Android视图控件架构分析之View、ViewGroup
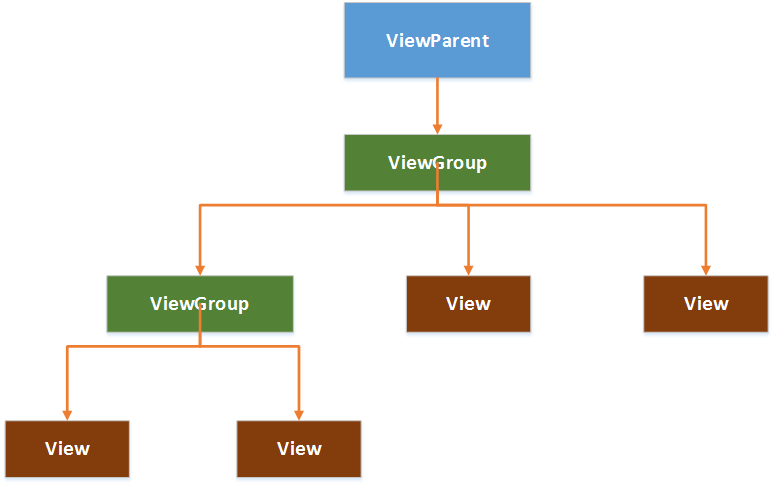
在Android中,视图控件大致被分为两类,即ViewGroup和View,ViewGroup控件作为父控件,包含并管理着子View,通过ViewGroup和View便形成了控件树,各个ViewGoup对象和View对象就是控件树中的节点。在控件树中,以树的深度来遍历查找对应的控件元素,同时,上层控件负责子控件的测量与绘制,并传递交互事件。
Android控件树:
AndroidUI界面架构图:

一.测量View的工具类:MeasureSpec
1.MeasureSpec包含了测量的模式和测量的大小,通过MeasureSpec.getMode()获取测量模式,通过MeasureSpec.getSize()获取测量大小;
2.MeasureSpec是一个32位的int值,高2位为测量的模式,低30位为测量的大小,使用位运算的目的在于提高优化效率。
二.测量的模式
1.EXACTLY,精确值模式:将layout_width或layout_height属性指定为具体数值或者match_parent。
2.AT_MOST,最大值模式:将layout_width或layout_height指定为wrap_content。
3.UNSPECIFIED: View想多大就多大
三.View类默认的onMeasure()方法只支持EXACTLY模式,如果要支持其它模式,就必须重写onMeasure(),重写onMeasure()的模板代码:
package com.example.demoapp.views; import android.content.Context;
import android.view.View; public class MeasuredView extends View {
public MeasuredView(Context context) {
super(context);
} @Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 调用父类的onMeasure()
super.onMeasure(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec), measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec));
// 或者直接调用父类的setMeasuredDimension(),因为父类的onMeasure()最终调用了setMeasuredDimension()
// setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec), measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec));
} /**
* 测量View的width
* @param measureSpec MeasureSpec对象
* @return View的width
*/
private int measureWidth(int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = 200;
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
result = Math.min(result, specSize);
}
}
return result;
} /**
* 测量View的height
* @param measureSpec MeasureSpec对象
* @return View的height
*/
private int measureHeight(int measureSpec) {
int result = 0;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); if (specMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
result = specSize;
} else {
result = 200;
if (specMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
result = Math.min(result, specSize);
}
}
return result;
}
}
四.View的绘制
1.2D绘图必备利器——Canvas
1)获取Canvas对象的方式:
a.由方法中的参数传入,例如,View的onDraw()中有一个参数就是Canvas对象
b.通过构造方法构造,即:Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bitmap),在Canvas的构造方法传入一个Bitmap对象,即可获取一个Canvas对象。通过传入Bitmap对象构造Canvas对象的过程称为“画布的装载”,传入的Bitmap对象承载了多有绘制在Canvas上的像素信息,调用Canvas.drawXXX方法(如:Canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, 0, 0, null))都将发生在该Bitmap对象上。
2)利用Canvas绘图
a.通过Canvas.drwaXXX进行绘制操作将直接作用于Bitmap对象,当再次刷新View的时候,我们将会被绘制的Bitmap对象发生了改变;
b.利用Canvas和Paint进行绘图;
c.不管多么复杂、精美的空间,都可以被拆分为一个个小的图形单元,我们只要找到这些图形单元,就可以将控件绘制出来。
五.ViewGroup的测量
1.ViewGroup的作用:管理子View,如子View的大小、位置;
2.ViewGroup通过遍历子View,调用子View的Measure()来获得每一个子View的测量结果;
3.ViewGroup测量完子View,调用子View的Layout()将子View放到合适的位置;
4.在自定义ViewGroup的时候,通常会重写onLayout()控制子View的显示;
5.如果需要支持wrap_content属性,必须重写onMeasure()。
六、ViewGroup的绘制
通常情况下,ViewGoup不需要绘制,但是ViewGroup会使用dispatchDraw()来绘制其子View。
七.自定义View
1.自定义View的时候,通常需要重写onDraw()来绘制View要显示的内容,如果还需要支持wrap_content属性,必须重写onMeasure();
2.通过自定义attrs属性,可以设置新的View属性;
3.View中一些重要的回调方法:
1)onFinishInflate():从XML中加载组建后回调;
2)onSizeChanged():组件大小改变时回调;
3)onMeasure():进行测量;
4)onLayout():设置显示的位置;
5)onTouchEvent():触摸事件。
4.实现自定义View的三种常用方法:
1)通过重写onDraw()对原生控件进行扩展;
2)通过组合实现新的控件,通常集成一个合适的额ViewGoup,再通过addView()给它添加指定功能的控件,从而组合成新的复合控件。
3)重写View实现全新的控件,通过重写onDraw(),onMeasure()实现绘制逻辑,重写onTouchEvent()实现交互逻辑。
5.自定义属性
1)自定义属性的方法:在res资源目录的values目录下创建一个attrs.xml的属性定义文件,文件模板:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="customAttr">
<attr name="title" format="string" />
<attr name="fontSize" format="dimension" />
<attr name="fontColor" format="color" />
<attr name="background" format="reference|color" />
<attr name="fontStyle" format="enum" />
<attr name="shadeSupport" format="boolean" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
2)通过TypedArray获取自定义属性集,通过TypedArray.getString()、TypedArray.getColor()等方法获取属性值,模板代码:
package com.jy.myrecyclerview.test; import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View; import com.jy.myrecyclerview.R; /**
* Created by 123 on 2016/5/6.
*/
public class TestCustomAttrs extends View {
private Context mContext;
private AttributeSet mAttrs;
private String mTitle;
private float mFontSize;
private int mFontColor;
private int mBackground;
private int mFontStyle;
private boolean mShadeSupport; public TestCustomAttrs(Context context) {
super(context);
this.mContext = context;
} public TestCustomAttrs(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
this.mContext = context;
this.mAttrs = attrs;
} public TestCustomAttrs(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
this.mContext = context;
this.mAttrs = attrs;
} private void getCustomAttrs() {
TypedArray ta = mContext.obtainStyledAttributes(mAttrs, R.styleable.customAttr);
mTitle = ta.getString(R.styleable.customAttr_title);
mFontSize = ta.getDimension(R.styleable.customAttr_fontSize, 10);
mFontColor = ta.getColor(R.styleable.customAttr_fontColor, 0);
mBackground = ta.getColor(R.styleable.customAttr_background, 0);
mFontStyle = ta.getInt(R.styleable.customAttr_fontStyle, 0);
mShadeSupport = ta.getBoolean(R.styleable.customAttr_shadeSupport, false);
ta.recycle();
}
}
6.定义回调接口,实现自定义控件的灵活控制;
7.引用UI模板
1)自定义控件需要使用命名空间进行引入:xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto",即将自定义控件的命名空间取名为custom
2)在XML文件中使用自定义属性的时候,就可以通过这个命名空间来引用,代码模板如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:custom="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" > <com.jy.myrecyclerview.test.TestCustomAttrs
android:id="@+id/id_recyclerview"
android:divider="#ffff0000"
android:dividerHeight="10dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
custom:title="title"
custom:fontSize="12sp"
custom:fontColor="@color/colorPrimary"
custom:background="@color/colorPrimary"
custom:shadeSupport="false" /> </RelativeLayout>
九.自定义ViewGroup
1.需要重写的方法:
1)onMeasure():对子View进行测量;
2)onLayout():设置子View的位置;
3)onTouchEvent():设置触摸交互事件。
注:本文参阅了徐宜生的《Android群英传》一书。
Android视图控件架构分析之View、ViewGroup的更多相关文章
- Android 控件架构及View、ViewGroup的测量
附录:示例代码地址 控件在Android开发的过程中是必不可少的,无论是我们在使用系统控件还是自定义的控件.下面我们将讲解一下Android的控件架构,以及如何实现自定义控件. 1.Android控件 ...
- 《Android群英传》读书笔记 (2) 第三章 控件架构与自定义控件详解 + 第四章 ListView使用技巧 + 第五章 Scroll分析
第三章 Android控件架构与自定义控件详解 1.Android控件架构下图是UI界面架构图,每个Activity都有一个Window对象,通常是由PhoneWindow类来实现的.PhoneWin ...
- 第二章 控件架构与自定义控件详解 + ListView使用技巧 + Scroll分析
1.Android控件架构下图是UI界面架构图,每个Activity都有一个Window对象,通常是由PhoneWindow类来实现的.PhoneWindow将DecorView作为整个应用窗口的根V ...
- Android群英传笔记——第三章:Android控件架构与自定义控件讲解
Android群英传笔记--第三章:Android控件架构与自定义控件讲解 真的很久没有更新博客了,三四天了吧,搬家干嘛的,心累,事件又很紧,抽时间把第三章大致的看完了,当然,我还是有一点View的基 ...
- Android下拉刷新上拉载入控件,对全部View通用!
转载请声明出处http://blog.csdn.net/zhongkejingwang/article/details/38868463 前面写过一篇关于下拉刷新控件的博客下拉刷新控件终结者:Pull ...
- android中倒计时控件CountDownTimer分析
android中倒计时控件CountDownTimer分析 1 示例代码 new CountDownTimer(10000, 1000) { public void onTick(long milli ...
- android 时间控件概述
android的自带时间选择控件,是一个让用户既能输入的又能选择的样子.这本来没有太大的问题了. 但是,坑爹的android是开源的.自带的时间控件在某些机型上,早已经是面目全非了,在用以一个普通用户 ...
- Android 开源控件与常用开发框架开发工具类
Android的加载动画AVLoadingIndicatorView 项目地址: https://github.com/81813780/AVLoadingIndicatorView 首先,在 bui ...
- Android M 控件:AppBarLayout,CoordinatorLayout,CollapsingToolbarLayout
AppBarLayout AppBarLayout跟它的名字一样,把容器类的组件全部作为AppBar.是继承LinerLayout实现的一个ViewGroup容器组件,它是为了Material Des ...
随机推荐
- 《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(十五)
线程的状态 线程对象在不同的运行时期有不同的状态,状态信息就存在与State枚举类中. 验证New,Runnable,Terminated new:线程实例化后还从未执行start()方法时的状态 r ...
- Java线程安全与多线程开发
互联网上充斥着对Java多线程编程的介绍,每篇文章都从不同的角度介绍并总结了该领域的内容.但大部分文章都没有说明多线程的实现本质,没能让开发者真正“过瘾”. 从Java的线程安全鼻祖内置锁介绍开始,让 ...
- 数据库路由中间件MyCat - 使用篇(4)
此文已由作者张镐薪授权网易云社区发布. 欢迎访问网易云社区,了解更多网易技术产品运营经验. 配置MyCat 3. 配置conf/rule.xml 1.5GA版本中的规则配置比较笨,2.0中优化了一些, ...
- Scrapy:Python的爬虫框架【转摘】
网络爬虫,是在网上进行数据抓取的程序,使用它能够抓取特定网页的HTML数据.虽然我们利用一些库开发一个爬虫程序,但是使用框架可以大大提高效率,缩短开发时间.Scrapy是一个使用Python编写的,轻 ...
- 大话Spark(1)-Spark概述与核心概念
说到Spark就不得不提MapReduce/Hadoop, 当前越来越多的公司已经把大数据计算引擎从MapReduce升级到了Spark. 至于原因当然是MapReduce的一些局限性了, 我们一起先 ...
- Docker环境下的前后端分离项目部署与运维(七)Redis高速缓存
Redis高速缓存 利用内存保存数据,读写速度远超硬盘:可以减少I/O操作,降低I/O压力. 发红包.抢红包的数据可以存在高速缓存中,加快处理速度,不需要经过数据库 淘宝首页一些优惠活动商品等热数据可 ...
- 《机器学习实战》-k近邻算法
目录 K-近邻算法 k-近邻算法概述 解析和导入数据 使用 Python 导入数据 实施 kNN 分类算法 测试分类器 使用 k-近邻算法改进约会网站的配对效果 收集数据 准备数据:使用 Python ...
- SqlConnectionStringBuilder的用法
SqlConnectionStringBuilder提供了一个很好的构建SQL连接字串的方式.不多说,见代码: SqlConnectionStringBuilder builder = new Sql ...
- git push error: ! [rejected] failed to push some refs to . . .
报错情况: 报错原因:远程库与本地库不一致造成的,需要把远程库同步到本地库! 解决办法: git pull --rebase origin master 这条指令是将远程库中的更新合并到本地库,--r ...
- echart option属性
option 图表选项,包含图表实例任何可配置选项: 公共选项 , 组件选项 , 数据选项 名称 描述 {color}backgroundColor 全图默认背景,(详见backgroundColor ...
