cluster KMeans need preprocessing scale????
Out:
n_digits: 10, n_samples 1797, n_features 64
__________________________________________________________________________________
init time inertia homo compl v-meas ARI AMI silhouette
k-means++ 0.30s 69432 0.602 0.650 0.625 0.465 0.598 0.146
random 0.23s 69694 0.669 0.710 0.689 0.553 0.666 0.147
PCA-based 0.04s 70804 0.671 0.698 0.684 0.561 0.668 0.118
__________________________________________________________________________________
print(__doc__) from time import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.preprocessing import scale np.random.seed(42) digits = load_digits()
data = scale(digits.data) n_samples, n_features = data.shape
n_digits = len(np.unique(digits.target))
labels = digits.target sample_size = 300 print("n_digits: %d, \t n_samples %d, \t n_features %d"
% (n_digits, n_samples, n_features)) print(82 * '_')
print('init\t\ttime\tinertia\thomo\tcompl\tv-meas\tARI\tAMI\tsilhouette') def bench_k_means(estimator, name, data):
t0 = time()
estimator.fit(data)
print('%-9s\t%.2fs\t%i\t%.3f\t%.3f\t%.3f\t%.3f\t%.3f\t%.3f'
% (name, (time() - t0), estimator.inertia_,
metrics.homogeneity_score(labels, estimator.labels_),
metrics.completeness_score(labels, estimator.labels_),
metrics.v_measure_score(labels, estimator.labels_),
metrics.adjusted_rand_score(labels, estimator.labels_),
metrics.adjusted_mutual_info_score(labels, estimator.labels_),
metrics.silhouette_score(data, estimator.labels_,
metric='euclidean',
sample_size=sample_size))) bench_k_means(KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=10),
name="k-means++", data=data) bench_k_means(KMeans(init='random', n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=10),
name="random", data=data) # in this case the seeding of the centers is deterministic, hence we run the
# kmeans algorithm only once with n_init=1
pca = PCA(n_components=n_digits).fit(data)
bench_k_means(KMeans(init=pca.components_, n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=1),
name="PCA-based",
data=data)
print(82 * '_') # #############################################################################
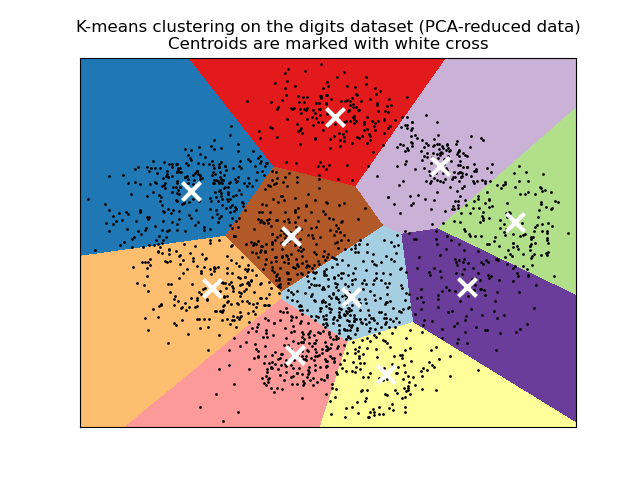
# Visualize the results on PCA-reduced data reduced_data = PCA(n_components=2).fit_transform(data)
kmeans = KMeans(init='k-means++', n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=10)
kmeans.fit(reduced_data) # Step size of the mesh. Decrease to increase the quality of the VQ.
h = .02 # point in the mesh [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max]. # Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
x_min, x_max = reduced_data[:, 0].min() - 1, reduced_data[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = reduced_data[:, 1].min() - 1, reduced_data[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h)) # Obtain labels for each point in mesh. Use last trained model.
Z = kmeans.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) # Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(1)
plt.clf()
plt.imshow(Z, interpolation='nearest',
extent=(xx.min(), xx.max(), yy.min(), yy.max()),
cmap=plt.cm.Paired,
aspect='auto', origin='lower') plt.plot(reduced_data[:, 0], reduced_data[:, 1], 'k.', markersize=2)
# Plot the centroids as a white X
centroids = kmeans.cluster_centers_
plt.scatter(centroids[:, 0], centroids[:, 1],
marker='x', s=169, linewidths=3,
color='w', zorder=10)
plt.title('K-means clustering on the digits dataset (PCA-reduced data)\n'
'Centroids are marked with white cross')
plt.xlim(x_min, x_max)
plt.ylim(y_min, y_max)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.show()
It depends on your data.
If you have attributes with a well-defined meaning. Say, latitude and longitude, then you should not scale your data, because this will cause distortion. (K-means might be a bad choice, too - you need something that can handle lat/lon naturally)
If you have mixed numerical data, where each attribute is something entirely different (say, shoe size and weight), has different units attached (lb, tons, m, kg ...) then these values aren't really comparable anyway; z-standardizing them is a best-practise to give equal weight to them.
If you have binary values, discrete attributes or categorial attributes, stay away from k-means. K-means needs to compute means, and the mean value is not meaningful on this kind of data.
from:https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/89809/is-it-important-to-scale-data-before-clustering
Importance of Feature Scaling
Feature scaling though standardization (or Z-score normalization) can be an important preprocessing step for many machine learning algorithms. Standardization involves rescaling the features such that they have the properties of a standard normal distribution with a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one.
While many algorithms (such as SVM, K-nearest neighbors, and logistic regression) require features to be normalized, intuitively we can think of Principle Component Analysis (PCA) as being a prime example of when normalization is important. In PCA we are interested in the components that maximize the variance. If one component (e.g. human height) varies less than another (e.g. weight) because of their respective scales (meters vs. kilos), PCA might determine that the direction of maximal variance more closely corresponds with the ‘weight’ axis, if those features are not scaled. As a change in height of one meter can be considered much more important than the change in weight of one kilogram, this is clearly incorrect.
To illustrate this, PCA is performed comparing the use of data with StandardScaler applied, to unscaled data. The results are visualized and a clear difference noted. The 1st principal component in the unscaled set can be seen. It can be seen that feature #13 dominates the direction, being a whole two orders of magnitude above the other features. This is contrasted when observing the principal component for the scaled version of the data. In the scaled version, the orders of magnitude are roughly the same across all the features.
The dataset used is the Wine Dataset available at UCI. This dataset has continuous features that are heterogeneous in scale due to differing properties that they measure (i.e alcohol content, and malic acid).
The transformed data is then used to train a naive Bayes classifier, and a clear difference in prediction accuracies is observed wherein the dataset which is scaled before PCA vastly outperforms the unscaled version.
from:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/preprocessing/plot_scaling_importance.html
cluster KMeans need preprocessing scale????的更多相关文章
- 聚类--K均值算法:自主实现与sklearn.cluster.KMeans调用
1.用python实现K均值算法 import numpy as np x = np.random.randint(1,100,20)#产生的20个一到一百的随机整数 y = np.zeros(20) ...
- 第八次作业:聚类--K均值算法:自主实现与sklearn.cluster.KMeans调用
import numpy as np x = np.random.randint(1,100,[20,1]) y = np.zeros(20) k = 3 def initcenter(x,k): r ...
- 【原】KMeans与深度学习模型结合提高聚类效果
这几天在做用户画像,特征是用户的消费商品的消费金额,原始数据(部分)是这样的: id goods_name goods_amount 男士手袋 1882.0 淑女装 2491.0 女士手袋 345.0 ...
- 【原】KMeans与深度学习自编码AutoEncoder结合提高聚类效果
这几天在做用户画像,特征是用户的消费商品的消费金额,原始数据(部分)是这样的: id goods_name goods_amount 男士手袋 1882.0 淑女装 2491.0 女士手袋 345.0 ...
- RFM模型的变形LRFMC模型与K-means算法的有机结合
应用场景: 可以应用在不同行业的客户分类管理上,比如航空公司,传统的RFM模型不再适用,通过RFM模型的变形LRFMC模型实现客户价值分析:基于消费者数据的精细化营销 应用价值: LRFMC模型构建之 ...
- 吴裕雄 数据挖掘与分析案例实战(14)——Kmeans聚类分析
# 导入第三方包import pandas as pdimport numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.cluster im ...
- 131.005 Unsupervised Learning - Cluster | 非监督学习 - 聚类
@(131 - Machine Learning | 机器学习) 零. Goal How Unsupervised Learning fills in that model gap from the ...
- Kmeans应用
1.思路 应用Kmeans聚类时,需要首先确定k值,如果k是未知的,需要先确定簇的数量.其方法可以使用拐点法.轮廓系数法(k>=2).间隔统计量法.若k是已知的,可以直接调用sklearn子模块 ...
- Scikit-Learn模块学习笔记——数据预处理模块preprocessing
preprocessing 模块提供了数据预处理函数和预处理类,预处理类主要是为了方便添加到 pipeline 过程中. 数据标准化 标准化预处理函数: preprocessing.scale(X, ...
随机推荐
- Linux 能PING IP 但不能PING 主机域名的解决方法 vim /etc/nsswitch.conf hosts: files dns wins
Linux 能PING IP 但不能PING 主机域名的解决方法 转载 2013年12月25日 10:24:27 13749 . vi /etc/nsswitch.conf hosts: files ...
- 蒙特卡洛方法计算圆周率的三种实现-MPI openmp pthread
蒙特卡洛方法实现计算圆周率的方法比较简单,其思想是假设我们向一个正方形的标靶上随机投掷飞镖,靶心在正中央,标靶的长和宽都是2 英尺.同时假设有一个圆与标靶内切.圆的半径是1英尺,面积是π平方英尺.如果 ...
- Linux 安装json神器 jq
wget -O jq https://github.com/stedolan/jq/releases/download/jq-1.6/jq-linux64 chmod +x ./jq cp jq /u ...
- 向MapReduce转换:通过部分成绩计算矩阵乘法
代码共分为四部分: <strong><span style="font-size:18px;">/*** * @author YangXin * @info ...
- 《转》PyQt4 精彩实例分析* 实例2 标准对话框的使用
和大多数操作系统一样,Windows及Linux都提供了一系列的标准对话框,如文件选择,字体选择,颜色选择等,这些标准对话框为应用程序提供了一致的观感.Qt对这些标准对话框都定义了相关的类.这些类让使 ...
- 解决Discuz安装时报错“该函数需要 php.ini 中 allow_url_fopen 选项开启…”
开启php的fsockopen函数 —— 解决DZ论坛安装问题“该函数需要 php.ini 中 allow_url_fopen 选项开启.请联系空间商,确定开启了此项功能 在安装dz论坛时遇到因为fs ...
- python爬虫学习研究
目标:做一个小爬虫项目 2017年6月4日13:32:17 mooc网教程Python爬虫入门一之综述要学习Python爬虫,我们要学习的共有以下几点:Python基础知识Python中u ...
- [Java开发之路](8)输入流和输出流
1. Java流的分类 按流向分: 输入流: 能够从当中读入一个字节序列的对象称作输入流. 输出流: 能够向当中写入一个字节序列的对象称作输出流. 这些字节序列的来源地和目的地能够是文件,并且通常都是 ...
- 记录-JQuery日历插件My97DatePicker日期范围限制
对于日期控件,有时会有不能选择今天以前的日期这种需求..... My97DatePicker是一个非常优秀的日历插件,不仅支持多种调用模式,还支持日期范围限制. 常规的调用比较简单,如下所示: 1 & ...
- term frequency–inverse document frequency
term frequency–inverse document frequency
