Understanding the JavaScript Engine—— two phase
Understanding the JavaScript Engine — Part 1

I have been a Ruby on Rails developer for the last 2 years. I have used JavaScript both in its vanilla form and in some frameworks. However, I learned JavaScript as most new programmers do, by going through a course, without quite understanding how the JavaScript engine works.
Before diving deep into JavaScript, I decided to take some time off and understand its core working principles. I’ll be sharing what I’ve learned so far in this, and subsequent blog posts.
First, let me define some terms you’ll come across. I’ll add examples where necessary.
Syntax Parser
When you write code, a compiler converts your code into a set of instructions that the computer can understand. Part of the compiler is what is known as a syntax parser. The syntax parser goes through your code character by character, and determines if the syntax is valid or not.
Lexical Environment
In simple terms, a Lexical environment refers to where something sits physically in your code. Where something is written gives an idea of how the computer will interpret it and how it will interact with other variables and functions e.g
function hello() {
var greet = "Hello world"
}
In the function above, we can say that var greet sits lexically in the function.
Execution Context
This is a wrapper that helps manage the code that is running. Looking at the gif below, you can see there’s an execution context stack and in it, we have a Global execution context. When functionA() is called, it is added to the Stack meaning that functionA() is currently being executed. The same goes for functionB().
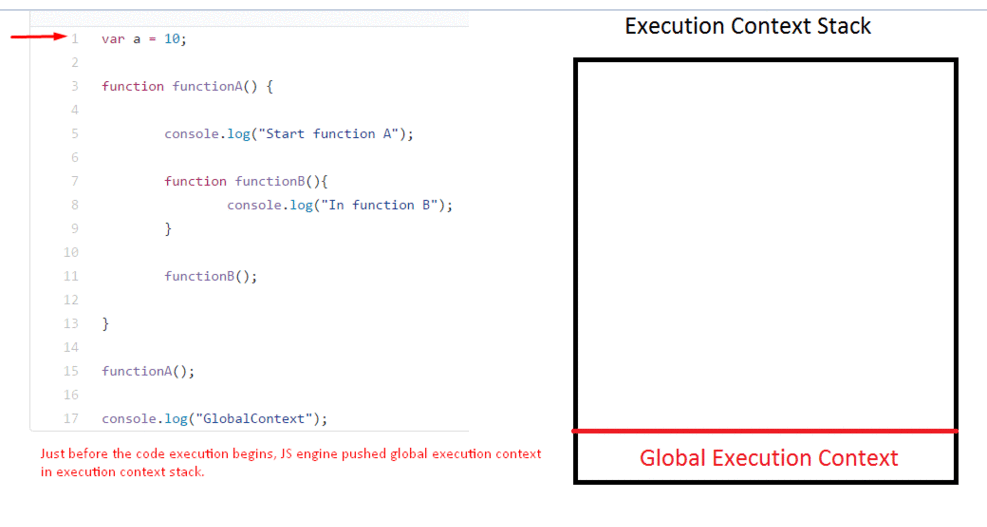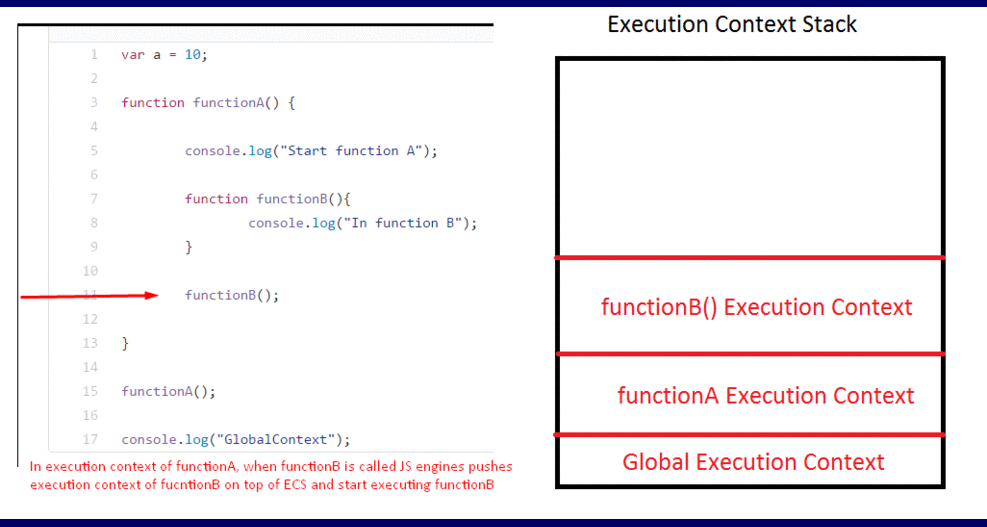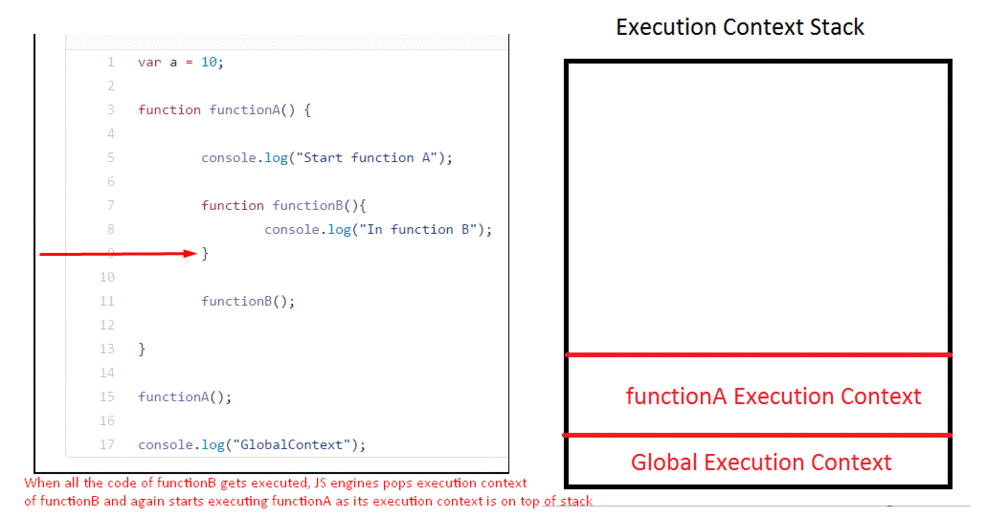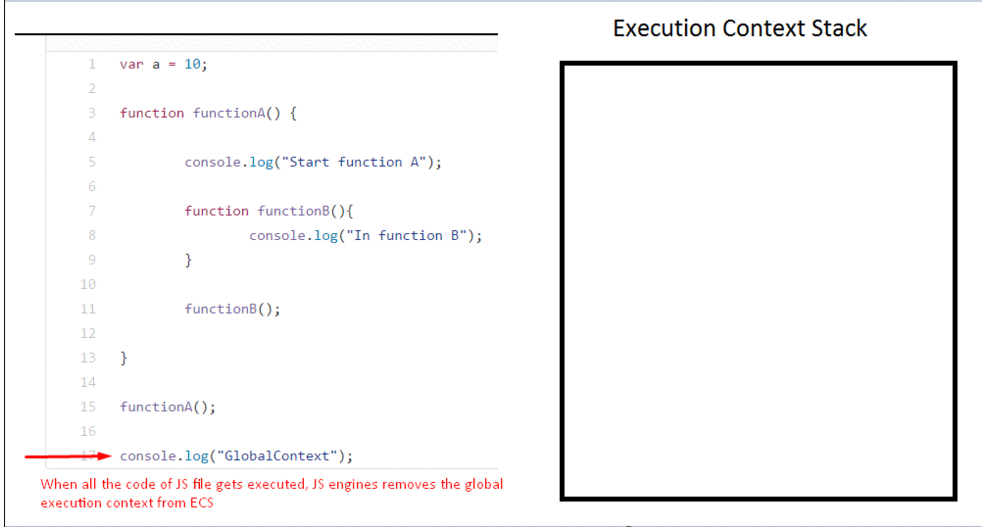
The execution context is created in two phases:
The first phase is called the creation phase. The global execution context creates two things for you, that you don’t have in your code; a global object(window) and a special variable called this. The window object is a global object inside a browser. This object is different depending on whether you are using node or running JavaScript on the server. But there is always a global object when you’re running JavaScript. Take a look at the following image from a browser console:
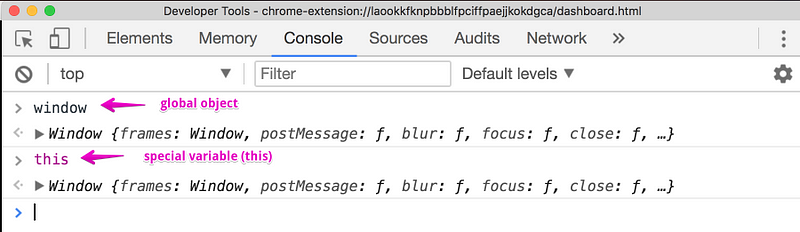
When you create a variable and function that is not inside a function, those variables and functions get attached to the global object.
var name = "Debby";
function greet() {
console.log("Hello", name)
}
If you run the above JavaScript code in the browser and you inspect the global object, you will see that the variable and the function were added to it.
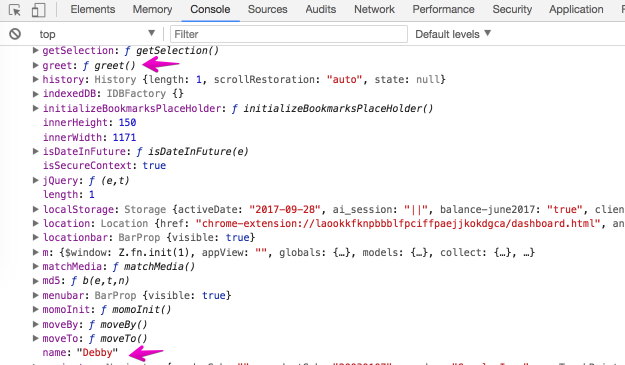
During the creation phase, the syntax parser recognizes where you have defined variables and functions. It therefore sets up memory space for the variables and functions. It’s not actually moving code to the top of the page. What this means is that before your code begins to be executed line by line, the JavaScript engine has already set aside memory space for the variables and functions that you’ve written. This is what is called Hoisting.
The next phase is the execution phase, where assignments are made. When the JavaScript engine sets up memory space for variables, it doesn’t know which values will be stored in them. Therefore, it puts a placeholder called undefined. That placeholder means; I don’t know what this value is yet. All variables in JavaScript are initially set to undefined while functions sit in memory in their entirety. This is why it’s possible to declare a variable without assigning it and the JavaScript engine will not throw any error.
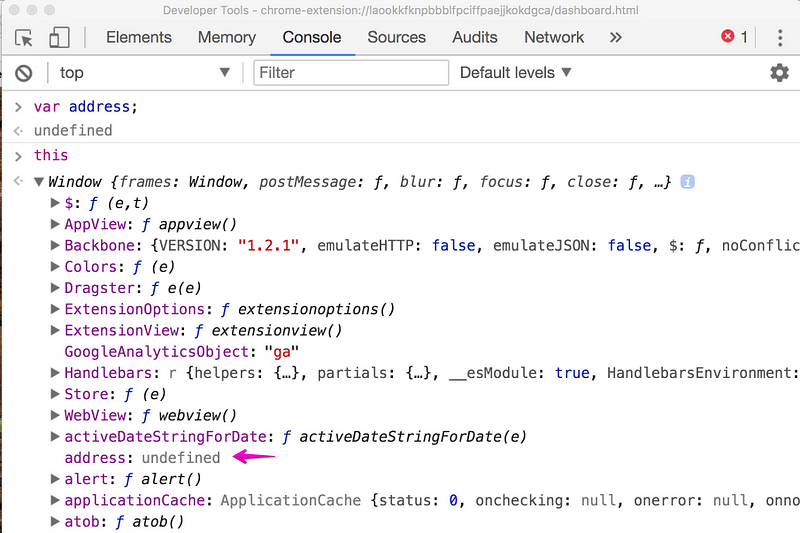
This is just a brief introduction to how the JavaScript engine executes the code you write. To know more, you can use the resources below:
JavaScript: Understanding the Weird Parts by Anthony Alicea on Udemy.Execution context, Scope chain and JavaScript internals by Rupesh Mishra.
Understanding the JavaScript Engine—— two phase的更多相关文章
- 「2014-3-13」Javascript Engine, Java VM, Python interpreter, PyPy – a glance
提要: url anchor (ajax) => javascript engine (1~4 articles) => java VM vs. python interpreter =& ...
- Javascript Engine, Java VM, Python interpreter, PyPy – a glance
提要: url anchor (ajax) => javascript engine (1~4 articles) => java VM vs. python interpreter =& ...
- Browser Render Engine & Javascript Engine
Browser Render Engine Programming Language Open Source Javascript Engine Comparation for CSS Compati ...
- JavaScript Engine 可视化
JavaScript Engine 可视化 图解 JavaScript Engine JavaScript 可视化 (7 部曲) ️ JavaScript Visualized: Event Loop
- Understanding Delegated JavaScript Events
While I ended up using a CSS-only implementation for this pen, I started by writing it mostly using ...
- v8 javascript engine
https://code.google.com/p/v8-wiki/wiki/BuildingWithGYP vs2013git v8 http://github.com/v8/v8-git-mirr ...
- Attacking JavaScript Engines: A case study of JavaScriptCore and CVE-2016-4622(转)
转:http://phrack.org/papers/attacking_javascript_engines.html Title : Attacking JavaScript Engines: A ...
- Bring JavaScript to your Java enterprise with Vert.x
转自:https://opensource.com/article/18/4/benefits-javascript-vertx If you are a Java programmer, chanc ...
- JavaScript Interview Questions: Event Delegation and This
David Posin helps you land that next programming position by understanding important JavaScript fund ...
随机推荐
- 如何解决pytorch 编译时CUDA版本与运行时CUDA版本不对应
转载请注明: 仰望高端玩家的小清新 http://www.cnblogs.com/luruiyuan/ 如何解决pytorch 编译时CUDA版本与运行时CUDA版本不对应 如果pytorch的编译时 ...
- Python函数-闭包的概念
一个函数和它的环境变量合在一起,就构成了一个闭包(closure).在Python中,所谓的闭包是一个包含有环境变量取值的函数对象.环境变量取值被保存在函数对象的__closure__属性中.比如下面 ...
- Spring MVC——搭建HelloWeb工程
1.确保环境配置配置正确(Myeclipse(eclipse)+Tomcat) 2.新建web project 3.将Spring MVC所需的jar包粘贴到WebRoot/WEB-INF/lib下 ...
- LongAdder & AtomicInteger
JDK8 推荐 LongAdder替代 AtomicInteger, AtomicInteger内部是实现使用 (网友使用jad反编译源码 参考 http://ifeve.com/enhanced- ...
- PHP 笔记——Array 数组
要点 说明 数组构成 数组是由一个或多个数组元素组成的 数组元素 每个数组元素由键(Key)和值(Value)构成 键 元素的识别名称,也被称为数组下标 值 元素的内容 映射 键 和 值 之间存在一种 ...
- [CC-ANUCBC]Cards, bags and coins
[CC-ANUCBC]Cards, bags and coins 题目大意: 给你\(n(n\le10^5)\)个数,\(q(q\le30)\)次询问,问从中选取若干个数使得这些数之和为\(m(m\l ...
- bzoj 3940: [Usaco2015 Feb]Censoring -- AC自动机
3940: [Usaco2015 Feb]Censoring Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MB Description Farmer John has ...
- C++ -- STL泛型编程(二)之set
set集合容器实现了红黑树的平衡二叉检索树的数据结构,在插入元素时候它会自动调整二叉树的排列,把元素放在适当的位置,以确保每个子树根节点的键值都大于左子树的所有节点的键值,而小于右子树的所有节点的键值 ...
- PAT甲级1066. Root of AVL Tree
PAT甲级1066. Root of AVL Tree 题意: 构造AVL树,返回root点val. 思路: 了解AVL树的基本性质. AVL树 ac代码: C++ // pat1066.cpp : ...
- Chrome无法播放m3u8格式的直播视频流的问题解决
出国,然后安装这个插件即可:Native HLS Playback https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/native-hls-playback/emnp ...
