商业爬虫学习笔记day7-------解析方法之bs4
一.Beautiful Soup
1.简介
Beautiful Soup 是python的一个库,最主要的功能是从网页抓取数据。其特点如下(这三个特点正是bs强大的原因,来自官方手册)
a. Beautiful Soup提供一些简单的、python式的函数用来处理导航、搜索、修改分析树等功能。它是一个工具箱,通过解析文档为用户提供需要抓取的数据,因为简单,所以不需要多少代码就可以写出一个完整的应用程序。
b. Beautiful Soup自动将输入文档转换为Unicode编码,输出文档转换为utf-8编码。你不需要考虑编码方式,除非文档没有指定一个编码方式,这时,Beautiful Soup就不能自动识别编码方式了。然后,你仅仅需要说明一下原始编码方式就可以了。
c. Beautiful Soup已成为和lxml、html6lib一样出色的python解释器,为用户灵活地提供不同的解析策略或强劲的速度。
2.Beautiful Soup支持的解析器
(1)python标准库(默认):python内置标准库,速度适中,文档容错能力强
使用方法:BeautifulSoup(data, “html.parser”)
(2)lxml HTML 解析器:速度快,文档容错能力强
使用方法:BeautifulSoup(data, “lxml”)
(3)lxml XML 解析器:速度快,唯一支持XML的解析器
使用方法:BeautifulSoup(markup, [“lxml”, “xml”]);BeautifulSoup(markup, “xml”)
(4)html5lib解析器:最好的容错性;以浏览器的方式解析文档;生成HTML5格式的文档;速度慢
二 创建soup对象
下面是官方手册上的一个案例
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> """
(1)导入bs4库
from bs4 imort import beautifulSoup
(2) 创建beautifulsoup对象
此处使用python默认的解析器,即html.parser
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc) # 等效于soup = BeautifulSoup(markup, “html.parser”)
这样运行的话会出现提醒,如下:
UserWarning: No parser was explicitly specified, so I'm using the best available HTML parser for this system ("lxml"). This usually isn't a problem, but if you run this code on another system, or in a different virtual environment, it may use a different parser and behave differently
To get rid of this warning, pass the additional argument 'features="lxml"' to the BeautifulSoup constructor.
如上提示,避免出现这种提示的话就自己选择一个解析器,如下
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, “lxml”)
格式化输出,有补全功能
result = soup.prettify()
print(result)
打印下result,格式化输出
<html>
<head>
<title>
The Dormouse's story
</title>
</head>
<body>
。。。。
</body>
</html>
三. 四大对象种类
Beautiful Soup将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是python对象,所有对象可归纳为以下4中:
Tag ;BeautifulSoup; Comment; NavigableString
(1)Tag
Tag是什么?通俗点讲就是HTML中的一个个标签,例如:
<head>
<title>
The Dormouse's story
</title>
</head>
此处的head,title等都是标签,以下为代码运行情况
result = soup.head
print(type(result)) # 打印的结果为 <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
print(result) # 打印的结果为 <head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
result = soup.title
print(type(result)) # 打印的结果为 <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
print(result) # 打印的结果为 <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
Tag的两个重要的属性:name;attr
name
print(soup.name) # 打印结果为 [document]
print(soup.head.name) # 打印结果为 title
soup对象本身比较特殊,它的name即为[document],对于其他内部标签,输出的值便为标签本身的名称,如上诉title
attrs
print(soup.a.attrs) # 打印的结果为 {'href': 'http://example.com/elsie', 'class': ['sister'], 'id': 'link1'}
在这里,我们把a标签的所有属性打印了出来,得到的类型是一个字典
如果我们想要单独获取某个属性,如下(以获取href为例)
print(soup.a['href']) # 打印结果 ['http://example.com/elsie']
print(soup.a.get('href')) # 打印结果 ['http://example.com/elsie']
(2) BeautifulSoup
BeautifulSoup 对象表示的是一个文档的全部内容.大部分时候,可以把它当作 Tag 对象,是一个特殊的 Tag,我们可以分别获取它的类型,名称,以及属性来感受一下
print(type(soup.name)) # <class 'str'>
print(soup.name) # [document]
print(soup.attrs) # {} 空字典
(3) NavigableString
既然我们已经得到了标签的内容,那么问题来了,我们要想获取标签内部的文字怎么办呢?很简单,用 .string 即可,例如
print(soup.a.string) # 打印结果为 Elsie
print(type(soup.a.string)) # 打印结果为 <class 'bs4.element.NavigableString'>,可得其类型
注意:只能获取第一个标签的内容(上面html_doc有多个a标签,但只能获取到第一个标签)
这样我们就轻松获取到了标签里面的内容,想想如果用正则表达式要多麻烦。它的类型是一个 NavigableString,翻译过来叫 可以遍历的字符串
(4) Comment
Comment 对象是一个特殊类型的 NavigableString 对象,其实输出的内容仍然不包括注释符号,但是如果不好好处理它,可能会对我们的文本处理造成意想不到的麻烦。
我们找一个带注释的标签
print(soup.p)
print(soup.p.string)
print(type(soup.p.string))
运行结果为:
<p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p>
哈哈
<class 'bs4.element.Comment'>
p 标签里的内容实际上是注释,但是如果我们利用 .string 来输出它的内容,我们发现它已经把注释符号去掉了,另外由上诉打印结果可知,它是一个Comment类型,所以,我们在使用前最好做一下判断,判断代码如下
if type(soup.p.string)==bs4.element.Comment:
print(soup.p.string)
上面的代码中,我们首先判断了它的类型,是否为 Comment 类型,然后再进行其他操作,如打印输出。
四. 节点选择器
直接调用节点的名称就可以选择节点元素,再调用string属性就可以得到节点内的文本了,这种选择方式速度非常快。如果单个节点层次非常清晰,可以选用这种方式来解析
上例子的html_doc写成的部分文档树如下(body部分只写出了其2个子节点)
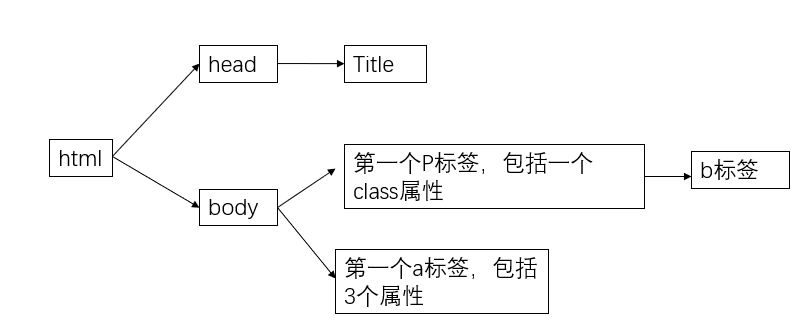
(1)直接子节点(.contents ; .children)
.contents
tag的 .contents属性可以将tag的子节点以列表的方式输出
print(soup.head.contents) # 打印结果为[<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]
输出方式为列表,我们可以用列表索引来获取它的某一个元素
.children
它返回的不是一个list,不过我们可以通过遍历获取所有子节点,我们打印输出.children看一下,可以发现它是一个list生成器
print(soup.head.children) # 结果 <list_iterator object at 0x000001D4E66107B8>
遍历获取里面的内容
for child in soup.body.children:
print(child)
打印结果为
<p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
(2)所有子孙节点(.descendants)
.contents 和 .children属性仅包含tag的直接子节点, .descendants属性可以对所有tag的子孙节点进行递归循环,和children类似(也是生成器),我们需要遍历获取其中的内容
for child in soup.descendants:
print (child)
打印结果如下,可以发现,所有的节点都被打印出来了,先生最外层的 HTML标签,其次从 head 标签一个个剥离,以此类推。
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
</body></html>
<head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> # 剥离html标签
<title>The Dormouse's story</title> # 剥离head标签
The Dormouse's story # 剥离title标签,进而得到内容,其它类似 <body>
<p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
</body> <p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p>
哈哈 <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<b>The Dormouse's story</b>
The Dormouse's story <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>
Elsie
, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
Lacie
and <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
Tillie
;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
(3)节点内容(.string)
直接使用当前节点 . string即可获得该节点的内容,但如果一个tag仅有一个子节点,那么这个tag也可以使用 .string 方法,输出当前子节点的内容
print(soup.head.string) # 打印结果:The Dormouse's story
print(soup.title.string) # 打印结果:The Dormouse's story
如果tag包含了多个子节点(或多个孙节点),tag就无法确定 .string应该获取哪个子节点的内容,.string的输出结果是None
print(soup.html.string) # 打印结果为 None
(4)多个内容(.strings)
上面讲了获取单个节点内容的方法,那么同时获取多个节点内容的方法是什么呢?
.strings,获取多个内容,但是需要遍历,如下:
for string in soup.strings:
print(repr(string)) # repr 返回规范化的字符串
打印结果为
'\n'
"The Dormouse's story"
'\n'
'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n'
'Elsie'
',\n'
'Lacie'
' and\n'
'Tillie'
';\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.'
'\n'
输出的字符串中若包含了很多空格或空行,可用 .stripped_strings 可以去除多余空白内容
for string in soup.stripped_strings:
print(repr(string))
打印结果如下(相比前面就少了空行):
"The Dormouse's story"
"The Dormouse's story"
'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were'
'Elsie'
','
'Lacie'
'and'
'Tillie'
';\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.'
五. 方法选择器
1. find_all( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
获取与给定条件匹配的Tag对象列表,可以指定Tag的名称以及希望Tag具有的任何属性。
六. CSS选择器
参考: https://cuiqingcai.com/1319.html
https://cuiqingcai.com/5548.html
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av42741352
商业爬虫学习笔记day7-------解析方法之bs4的更多相关文章
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day1
day1 一. HTTP 1.介绍: https://www.cnblogs.com/vamei/archive/2013/05/11/3069788.html http://blog.csdn.ne ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day2
1. get传参 (1)url中包含中文报错解决方法 urllib.request.quote("包含中文的url", safe = "string.printtable ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day6
一. 正则解析数据 解析百度新闻中每个新闻的title,url,检查每个新闻的源码可知道,其title和url都位于<a></a>标签中,因为里面参数的具体形式不一样,同一个正 ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day5
一. 发送post请求 import requests url = "" # 发送post请求 data = { } response = requests.post(url, d ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day4
一.获取登录后页面信息的两种方法 1.第一种方法: 人为把有效cookies加到请求头中,代码如下 import urllib.request # 确定url url = "https:// ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day8-------json的使用
一. 简介 JSON,全称为JavaScript Object Notation(JavaScript对象标记),它通过对象和数组的组合来表示数据,是一种轻量级的数据交换格式.它基于 ECMAScri ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day3
一. 付费代理发送请求的两种方式 第一种方式: (1)代理ip,形式如下: money_proxy = {"http":"username:pwd@192.168.12. ...
- Python爬虫beautifulsoup4常用的解析方法总结(新手必看)
今天小编就为大家分享一篇关于Python爬虫beautifulsoup4常用的解析方法总结,小编觉得内容挺不错的,现在分享给大家,具有很好的参考价值,需要的朋友一起跟随小编来看看吧摘要 如何用beau ...
- python网络爬虫学习笔记
python网络爬虫学习笔记 By 钟桓 9月 4 2014 更新日期:9月 4 2014 文章文件夹 1. 介绍: 2. 从简单语句中開始: 3. 传送数据给server 4. HTTP头-描写叙述 ...
随机推荐
- Cnetos 8 DNS解析慢
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u014401141/article/details/105869242/ 修改 /etc/resolv.conf配置文件,最上方加入 optio ...
- oracle 账号解锁 java.sql.SQLException: ORA-28000: the account is locked
日志报错:ORA-28000: the account is locked 1.plsql登录提示用户被锁定 2.sys登录sqlplus登录查看 SQL> select username,ac ...
- Java安全之Thymeleaf SSTI分析
Java安全之Thymeleaf SSTI分析 写在前面 文章首发:https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/254519 最近看了一遍Thymeleaf,借此机会学习一下Th ...
- dotnet 6 使用 CreateSymbolicLink 创建文件夹符号链接
本文告诉大家如何使用 dotnet 6 提供的 Directory.CreateSymbolicLink 和 File.CreateSymbolicLink 方法创建文件夹和文件的符号链接 Direc ...
- MySQL高级篇 | 分析sql性能
在应用的的开发过程中,由于初期数据量小,开发人员写 SQL 语句时更重视功能上的实现,但是当应用系统正式上线后,随着生产数据量的急剧增长,很多 SQL 语句开始逐渐显露出性能问题,对生产的影响也越来越 ...
- silky微服务业务主机简介
目录 主机的概念 通用主机 web主机 业务主机类型 使用web主机构建微服务应用 使用通用主机构建微服务应用 构建具有websocket能力的微服务应用 构建网关 开源地址 在线文档 主机的概念 s ...
- 3组-Alpha冲刺-3/6
一.基本情况 队名:发际线和我作队 组长博客:链接 小组人数:10 二.冲刺概况汇报 黄新成(组长) 过去两天完成了哪些任务 文字描述 使用labelimg工具对采集的数据进行标注,安装alphapo ...
- 菜鸡的Java笔记 - java 正则表达式
正则表达式 RegularExpression 了解正则表达式的好处 正则表达式的基础语法 正则表达式的具体操作 content (内容 ...
- SpringCloud升级之路2020.0.x版-36. 验证断路器正确性
本系列代码地址:https://github.com/JoJoTec/spring-cloud-parent 上一节我们通过单元测试验证了线程隔离的正确性,这一节我们来验证我们断路器的正确性,主要包括 ...
- win10的pycharm中安装ansible模块过程
前面的安装报错信息 ansible模块安装报错:Could not install packages due to an OSError: [Errno 2] No such file or dire ...
