快速遍历OpenCV Mat图像数据的多种方法和性能分析 | opencv mat for loop
本文首发于个人博客https://kezunlin.me/post/61d55ab4/,欢迎阅读!
opencv mat for loop
Series
- Part 1: compile opencv on ubuntu 16.04
- Part 2: compile opencv with CUDA support on windows 10
- Part 3: opencv mat for loop
- Part 4: speed up opencv image processing with openmp
Guide
Mat
- for gray image, use type
<uchar> - for RGB color image,use type
<Vec3b>
gray format storage
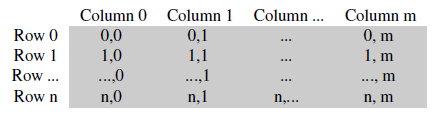
color format storage: BGR
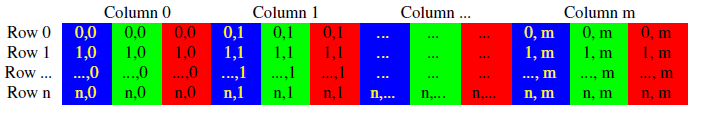
we can use method
isContinuous()to judge whether the memory buffer is continuous or not.
color space reduction
uchar color_space_reduction(uchar pixel)
{
/*
0-9 ===>0
10-19===>10
20-29===>20
...
240-249===>24
250-255===>25
map from 256*256*256===>26*26*26
*/
int divideWith = 10;
uchar new_pixel = (pixel / divideWith)*divideWith;
return new_pixel;
}
color table
void get_color_table()
{
// cache color value in table[256]
int divideWith = 10;
uchar table[256];
for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)
table[i] = divideWith* (i / divideWith);
}
C++
ptr []
// C ptr []: faster but not safe
Mat& ScanImageAndReduce_Cptr(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
int channels = I.channels();
int nRows = I.rows;
int nCols = I.cols* channels;
if (I.isContinuous())
{
nCols *= nRows;
nRows = 1;
}
int i, j;
uchar* p;
for (i = 0; i < nRows; ++i)
{
p = I.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (j = 0; j < nCols; ++j)
{
p[j] = table[p[j]];
}
}
return I;
}
ptr ++
// C ptr ++: faster but not safe
Mat& ScanImageAndReduce_Cptr2(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
int channels = I.channels();
int nRows = I.rows;
int nCols = I.cols* channels;
if (I.isContinuous())
{
nCols *= nRows;
nRows = 1;
}
uchar* start = I.ptr<uchar>(0); // same as I.ptr<uchar>(0,0)
uchar* end = start + nRows * nCols;
for (uchar* p=start; p < end; ++p)
{
*p = table[*p];
}
return I;
}
at(i,j)
// at<uchar>(i,j): random access, slow
Mat& ScanImageAndReduce_atRandomAccess(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
const int channels = I.channels();
switch (channels)
{
case 1:
{
for (int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j)
I.at<uchar>(i, j) = table[I.at<uchar>(i, j)];
break;
}
case 3:
{
Mat_<Vec3b> _I = I;
for (int i = 0; i < I.rows; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; ++j)
{
_I(i, j)[0] = table[_I(i, j)[0]];
_I(i, j)[1] = table[_I(i, j)[1]];
_I(i, j)[2] = table[_I(i, j)[2]];
}
I = _I;
break;
}
}
return I;
}
Iterator
// MatIterator_<uchar>: safe but slow
Mat& ScanImageAndReduce_Iterator(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
// accept only char type matrices
CV_Assert(I.depth() != sizeof(uchar));
const int channels = I.channels();
switch (channels)
{
case 1:
{
MatIterator_<uchar> it, end;
for (it = I.begin<uchar>(), end = I.end<uchar>(); it != end; ++it)
*it = table[*it];
break;
}
case 3:
{
MatIterator_<Vec3b> it, end;
for (it = I.begin<Vec3b>(), end = I.end<Vec3b>(); it != end; ++it)
{
(*it)[0] = table[(*it)[0]];
(*it)[1] = table[(*it)[1]];
(*it)[2] = table[(*it)[2]];
}
}
}
return I;
}
opencv LUT
// LUT
Mat& ScanImageAndReduce_LUT(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
Mat lookUpTable(1, 256, CV_8U);
uchar* p = lookUpTable.data;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)
p[i] = table[i];
cv::LUT(I, lookUpTable, I);
return I;
}
forEach
forEachmethod of theMatclass that utilizes all the cores on your machine to apply any function at every pixel.
// Parallel execution with function object.
struct ForEachOperator
{
uchar m_table[256];
ForEachOperator(const uchar* const table)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
m_table[i] = table[i];
}
}
void operator ()(uchar& p, const int * position) const
{
// Perform a simple operation
p = m_table[p];
}
};
// forEach use multiple processors, very fast
Mat& ScanImageAndReduce_forEach(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
I.forEach<uchar>(ForEachOperator(table));
return I;
}
forEach with lambda
// forEach lambda use multiple processors, very fast (lambda slower than ForEachOperator)
Mat& ScanImageAndReduce_forEach_with_lambda(Mat& I, const uchar* const table)
{
I.forEach<uchar>
(
[=](uchar &p, const int * position) -> void
{
p = table[p];
}
);
return I;
}
time cost
no foreach
[1 Cptr ] times=5000, total_cost=988 ms, avg_cost=0.1976 ms
[1 Cptr2 ] times=5000, total_cost=1704 ms, avg_cost=0.3408 ms
[2 atRandom] times=5000, total_cost=9611 ms, avg_cost=1.9222 ms
[3 Iterator] times=5000, total_cost=20195 ms, avg_cost=4.039 ms
[4 LUT ] times=5000, total_cost=899 ms, avg_cost=0.1798 ms
[1 Cptr ] times=10000, total_cost=2425 ms, avg_cost=0.2425 ms
[1 Cptr2 ] times=10000, total_cost=3391 ms, avg_cost=0.3391 ms
[2 atRandom] times=10000, total_cost=20024 ms, avg_cost=2.0024 ms
[3 Iterator] times=10000, total_cost=39980 ms, avg_cost=3.998 ms
[4 LUT ] times=10000, total_cost=103 ms, avg_cost=0.0103 ms
foreach
[5 forEach ] times=200000, total_cost=199 ms, avg_cost=0.000995 ms
[5 forEach lambda] times=200000, total_cost=521 ms, avg_cost=0.002605 ms
[5 forEach ] times=20000, total_cost=17 ms, avg_cost=0.00085 ms
[5 forEach lambda] times=20000, total_cost=23 ms, avg_cost=0.00115 ms
results
Loop Type | Time Cost (us)
:----: |
ptr [] | 242
ptr ++ | 339
at | 2002
iterator | 3998
LUT | 10
forEach | 0.85
forEach lambda | 1.15
forEach is 10x times faster than LUT, 240~340x times faster than ptr [] and ptr ++, and 2000~4000x times faster than at and iterator.
code
Python
pure python
# import the necessary packages
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
print(cv2.__version__)
%matplotlib inline
3.4.2
# load the original image, convert it to grayscale, and display
# it inline
image = cv2.imread("cat.jpg")
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
print(image.shape)
#plt.imshow(image, cmap="gray")
(360, 480)
%load_ext cython
The cython extension is already loaded. To reload it, use:
%reload_ext cython
%%cython -a
def threshold_python(T, image):
# grab the image dimensions
h = image.shape[0]
w = image.shape[1]
# loop over the image, pixel by pixel
for y in range(0, h):
for x in range(0, w):
# threshold the pixel
image[y, x] = 255 if image[y, x] >= T else 0
# return the thresholded image
return image
%timeit threshold_python(5, image)
263 ms ± 20.2 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
cython
%%cython -a
import cython
@cython.boundscheck(False)
cpdef unsigned char[:, :] threshold_cython(int T, unsigned char [:, :] image):
# set the variable extension types
cdef int x, y, w, h
# grab the image dimensions
h = image.shape[0]
w = image.shape[1]
# loop over the image
for y in range(0, h):
for x in range(0, w):
# threshold the pixel
image[y, x] = 255 if image[y, x] >= T else 0
# return the thresholded image
return image
numba
%timeit threshold_cython(5, image)
150 µs ± 7.14 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
from numba import njit
@njit
def threshold_njit(T, image):
# grab the image dimensions
h = image.shape[0]
w = image.shape[1]
# loop over the image, pixel by pixel
for y in range(0, h):
for x in range(0, w):
# threshold the pixel
image[y, x] = 255 if image[y, x] >= T else 0
# return the thresholded image
return image
%timeit threshold_njit(5, image)
43.5 µs ± 142 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
numpy
def threshold_numpy(T, image):
image[image > T] = 255
return image
%timeit threshold_numpy(5, image)
111 µs ± 334 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
conclusions
image = cv2.imread("cat.jpg")
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
print(image.shape)
%timeit threshold_python(5, image)
%timeit threshold_cython(5, image)
%timeit threshold_njit(5, image)
%timeit threshold_numpy(5, image)
(360, 480)
251 ms ± 6.5 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
143 µs ± 1.19 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
43.8 µs ± 284 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
113 µs ± 957 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
image = cv2.imread("big.jpg")
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
print(image.shape)
%timeit threshold_python(5, image)
%timeit threshold_cython(5, image)
%timeit threshold_njit(5, image)
%timeit threshold_numpy(5, image)
(2880, 5120)
21.8 s ± 460 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
12.3 ms ± 231 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
3.91 ms ± 66.1 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
10.3 ms ± 179 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
60,480
- python: 251 ms
- cython: 143 us
- numba: 43 us
- numpy: 113 us
2880, 5120
- python: 21 s
- cython: 12 ms
- numba: 4 ms
- numpy: 10 ms
Reference
- Part1: OpenCV访问Mat图像中每个像素的值 4种对比
- Part2: OpenCV访问Mat图像中每个像素的值 13种对比
- parallel-pixel-access-in-opencv-using-foreach
- fast-optimized-for-pixel-loops-with-opencv-and-python
- python performance tips
History
- 20180823: created.
Copyright
- Post author: kezunlin
- Post link: https://kezunlin.me/post/61d55ab4/
- Copyright Notice: All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 unless stating additionally.
快速遍历OpenCV Mat图像数据的多种方法和性能分析 | opencv mat for loop的更多相关文章
- 用 Python 排序数据的多种方法
用 Python 排序数据的多种方法 目录 [Python HOWTOs系列]排序 Python 列表有内置就地排序的方法 list.sort(),此外还有一个内置的 sorted() 函数将一个可迭 ...
- Python的list循环遍历中,删除数据的正确方法
在遍历list,删除符合条件的数据时,总是报异常,代码如下: num_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print(num_list) for i in range(len(num_lis ...
- Delphi导出数据的多种方法
//Dxdbgrid,则直接用SaveToexcel即可//使用 ExcelWithOdbc 控件function TDataModule1.GetDataToFile(DsData: TObject ...
- php遍历目录与文件夹的多种方法详解
遍历目录或遍历目录下指定类型的文件,这是每一个童鞋在写程序的时候难免会用到的.PHP本身也提供了很多灰常有用的函数,正确地使用它们,不会有错滴.下面就我个人学习过程中的一些总结,希望对想学PHP的童鞋 ...
- 遍历Map和List的几种方法和性能比较
public static void main(String[] args) { Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, Stri ...
- android+opencv+opencl: cv::dft()的opencl版本的性能分析
在小米mix 2s + 高通骁龙 845 + Adreno 630 上测试了opencl版本的cv::dft(). 测试数据 先看表格里面的描述: 名称 函数名 最大时间(ms) 平均时间(ms) 说 ...
- OpenCV图像数据字节对齐
目录 1. IplImage的data字段,是char*类型,是4字节对齐. 2. 手动创建的Mat通常是没有字节对齐的 3. 从IplImage转过来的Mat,是字节对齐的 4. 总结 图像数据是否 ...
- opencv-4-成像系统与Mat图像颜色空间
opencv-4-成像系统与Mat图像颜色空间 opencvc++qtmat 目标 知道 opencv 处理图像数据的格式 介绍 mat 基础内容 知道 BGR 颜色 显示 颜色转换 BGR 到 灰度 ...
- Python使用plotly绘制数据图表的方法
转载:http://www.jb51.net/article/118936.htm 本篇文章主要介绍了Python使用plotly绘制数据图表的方法,实例分析了plotly绘制的技巧. 导语:使用 p ...
随机推荐
- Java根据参数返回相应类
问题初衷:如何根据参数变换方法的返回类型(参数为 类) 解决方案: 下面方法是放在工具类(例:YslRequestUtil) public <T> T response(Object re ...
- 网络攻防实验任务三_(2)X-Scan通用漏洞扫描实验
首先在宿主机中打开xscan_gui.exe,结果系统直接将它删掉了. 大概是因为开了防火墙的缘故. 于是我在win7虚拟机中运行这个程序. 并且关闭防火墙,在win7中可以运行 我再试了一下win1 ...
- java实现,使用opencv合成全景图,前端使用krpano展示
这周花三天做了一demo,算上之前的,怎么也有五天,上一篇是opencv介绍,以及定义native方法,通过本地图片路径传参,底层调用Opencv图像库合成,有兴趣的可以看看,这篇重点在于krpano ...
- Java11新特性 - Epsilon GC和ZGC
Java11中新增了两个GC,Epsilon GC和ZGC. Epsilon垃圾收集器 A NoOp Garbage Collector 没有操作的垃圾收集器 JDK上对这个特性的描述是:开发一个处理 ...
- Ubuntu svn 安装 Rabbitvcs
先添加源 sudo add-apt-repository ppa:rabbitvcs/ppa 必要的话在源清单里面也添加一下 sudo gedit /etc/apt/sources.list 内容是 ...
- 【IDEA】IDEA自动生成文档注释的设置方法
Digest:今天和大家分享一下如何使用IntelliJ IDEA快速生成文档注释 IntelliJ IDEA创建自定义文档注释模板 1.打开IntelliJ IDEA,依次点击 File --> ...
- c# 保留两位小数点
保留两位小数点 由于简单的原因大家直接看代码块. using System; namespace HelloWorld { class Program { static void Main(strin ...
- C++学习笔记4_new和delete
1. 默认的new和delete操作符new和delete是和c里面的mlloc和free是一样的,在堆中创建空间.堆中创建的,都要自己释放.C中void test(){ int *p=(int *) ...
- Spring Boot实战之定制type Formatters
本文首发于个人网站:Spring Boot实战之定制type Formatters 前面我们有篇文章介绍了PropertyEditors,是用来将文本类型转换成指定的Java类型,不过,考虑到Prop ...
- 「Usaco2005 Dec」清理牛棚(spfa秒杀线段树dp)
约翰的奶牛们从小娇生惯养,她们无法容忍牛棚里的任何脏东西. 约翰发现,如果要使这群有洁癖的奶牛满意,他不得不雇佣她们中的一些来清扫牛棚, 约翰的奶牛中有N(1≤N≤10000)头愿意通过清扫牛棚来挣一 ...
