HDU 1885 Key Task 国家压缩+搜索
Key Task
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1176 Accepted Submission(s): 462
long corridors that fork and join at absolutely unexpected places.
The result is that some first-graders have often di?culties finding the right way to their classes. Therefore, the Student Union has developed a computer game to help the students to practice their orientation skills. The goal of the game is to find the way
out of a labyrinth. Your task is to write a verification software that solves this game.
The labyrinth is a 2-dimensional grid of squares, each square is either free or filled with a wall. Some of the free squares may contain doors or keys. There are four di?erent types of keys and doors: blue, yellow, red, and green. Each key can open only doors
of the same color.
You can move between adjacent free squares vertically or horizontally, diagonal movement is not allowed. You may not go across walls and you cannot leave the labyrinth area. If a square contains a door, you may go there only if you have stepped on a square
with an appropriate key before.
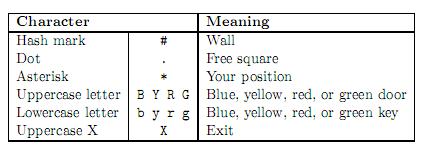
Note that it is allowed to have
You may assume that the marker of your position (“*”) will appear exactly once in every map.
There is one blank line after each map. The input is terminated by two zeros in place of the map size.
One step is defined as a movement between two adjacent cells. Grabbing a key or unlocking a door does not count as a step.
1 10
*........X 1 3
*#X 3 20
####################
#XY.gBr.*.Rb.G.GG.y#
#################### 0 0
Escape possible in 9 steps.
The poor student is trapped!
Escape possible in 45 steps.
每一个位置有16种状态,能够用一个vis三维数组表示每一个点的16种状态,对于四种锁,每种锁用一位来表示,有钥匙标记为1。否则标记为0.然后bfs搜索一下即可了。
//109MS 556K
#include<stdio.h>
#include<queue>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#define M 107
using namespace std;
int n,m,s,t;
int dir[4][2]={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
char g[M][M];
bool vis[M][M][17];
char up[4]={'B','Y','R','G'};
char low[4]={'b','y','r','g'};
struct node
{
int step,x,y,key;
};
int bfs()
{
queue<node>q;
node now,next;
now.x=s;now.y=t;now.step=now.key=0;
vis[s][t][0]=true;
q.push(now);
while(!q.empty())
{
now=q.front();
q.pop();
if(g[now.x][now.y]=='X')return now.step;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
next.x=now.x+dir[i][0];
next.y=now.y+dir[i][1];
next.step=now.step+1;
next.key=now.key;
if(next.x<1||next.x>n||next.y<1||next.y>m||g[next.x][next.y]=='#')continue;//假设越界
if(g[next.x][next.y]>='A'&&g[next.x][next.y]<='Z'&&g[next.x][next.y]!='X')
{
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
if(g[next.x][next.y]==up[j])
{
if(next.key&(1<<j)&&!vis[next.x][next.y][next.key])//假设没有訪问过且拥有此锁的钥匙
{
vis[next.x][next.y][next.key]=true;
q.push(next);
}
break;
}
}
else if(g[next.x][next.y]>='a'&&g[next.x][next.y]<='z')
{
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
if(g[next.x][next.y]==low[j])
{
if((next.key&(1<<j))==0)//假设没有此钥匙
next.key+=(1<<j);
if(!vis[next.x][next.y][next.key])
{
vis[next.x][next.y][next.key]=true;
q.push(next);
}
}
}
else
{
if(!vis[next.x][next.y][next.key])
{
vis[next.x][next.y][next.key]=true;
q.push(next);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m),n|m)
{
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%s",g[i]+1);
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
if(g[i][j]=='*'){s=i;t=j;}
}
int ans=bfs();
if(ans==-1)printf("The poor student is trapped!\n");
else printf("Escape possible in %d steps.\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}
版权声明:本文博主原创文章。博客,未经同意不得转载。
HDU 1885 Key Task 国家压缩+搜索的更多相关文章
- HDU 1885 Key Task (带门和钥匙的迷宫搜索 bfs+二进制压缩)
传送门: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1885 Key Task Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task
题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1885 Key Task Description The Czech Technical Univers ...
- HDU 1885 Key Task(三维BFS)
题目链接 题意 : 出口不止一个,一共有四种颜色不同的门由大写字母表示,而钥匙则是对应的小写字母,当你走到门前边的位置时,如果你已经走过相应的钥匙的位置这个门就可以走,只要获得一把钥匙就可以开所有同颜 ...
- HDU 1885 Key Task (BFS + 状态压缩)
题意:给定一个n*m的矩阵,里面有门,有钥匙,有出口,问你逃出去的最短路径是多少. 析:这很明显是一个BFS,但是,里面又有其他的东西,所以我们考虑状态压缩,定义三维BFS,最后一维表示拿到钥匙的状态 ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task(bfs+状态压缩)
Problem Description The Czech Technical University years of its existence . Some of the university b ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task(bfs+位运算)
题意:矩阵中'#'表示墙,'.'表示通路,要求从起点'*'到达终点'X',途中可能遇到一些门(大写字母),要想经过,必须有对应的钥匙(小写字母).问能否完成,若能,花费的时间是多少. 分析:同hdu ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task (三维bfs)
题目 之前比赛的一个题, 当时是崔老师做的,今天我自己做了一下.... 还要注意用bfs的时候 有时候并不是最先到达的就是答案,比如HDU 3442 这道题是要求最小的消耗血量伤害,但是并不是最先到 ...
- hdu 1885 Key Task(bfs)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1885 再贴一个链接http://blog.csdn.net/u013081425/article/details ...
- HDU 1557 权利指数 国家压缩 暴力
HDU 1557 权利指数 状态压缩 暴力 ACM 题目地址:HDU 1557 权利指数 题意: 中文题,不解释. 分析: 枚举全部集合,计算集合中的和,推断集合里面的团体是否为关键团队. 代码: ...
随机推荐
- Hive Metastore ObjectStore PersistenceManager自动关闭bug解析
最近在测试HCatalog,由于Hcatalog本身就是一个独立JAR包,虽然它也可以运行service,但是其实这个service就是metastore thrift server,我们在写基于Hc ...
- uva796(求桥数目)
传送门:Critical Links 题意:给出一个无向图,按顺序输出桥. 分析:模板题,求出桥后排个序输出. #include <cstdio> #include <cstring ...
- 基于Andoird 4.2.2的Account Manager源代码分析学习:创建选定类型的系统帐号
AccountManager.addAccount() public AccountManagerFuture<Bundle> addAccount(final String accoun ...
- JVM学习03_new对象的内存图讲解,以及引出static方法(转)
目录 -=-讲解对象创建过程中,-=-堆内存和栈内存的情况 -=-构造函数对类对象的成员变量的初始化过程 -=-构造函数出栈 -=-类的方法在不访问类对象的成员变量时造成的内存资源浪费怎么解决? -= ...
- Compass用法指南
Compass用法指南 Sass是一种"CSS预处理器",可以让CSS的开发变得简单和可维护.但是,只有搭配Compass,它才能显出真正的威力. 本文介绍Compass的用法 ...
- 【翻译自mos文章】11gR2中的asm后台进程
11gR2中的asm后台进程 參考原文: ASM Background Processes in 11.2 (Doc ID 1641678.1) 适用于: Oracle Database - Ente ...
- IIS设置允许下载.exe文件解决方法
最近很多客户使用IIS服务器,然后提示返现宝下载无法找到等无法下载的问题. 返现宝是.exe安装文件,部分服务器或主机可能无法下载. 第一.如果是自己服务器或VPS请按如下设置: 1.设置MIME,让 ...
- 利用SVNKit进行版本库的树的导出
public List searchByTree(String userName,String passwd,String SVNServerUrl,String dirUrl){ //这里有点像 s ...
- Cocos2D & SpriteBuilder Developer Guide
https://www.makegameswith.us/docs/#!/cocos2d/1.0/overview
- include设置属性在relativelayout布局中无效
转自:http://4265337.blog.163.com/blog/static/195375820127935731114/ 再来说一个在使用这两个标签时最容易出现的问题. 经常会有同学在Rel ...
