from s, taking the action a, and thereafter following policy $\pi$)
We call $ q_{\pi}$ the action-value function for policy $\pi$
Bellman equation for $v_{\pi}$: It expresses a relationship between the value of a state and the values of its successor states.
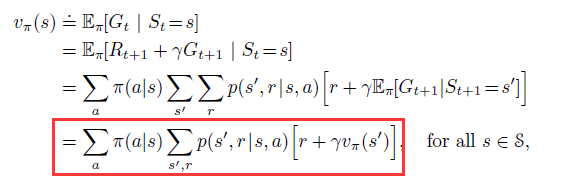
Optimal Policies and Optimal Value Functions
Value functions define a partial ordering over policies. $\pi> \pi'$ if and only if $v_{\pi}(s) > v_{\pi'}(s)$, for all $s \in S$. The optimal value functions assign to each state, or state–action pair, the largest expected return achievable by any policy.
Optimal policy $\pi_{*}$:A policy whose value functions are optimal. There is always at least one (can be many) policy that is better than or equal to all other policies.
Optimal state-value function:
Optimal action-value function:
用$v_{*}$来表示$q_{*}$:
Any policy that is greedy with respect to the optimal value functions must be an optimal policy. The Bellman optimality equations are special consistency conditions that the optimal value functions must satisfy and that can, in principle, be solved for the optimal value functions.
Bellman optimality equation for $v_{*}$:
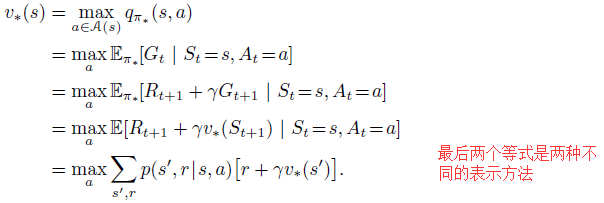
Bellman optimality equation for $q_{*}$:
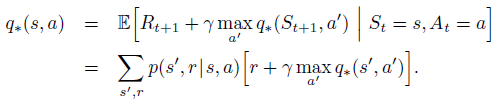
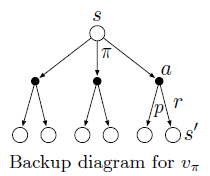
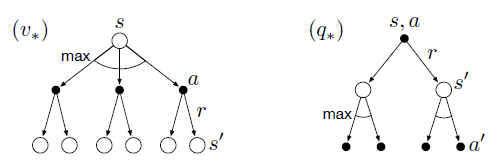
Backup diagrams for $v_{*}$ and $q_{*}$:
Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction读书笔记(3)--finite MDPs的更多相关文章
- Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction读书笔记(4)--动态规划
> 目 录 < Dynamic programming Policy Evaluation (Prediction) Policy Improvement Policy Iterat ...
- Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction读书笔记(1)--Introduction
> 目 录 < learning & intelligence 的基本思想 RL的定义.特点.四要素 与其他learning methods.evolutionary m ...
- Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction读书笔记(2)--多臂机
> 目 录 < k-armed bandit problem Incremental Implementation Tracking a Nonstationary Problem ...
- 《Machine Learning Yearing》读书笔记
——深度学习的建模.调参思路整合. 写在前面 最近偶尔从师兄那里获取到了吴恩达教授的新书<Machine Learning Yearing>(手稿),该书主要分享了神经网络建模.训练.调节 ...
- Machine Learning for hackers读书笔记(六)正则化:文本回归
data<-'F:\\learning\\ML_for_Hackers\\ML_for_Hackers-master\\06-Regularization\\data\\' ranks < ...
- Machine Learning for hackers读书笔记(三)分类:垃圾邮件过滤
#定义函数,打开每一个文件,找到空行,将空行后的文本返回为一个字符串向量,该向量只有一个元素,就是空行之后的所有文本拼接之后的字符串 #很多邮件都包含了非ASCII字符,因此设为latin1就可以读取 ...
- Machine Learning for hackers读书笔记_一句很重要的话
为了培养一个机器学习领域专家那样的直觉,最好的办法就是,对你遇到的每一个机器学习问题,把所有的算法试个遍,直到有一天,你凭直觉就知道某些算法行不通.
- Machine Learning for hackers读书笔记(十二)模型比较
library('ggplot2')df <- read.csv('G:\\dataguru\\ML_for_Hackers\\ML_for_Hackers-master\\12-Model_C ...
- Machine Learning for hackers读书笔记(十)KNN:推荐系统
#一,自己写KNN df<-read.csv('G:\\dataguru\\ML_for_Hackers\\ML_for_Hackers-master\\10-Recommendations\\ ...
随机推荐
- Monad Explained in One Picture
The point of Monad is composability. In the green category, T -> Monad<U> and U -> Monad ...
- 背水一战 Windows 10 (111) - 通知(Tile): secondary tile 模板之图片, secondary tile 模板之分组
[源码下载] 背水一战 Windows 10 (111) - 通知(Tile): secondary tile 模板之图片, secondary tile 模板之分组 作者:webabcd 介绍背水一 ...
- Docker应用:Kubernetes(容器集群)
阅读目录: Docker应用:Hello World Docker应用:Docker-compose(容器编排) Docker应用:Kubernetes(容器集群) 前言: 终于出第三篇了,上个月就已 ...
- 微信团队分享:Kotlin渐被认可,Android版微信的技术尝鲜之旅
本文由微信开发团队工程是由“oneliang”原创发表于WeMobileDev公众号,内容稍有改动. 1.引言 Kotlin 是一个用于现代多平台应用的静态编程语言,由 JetBrains 开发( ...
- 关键字提取算法TF-IDF
在文本分类的学习过程中,在“如何衡量一个关键字在文章中的重要性”的问题上,遇到了困难.在网上找了很多资料,大多数都提到了这个算法,就是今天要讲的TF-IDF. 总起 TF-IDF,理解起来相当简单,他 ...
- Metasploit Framework(5)弱点扫描
文章的格式也许不是很好看,也没有什么合理的顺序 完全是想到什么写一些什么,但各个方面都涵盖到了 能耐下心看的朋友欢迎一起学习,大牛和杠精们请绕道 当我们发现了目标机器开放的端口,开启的服务等等之后 就 ...
- 一句话的事儿,Head first 设计模式
head first 设计模式,是比较有趣的一本设计模式的书. 在学校里看书和在工作时看书,意义是不一样的.在学校时是为读书而读书,我们可以从0到1,我们有的是时间.但是工作后就不一样. 我觉得这时的 ...
- SpringMVC项目容易出现的BUG
1.400错误:1.语义有误,当前请求无法被服务器理解.除非进行修改,否则客户端不应该重复提交这个请求. 2.请求参数有误. 你发送的请求有误,这个问题去页面提交的地方看. 如:你想删除一条数据,id ...
- java开发个人简历
求职意向 Java开发工程师 陈 楠 性 别:男 出生年月 :1995.07 民 族:汉族 联系方式 :159-3306-7520 学 历:本科 电子邮件 :15933067520@163.com 教 ...
- asp.net core 2.0发布到IIS流程及报错解决方案
我这是个新装的服务器,没有安装任何软件. 一.发布流程 1.安装AspNetCoreModule托管模块,同时会自动安装..net core runtime DotNetCore.2.0.8-Wi ...
