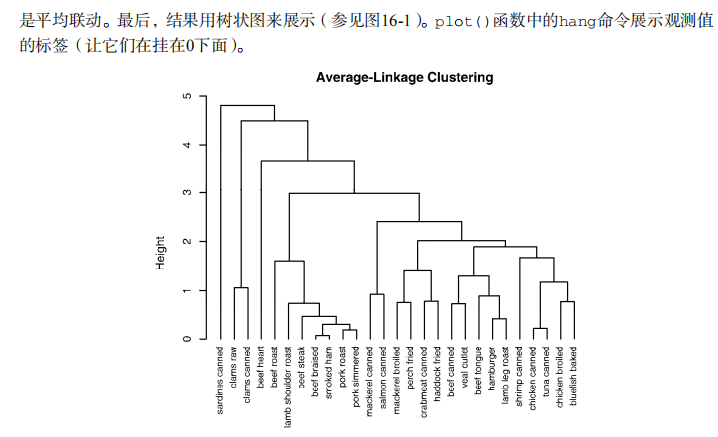
吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:聚类分析















#-------------------------------------------------------#
# R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 16 #
# Cluster analysis #
# requires packaged NbClust, flexclust, rattle #
# install.packages(c("NbClust", "flexclust", "rattle")) #
#-------------------------------------------------------# par(ask=TRUE)
opar <- par(no.readonly=FALSE) # Calculating Distances
data(nutrient, package="flexclust")
head(nutrient, 2)
d <- dist(nutrient)
as.matrix(d)[1:4,1:4] # Listing 16.1 - Average linkage clustering of nutrient data
data(nutrient, package="flexclust")
row.names(nutrient) <- tolower(row.names(nutrient))
nutrient.scaled <- scale(nutrient)
d <- dist(nutrient.scaled)
fit.average <- hclust(d, method="average")
plot(fit.average, hang=-1, cex=.8, main="Average Linkage Clustering") # Listing 16.2 - Selecting the number of clusters
library(NbClust)
nc <- NbClust(nutrient.scaled, distance="euclidean",
min.nc=2, max.nc=15, method="average")
par(opar)
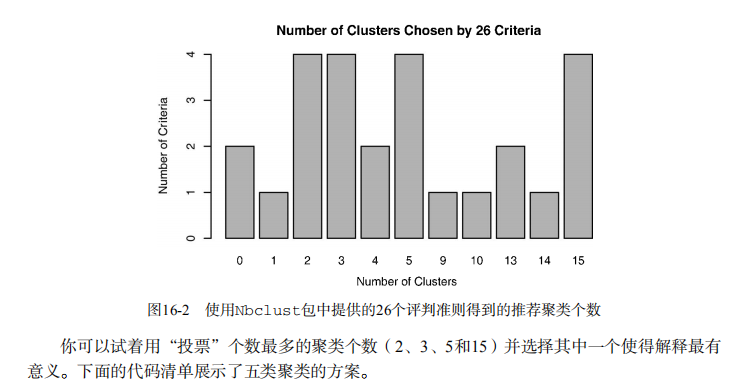
table(nc$Best.n[1,])
barplot(table(nc$Best.n[1,]),
xlab="Numer of Clusters", ylab="Number of Criteria",
main="Number of Clusters Chosen by 26 Criteria") # Listing 16.3 - Obtaining the final cluster solution
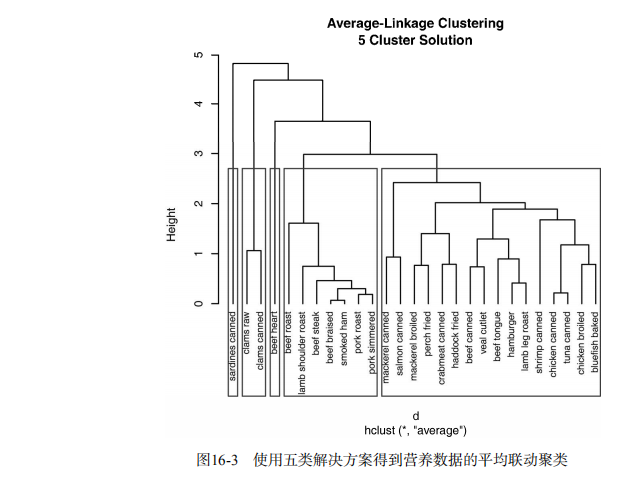
clusters <- cutree(fit.average, k=5)
table(clusters)
aggregate(nutrient, by=list(cluster=clusters), median)
aggregate(as.data.frame(nutrient.scaled), by=list(cluster=clusters),
median)
plot(fit.average, hang=-1, cex=.8,
main="Average Linkage Clustering\n5 Cluster Solution")
rect.hclust(fit.average, k=5) # Plot function for within groups sum of squares by number of clusters
wssplot <- function(data, nc=15, seed=1234){
wss <- (nrow(data)-1)*sum(apply(data,2,var))
for (i in 2:nc){
set.seed(seed)
wss[i] <- sum(kmeans(data, centers=i)$withinss)}
plot(1:nc, wss, type="b", xlab="Number of Clusters",
ylab="Within groups sum of squares")} # Listing 16.4 - K-means clustering of wine data
data(wine, package="rattle")
head(wine)
df <- scale(wine[-1])
wssplot(df)
library(NbClust)
set.seed(1234)
nc <- NbClust(df, min.nc=2, max.nc=15, method="kmeans")
par(opar)
table(nc$Best.n[1,])
barplot(table(nc$Best.n[1,]),
xlab="Numer of Clusters", ylab="Number of Criteria",
main="Number of Clusters Chosen by 26 Criteria")
set.seed(1234)
fit.km <- kmeans(df, 3, nstart=25)
fit.km$size
fit.km$centers
aggregate(wine[-1], by=list(cluster=fit.km$cluster), mean) # evaluate clustering
ct.km <- table(wine$Type, fit.km$cluster)
ct.km
library(flexclust)
randIndex(ct.km) # Listing 16.5 - Partitioning around mediods for the wine data
library(cluster)
set.seed(1234)
fit.pam <- pam(wine[-1], k=3, stand=TRUE)
fit.pam$medoids
clusplot(fit.pam, main="Bivariate Cluster Plot") # evaluate clustering
ct.pam <- table(wine$Type, fit.pam$clustering)
ct.pam
randIndex(ct.pam) ## Avoiding non-existent clusters
library(fMultivar)
set.seed(1234)
df <- rnorm2d(1000, rho=.5)
df <- as.data.frame(df)
plot(df, main="Bivariate Normal Distribution with rho=0.5") wssplot(df)
library(NbClust)
nc <- NbClust(df, min.nc=2, max.nc=15, method="kmeans")
par(opar)
barplot(table(nc$Best.n[1,]),
xlab="Numer of Clusters", ylab="Number of Criteria",
main ="Number of Clusters Chosen by 26 Criteria") library(ggplot2)
library(cluster)
fit <- pam(df, k=2)
df$clustering <- factor(fit$clustering)
ggplot(data=df, aes(x=V1, y=V2, color=clustering, shape=clustering)) +
geom_point() + ggtitle("Clustering of Bivariate Normal Data") plot(nc$All.index[,4], type="o", ylab="CCC",
xlab="Number of clusters", col="blue")
吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:聚类分析的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:R语言的安装与配置
下载R语言和开发工具RStudio安装包 先安装R
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:数据集和数据结构
数据集的概念 数据集通常是由数据构成的一个矩形数组,行表示观测,列表示变量.表2-1提供了一个假想的病例数据集. 不同的行业对于数据集的行和列叫法不同.统计学家称它们为观测(observation)和 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:导入数据
2.3.6 导入 SPSS 数据 IBM SPSS数据集可以通过foreign包中的函数read.spss()导入到R中,也可以使用Hmisc 包中的spss.get()函数.函数spss.get() ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:使用键盘、带分隔符的文本文件输入数据
R可从键盘.文本文件.Microsoft Excel和Access.流行的统计软件.特殊格 式的文件.多种关系型数据库管理系统.专业数据库.网站和在线服务中导入数据. 使用键盘了.有两种常见的方式:用 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:R语言的简单介绍和使用
假设我们正在研究生理发育问 题,并收集了10名婴儿在出生后一年内的月龄和体重数据(见表1-).我们感兴趣的是体重的分 布及体重和月龄的关系. 可以使用函数c()以向量的形式输入月龄和体重数据,此函 数 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:基础知识
1.基础数据结构 1.1 向量 # 创建向量a a <- c(1,2,3) print(a) 1.2 矩阵 #创建矩阵 mymat <- matrix(c(1:10), nrow=2, n ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:图形初阶(续二)
# ----------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 3 # # Gettin ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:图形初阶(续一)
# ----------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 3 # # Gettin ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:图形初阶
# ----------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 3 # # Gettin ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:基本图形(续二)
#---------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 6 ...
随机推荐
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 JAVA开发学习:String 类
public class StringDemo{ public static void main(String args[]){ char[] helloArray = { 'r', 'u', 'n' ...
- .jar文件不能解析、识别
- java的io字符流关闭和刷新.flush();
因为内置缓冲区的原因,如果不关闭输出流,无法写出字符到文件中. 但是关闭的流对象,是无法继续写出数据 的.如果我们既想写出数据,又想继续使用流,就需要 flush 方法了. flush :刷新缓冲区, ...
- JavaScript详解(三)
JavaScript的数组 JavaScript中的数组具有相当的灵活性,除了能存储数据外,还提供了一系列的属性和方法.因为JavaScript本身是一个弱类型语言,故其数组不会限制存放数据的类型. ...
- Matlab高级教程_第四篇:Matlab高级函数_关键词:drawnow,addpoints,animatedline,getpoints
0. MATLAB真实航母基本的工具,其中的函数/工具不计其数,而且有些函数/工具非常的炫酷.在MATLAB第四篇章把平时工作中用到的些许函数进行使用的讲解 主题1.:drawnow 解释:更新图窗并 ...
- E. Arson In Berland Forest(思维,找二维阵列中的矩阵,二分)
题:https://codeforces.com/contest/1262/problem/E 分析:预处理出阵列中的矩阵,然后二分答案还原题目的烧火过程,判断是否满足要求 #include<b ...
- Kafa 的安装配置及使用
1.kafka 的简介及应用场景 Apache Kafka是一个分布式的消息系统,可用于统计,日志及流处理 2.kafka 基本原理 3.kafka 集群体系结构 4.kafka实例 https:// ...
- Pickle的简单使用
单词Pickle的中文意思是“泡菜.腌菜.菜酱”的意思,Pickle是Python的一个包,主要功能是对数据进行序列化和反序列化.那么什么叫序列化和反序列化呢? 其序列化过程就是把数据转化成二进制数据 ...
- Graylog
Graylog #Graylog 是与 ELK 可以相提并论的一款集中式日志管理方案,支持数据收集.检索.可视化 #Graylog 架构 - Graylog 负责接收来自各种设备和应用的日志,并为用 ...
- Linux_切换,创建,和删除目录
切换目录 cd /tmp cd ..切换到上一个目录 cd ~ 进入当前用户的家目录 cd ~nbzyh 进入zyh用户 创建目录 当当前在tmp中时:mkdir /tmp/sam 这里用的是绝对 ...
