C++ STL:lower_bound与upper_bound实现
lower_bound
lower_bound(begin, end, target)用来查找一个已排序的序列中[begin, end)第一个大于等于target的元素index。数组A如下:
value: 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7
index: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
这样的一个序列,如果查找5的lower_bound,返回的应该是第一个5即A[5]。下面是摘自cplusplus.com上的lower_bound代码
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator lower_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val)
{
ForwardIterator it;
iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::difference_type count, step;
count = distance(first,last);
while (count>)
{
it = first; step=count/; advance (it,step);
if (*it < val) { // or: if (comp(*it,val)), for version (2)
first = ++it;
count -= step+;
}
else count = step;
}
return first;
}
如果搜索对象只是数组的话还可以再简化一点:
count = last - start;
while (count > ) {
step = count/;
int* it = first + step;
if (*it < target) {
count = count - (step + );
first = it + ;
} else {
count=step;
}
}
return first;
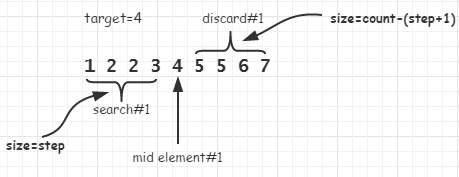
基本情况: 当输入只有一个元素时,而该元素不是要查找的元素时返回last,即该元素的后一个位置
case: target=4
当在上图中的数组中找4的lower_bound时,第一次*it取到的值是4,因为这不是简单的二分搜索,而是要返回第一大于等于查找元素的位置,所以搜索不能在此时结束。但是可以确定5~7这一部分可以不用搜索了,因为当前至少有一个元素即*it是大于等于4了,因而缩小查找范围(count=step)。这个查找范围并不包括已找到的4,为什么是这样?分情况讨论:
1. 当前面的这个范围没有符合条件的数时,就会将范围最后的位置的后一位置返回,而此位置正好是4所在的位置(*it>= target时it所在的位置,它是符合查找条件的),其正好是lower_bound。
2. 当前面的这个方位含有符合条件的数时,此时当前的这个4就不是lower_bound,真正的lower_bound会在该区间内产生
case: target=5
当求5的lower_bound时,第一次找到中间元素时4,4<5,所以4和4前面的所有都不会含有5的lower_bound,因而下一次搜索只会在5~7这个区间进行,这个就和一个全新的问题一样了。
upper_bound
upper_bound用来在[begin, end)中找到第一个大于target的index
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
ForwardIterator upper_bound (ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, const T& val)
{
ForwardIterator it;
iterator_traits<ForwardIterator>::difference_type count, step;
count = std::distance(first,last);
while (count>)
{
it = first; step=count/; std::advance (it,step);
if (!(val<*it)) // or: if (!comp(val,*it)), for version (2)
{ first=++it; count-=step+; }
else count=step;
}
return first;
}
简化版本:
lower_bound:
int lo = , hi = n;
// lower_bound
while (lo < hi) {
int mid = (lo + hi) / ;
if (A[mid] < target) {
lo = mid + ;
} else {
hi = mid;
}
} return lo;
upper_bound:
lo = , hi = n;
// upper_bound
while (lo < hi) {
int mid = (lo + hi) / ;
if (A[mid] <= target) {
lo = mid + ;
} else {
hi = mid;
}
}
return lo;
就在判断条件上多了个等号
C++ STL:lower_bound与upper_bound实现的更多相关文章
- [STL] lower_bound和upper_bound
STL中的每个算法都非常精妙, ForwardIter lower_bound(ForwardIter first, ForwardIter last,const _Tp& val)算法返回一 ...
- C++ STL lower_bound()和upper_bound()
lower_bound()和upper_bound()用法 1.在数组上的用法 假设a是一个递增数组,n是数组长度,则 lower_bound(a, a+n, x):返回数组a[0]~a[n-1]中, ...
- STL源码学习----lower_bound和upper_bound算法
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/cobbliu/archive/2012/05/21/2512249.html 先贴一下自己的二分代码: #include <cstdio&g ...
- STL lower_bound upper_bound binary-search
STL中的二分查找——lower_bound .upper_bound .binary_search 二分查找很简单,原理就不说了.STL中关于二分查找的函数有三个lower_bound .upper ...
- STL中的lower_bound和upper_bound的理解
STL迭代器表述范围的时候,习惯用[a, b),所以lower_bound表示的是第一个不小于给定元素的位置 upper_bound表示的是第一个大于给定元素的位置. 譬如,值val在容器内的时候,从 ...
- STL 源码分析《5》---- lower_bound and upper_bound 详解
在 STL 库中,关于二分搜索实现了4个函数. bool binary_search (ForwardIterator beg, ForwardIterator end, const T& v ...
- STL源码学习----lower_bound和upper_bound算法[转]
STL中的每个算法都非常精妙,接下来的几天我想集中学习一下STL中的算法. ForwardIter lower_bound(ForwardIter first, ForwardIter last,co ...
- [转] STL源码学习----lower_bound和upper_bound算法
http://www.cnblogs.com/cobbliu/archive/2012/05/21/2512249.html PS: lower_bound of value 就是最后一个 < ...
- STL之std::set、std::map的lower_bound和upper_bound函数使用说明
由于在使用std::map时感觉lower_bound和upper_bound函数了解不多,这里整理并记录下相关用法及功能. STL的map.multimap.set.multiset都有三个比较特殊 ...
- STL中的二分查找——lower_bound 、upper_bound 、binary_search
STL中的二分查找函数 1.lower_bound函数 在一个非递减序列的前闭后开区间[first,last)中.进行二分查找查找某一元素val.函数lower_bound()返回大于或等于val的第 ...
随机推荐
- [原创]Laravel 的缓存源码解析
目录 前言 使用 源码 Cache Facade CacheManager Repository Store 前言 Laravel 支持多种缓存系统, 并提供了统一的api接口. (Laravel 5 ...
- 关于Vue中main.js,App.vue,index.html之间关系进行总结
在初始化的Vue项目中,我们最先接触到的就是main.js,App.vue,index.html这三个文件,我们从培训视频或者官方文档上可以了解到: index.html---主页,项目入口 App. ...
- springcloud(六)-Ribbon配置自定义算法
前言 很多场景下,可能根据需要自定义Ribbon的配置,例如修改Ribbon的负载均衡规则等.Spring Cloud Edgware允许使用java代码或属性自定义Ribbon 的配置,两种方式等价 ...
- hdu1024 Max Sum Plus Plus 滚动dp
Max Sum Plus Plus Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others ...
- (转)一次棘手的rootvg更换硬盘处理过程
一次棘手的rootvg更换硬盘处理过程 原文:http://www.talkwithtrend.com/Article/160857 事件起因 下午接到现场工程师电话,一台双系统抽屉IBM P570一 ...
- Docker 拷贝文件
1.从容器里面拷文件到宿主机? 答:在宿主机里面执行以下命令 docker cp 容器名:要拷贝的文件在容器里面的路径 要拷贝到宿主机的相应路径 示例: 假设容器名为testtomcat, ...
- easyui的datagrid对应的java对象
Easyui中datagrid控件要求的数据格式为: {total:”2”,rows:[{“id”:”1”,”name”,”张三”},{“id”:”2”,”name”,”李四”}]} 所以可以建一个对 ...
- Idea查看代码相关技巧
(1)查看类中的属性与方法快捷键 Alt+7 (2)查看方法被调用 在方法上右键find usages (3)查看方法说明 Ctrl+Q
- android Application类的详细介绍(转)
在代码中经常看到application这个类,一直不知道这个是干什么用的,今天刚好有点时间,所以进行了详细的学习. 一.先对它的整体概念解释: 在android源码中对他的描述是; * Base cl ...
- ActionController::UnfilteredParameters: unable to convert unpermitted parameters to hash
rails 开发中 5.1版本使用binding.pry会报 ActionController::UnfilteredParameters: unable to convert unpermitted ...
