PAT A1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in "zigzagging order" -- that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
8
12 11 20 17 1 15 8 5
12 20 17 11 15 8 5 1
Sample Output:
1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15
result:
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = ;
int n,postOrder[maxn],inOrder[maxn];
vector<vector<int> > ans(maxn);
int level1=; void createTree(int inL,int inR,int postL,int postR,int level2){
if(postR<postL || inR<inL) return ;
int data = postOrder[postR];
ans[level2].push_back(data);
// printf("%d ",data);
level1 = max(level1,level2);
int num=;
while(inOrder[inL+num] != postOrder[postR]){
num++;
}
// 这样生成的num指的是有num个lchild;
createTree(inL,inL+num-,postL,postL +num-,level2+);
createTree(inL+num+,inR,postL +num,postR - ,level2+);
return ;
} int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&inOrder[i]);
}
for(int i=;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&postOrder[i]);
}
createTree(,n-,,n-,);
int s = ;
bool flag = false;
for(vector<vector<int> >::iterator i=ans.begin();i!=ans.end();++i){
if(flag){
for(vector<int>::iterator j=(*i).begin();j !=(*i).end();++j){
printf("%d",(*j));
s++;
if(s<n) printf(" ");
}
flag=false;
}else{
reverse((*i).begin(),(*i).end());
for(vector<int>::iterator j=(*i).begin(); j !=(*i).end();++j){
printf("%d",(*j));
s++;
if(s<n) printf(" ");
}
flag=true;
}
}
}
收获:
此题主要的问题是如何生成蛇形层次排序法。首先想到的存储结构是按照二维数组ans[level][]保存结果。
如果以int ans[][]定义的话需要面对阈值问题,以及设计计数器问题。看题目里是没有阈值限制的,所以还需要自己设置。对于考试来说,也是可以实现的。
另外一种方式是利用vector<int>;在此题我首次体验了一下二维的vector<vector<int> >; 需要注意的是,普通二维数组需要确定第二维度的阈值;而在vector中,需要声明第一维度的阈值。而且设置阈值的方式是用小括号,而非数组形式的中括号。
对于vector<>进行迭代有两种方法,一种是用下标进行访问。使用下标访问需要结合vector<>的生成方式配合使用。一般是int i =0;i< vector.size();i++的方式;但是对于比较妖怪的存储方法,或者间断的存储方式,下标访问不是很方便。
一种是用迭代器访问,如上代码,清晰的给出了二维向量的访问方法。这里需要注意的是对于vector<>,弄清楚 front,back,begin,end四个方法的具体区别。简单说front,back可以直接引用首尾向量;begin,end返回的是vector<>首尾的迭代器。其中begin和front效果一致,但end指的是空迭代器;这也是为何遍历的时候结束条件是i!=vector.end();
使用迭代器还需要掌握一点是逆序遍历迭代器。逆序遍历有两种方法可以实现。
1)利用algorithm::reverse(a,b)先互换begin(),end();其他完全不变的方式实现。(如上代码);
同样的方法也可以换个写法:
// sorts vector in "normal" order
sort(vector.begin(), vector.end());
// sorts in reverse: puts smallest element at the end of vector
sort(vector.rbegin(), vector.rend());
这是利用了vector<>自身方法的解决方案,下图是begin(),end(),rend(),rbegin()四者的关系。
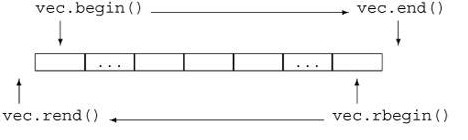
2)生成反向迭代器
for(vector<int>::reverse_iterator j=(*i).rbegin(); j !=(*i).rend();++j){
printf("%d",(*j));
s++;
if(s<n) printf(" ");
}
PAT A1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)的更多相关文章
- PAT A1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分)——二叉树,建树,层序遍历
Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can ...
- PAT甲级:1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分)
PAT甲级:1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分) 题干 A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as ...
- PAT甲级 1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)
1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- pat 甲级 1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30)
1127. ZigZagging on a Tree (30) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- PAT 甲级 1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 分)(不会做,重点复习,模拟中序遍历)
1064 Complete Binary Search Tree (30 分) A Binary Search Tree (BST) is recursively defined as a bin ...
- PTA 04-树6 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分)
题目地址 https://pta.patest.cn/pta/test/16/exam/4/question/669 5-7 Complete Binary Search Tree (30分) A ...
- PAT-2019年冬季考试-甲级 7-4 Cartesian Tree (30分)(最小堆的中序遍历求层序遍历,递归建树bfs层序)
7-4 Cartesian Tree (30分) A Cartesian tree is a binary tree constructed from a sequence of distinct ...
- PAT 1127 ZigZagging on a Tree[难]
1127 ZigZagging on a Tree (30 分) Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive in ...
- [PAT] 1143 Lowest Common Ancestor(30 分)
1143 Lowest Common Ancestor(30 分)The lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes U and V in a tree is ...
随机推荐
- mysqldump导出sql文件中insert多行问题
mysqldump为了加快导入导出,默认把数据都缩减在一行里面. 查看和修改不方便,为此,我们可以使用--skip-extended-insert选项来使导出的数据,是多行插入形式的. mysqldu ...
- Python初学者第八天 元组和字典
8day 1.数据类型:元组 元组:有序的,不可变地数据的集合.但若包含其他可变元素,这些元素可变.显示的告诉别人,此处不可修改: a = (1,2,3,4,5,['1','a']) 2.数据类型:字 ...
- Linux 命令行浏览器
真是没有做不到只有想不到! Linux下竟然有命令行式的浏览器:W3m SPC向下翻页 b向上翻页 J 向下滚动一行 K 向上滚动一行 > 右移一屏 < 左移一屏 TAB 转到下个超链接 ...
- 模糊搜索框(H5),兼容安卓和ios(令人头大的ios输入法)
项目里要可以实现,按照模糊,于是从jq22网站找到一个代码,效果如图: 具体的html代码:(复制,需要引入jq相关的支持文件) <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W ...
- MATLAB入门学习(六)
今天学三维作图 (*^__^*)…… 三维曲线作图 用到的命令:plot3 基本格式:plot3(x,y,z,s) 这里要画曲线,你需要知道该曲线的参数方程x=x(t),y=y(t),z=z(t) 然 ...
- Android(java)学习笔记209:Android线程形态之 HandlerThread
1. HandlerThread Android HandlerThread 完全解析 Handler与HandlerThread区别,HandlerThread应用(对比AsyncTask) 备注 ...
- VOC 数据集
可变形网络 :https://github.com/msracver/Deformable-ConvNets VOC数据集: Test 参数 ('PascalVOC', '2007_test', '. ...
- ROBOCOPY——Windows 的可靠文件复制
复制指定类型文件 (-s :含子目录 不包括空目录) 复制所有 (-e :含子目录 包括空目录) 复制指定成层级内的 (-lev:n 仅复制源目录树的前 n 层) 复制排除给定类型后的 (-xf) ...
- shiro之cache问题
错误原因分析加解决方案,以供大家参考: 1.错误信息:net.sf.ehcache.ObjectExistsException: Cache shiro-activeSessionCache alre ...
- Linux脚本开头#!/bin/bash和#!/bin/sh是什么意思以及区别
一.意思 #!/bin/sh是指此脚本使用/bin/sh来解释执行,#!是特殊的表示符,其后面根的是此解释此脚本的shell的路径. 其实第一句的#!是对脚本的解释器程序路径,脚本的内容是由解释器解释 ...
