live555库中的testRTSPClient实例
1、testRTSPClient简介
testRTSPClient是个简单的客户端实例,这个实例对rtsp数据交互作了详细的描述,其中涉及到rtsp会话的两个概念Source和Sink.
Source是生产数据,Sink是消费数据.
testRTSPClient非常简洁,除了接收服务端发送过来的数据,什么都没干,所以我们很方便在这个基础上改造,做我们自己的项目.
2、testRTSPClient编译,运行
在linux下编译运行更方便,鉴于我的电脑太渣,虚拟机跑起来费劲,就转到windows下来折腾.
在windows下只需要加载这一个文件就可以编译,我们以mediaServer为服务端,以testRTSPClient为客户端。
当然也可以用支持rtsp协议的摄像机或其他实体设备作为服务端。

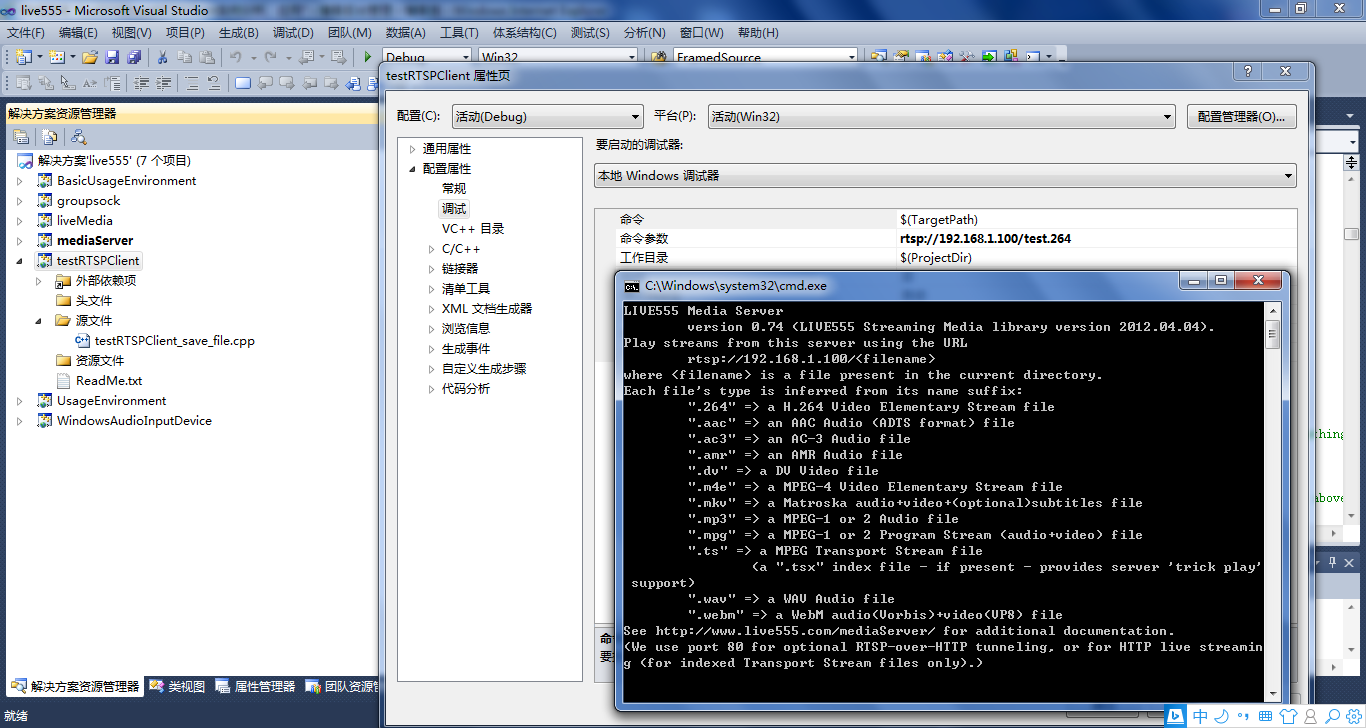
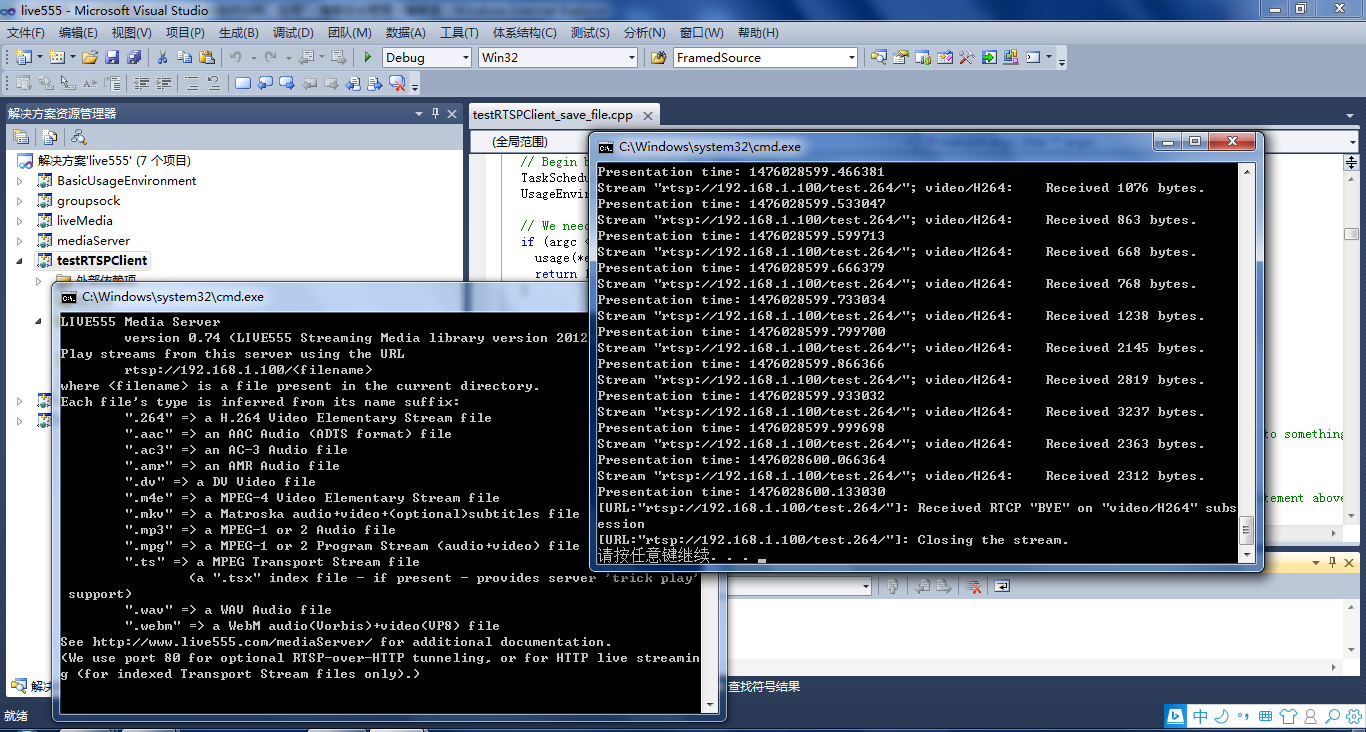
先启动mediaServer,然后在testRTSPClient项目的命令菜单里填入mediaServer 提示的IP, 再启动testRTSPClient即可。
3、testRTSPClient核心代码解读
1)看代码之前可以大致浏览一下总体的框架,这位博主画了个流程图http://blog.csdn.net/smilestone_322/article/details/17297817
void DummySink::afterGettingFrame(unsigned frameSize, unsigned numTruncatedBytes,
struct timeval presentationTime, unsigned /*durationInMicroseconds*/) {
// We've just received a frame of data. (Optionally) print out information about it:
#ifdef DEBUG_PRINT_EACH_RECEIVED_FRAME
if (fStreamId != NULL) envir() << "Stream \"" << fStreamId << "\"; ";
envir() << fSubsession.mediumName() << "/" << fSubsession.codecName() << ":\tReceived " << frameSize << " bytes";
if (numTruncatedBytes > 0) envir() << " (with " << numTruncatedBytes << " bytes truncated)";
char uSecsStr[6+1]; // used to output the 'microseconds' part of the presentation time
sprintf(uSecsStr, "%06u", (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_usec);
envir() << ".\tPresentation time: " << (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_sec << "." << uSecsStr;
if (fSubsession.rtpSource() != NULL && !fSubsession.rtpSource()->hasBeenSynchronizedUsingRTCP()) {
envir() << "!"; // mark the debugging output to indicate that this presentation time is not RTCP-synchronized
}
envir() << "\n";
#endif // Then continue, to request the next frame of data:
continuePlaying();
} Boolean DummySink::continuePlaying() {
if (fSource == NULL) return False; // sanity check (should not happen) // Request the next frame of data from our input source. "afterGettingFrame()" will get called later, when it arrives:
fSource->getNextFrame(fReceiveBuffer, DUMMY_SINK_RECEIVE_BUFFER_SIZE,
afterGettingFrame, this,
onSourceClosure, this);
return True;
}
2)有网友在testRTSPClient基础上,把接收的数据写成h264文件了http://blog.csdn.net/occupy8/article/details/36426821
void DummySink::afterGettingFrame(void* clientData, unsigned frameSize, unsigned numTruncatedBytes,
struct timeval presentationTime, unsigned durationInMicroseconds) {
DummySink* sink = (DummySink*)clientData;
sink->afterGettingFrame(frameSize, numTruncatedBytes, presentationTime, durationInMicroseconds);
} // If you don't want to see debugging output for each received frame, then comment out the following line:
#define DEBUG_PRINT_EACH_RECEIVED_FRAME 1 void DummySink::afterGettingFrame(unsigned frameSize, unsigned numTruncatedBytes,
struct timeval presentationTime, unsigned /*durationInMicroseconds*/) {
// We've just received a frame of data. (Optionally) print out information about it:
#ifdef DEBUG_PRINT_EACH_RECEIVED_FRAME
if (fStreamId != NULL) envir() << "Stream \"" << fStreamId << "\"; ";
envir() << fSubsession.mediumName() << "/" << fSubsession.codecName() << ":\tReceived " << frameSize << " bytes";
if (numTruncatedBytes > 0) envir() << " (with " << numTruncatedBytes << " bytes truncated)";
char uSecsStr[6+1]; // used to output the 'microseconds' part of the presentation time
sprintf(uSecsStr, "%06u", (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_usec);
envir() << ".\tPresentation time: " << (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_sec << "." << uSecsStr;
if (fSubsession.rtpSource() != NULL && !fSubsession.rtpSource()->hasBeenSynchronizedUsingRTCP()) {
envir() << "!"; // mark the debugging output to indicate that this presentation time is not RTCP-synchronized
}
envir() << "\n";
#endif //todo one frame
//save to file
if(!strcmp(fSubsession.mediumName(), "video"))
{
if(firstFrame)
{
unsigned int num;
SPropRecord *sps = parseSPropParameterSets(fSubsession.fmtp_spropparametersets(), num);
// For H.264 video stream, we use a special sink that insert start_codes:
struct timeval tv= {0,0};
unsigned char start_code[4] = {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01};
FILE *fp = fopen("test.264", "a+b");
if(fp)
{
fwrite(start_code, 4, 1, fp);
fwrite(sps[0].sPropBytes, sps[0].sPropLength, 1, fp);
fwrite(start_code, 4, 1, fp);
fwrite(sps[1].sPropBytes, sps[1].sPropLength, 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = NULL;
}
delete [] sps;
firstFrame = False;
} char *pbuf = (char *)fReceiveBuffer;
char head[4] = {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01};
FILE *fp = fopen("test.264", "a+b");
if(fp)
{
fwrite(head, 4, 1, fp);
fwrite(fReceiveBuffer, frameSize, 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = NULL;
}
} // Then continue, to request the next frame of data:
continuePlaying();
} Boolean DummySink::continuePlaying() {
if (fSource == NULL) return False; // sanity check (should not happen) // Request the next frame of data from our input source. "afterGettingFrame()" will get called later, when it arrives:
fSource->getNextFrame(fReceiveBuffer, DUMMY_SINK_RECEIVE_BUFFER_SIZE,
afterGettingFrame, this,
onSourceClosure, this);
return True;
}
testRTSPClient接收的fReceiveBuffer缓存没有起始码,start_code[4] = {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01}; 写成文件或者播放都需要自行加上。
3)testRTSPClient这个实例还支持多路录放,网上搜到有人已经实现了,搬过来.
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-15063109-id-4482932.html
——缺什么补什么
live555库中的testRTSPClient实例的更多相关文章
- RTSP客户端接收存储数据(live555库中的testRTSPClient实例)
1.testRTSPClient简介 testRTSPClient是个简单的客户端实例,这个实例对rtsp数据交互作了详细的描述,其中涉及到rtsp会话的两个概念Source和Sink. Source ...
- live555库中的testH264VideoStreamer实例
1.h264文件的推送 testH264VideoStreamer.cpp文件的开头就定义了 char const* inputFileName = "test.264"; 后面接 ...
- live555库中的openRTSP实例
一.openRTSP编译运行 a)windows下编译运行 还是以mediaServer作为服务端,openRTSP作为客户端 b)Linux下编译运行 转自http://kuafu80.blog.1 ...
- RTSP客户端接收存储数据(live555库中的openRTSP实例)
一.openRTSP编译运行 a)windows下编译运行 还是以mediaServer作为服务端,openRTSP作为客户端 b)Linux下编译运行 转自http://kuafu80.blog.1 ...
- RTSP服务端转发服务(live555库中的testH264VideoStreamer.cpp和testOnDemandRTSPServer.cpp实例)
1.h264文件的推送 testH264VideoStreamer.cpp文件的开头就定义了 char const* inputFileName = "test.264"; 后面接 ...
- 宣布在 Azure 镜像库中正式推出 Windows Server 2012 R2 并降低 Windows Azure 的实例定价
我们今天将宣布两条消息,为使用基础结构服务的客户提供更多选择和成本节约:在镜像库中推出 Windows Server 2012 R2 以及降低 Memory Intensive 计算实例定价. 虚拟机 ...
- NSClassFromString 实例话静态库中的类
Class myClass = NSClassFromString("StaticLibyClassName"); StaticLibyClassName是从静态库中实例化一个Cl ...
- Solr的原理及在项目中的使用实例.
前面已经讲过 如果安装及配置Solr服务器了, 那么现在我们就来正式在代码中使用Solr.1,这里Solr主要是怎么使用的呢? 当我们在前台页面搜索商品名称关键词时, 我们这时是在Solr库中去查找 ...
- linux静态与动态库创建及使用实例
一,gcc基础语法: 基本语法结构:(由以下四部分组成) gcc -o 可执行文件名 依赖文件集(*.c/*.o) 依赖库文件及其头文件集(由-I或-L与-l指明) gcc 依赖文件集(*.c/*.o ...
随机推荐
- Java设计模式(二) 观察者模式
观察者模式: 定义了对象之间的一对多依赖,这样一来,当一个对象改变状态时,他的所有依赖者都会受到通知并自动更新. 1,定义事件源接口 package com.pattern.observer; pub ...
- Maven-eclipse运行maven命令
右击项目,点击Run as,如下图: 即可看到有很多现有的maven命令,点击即可运行,并在控制台可以看到运行信息 如果你想运行的maven命令在这里没有找到,点击Maven build创建新的命令, ...
- HTML文本域属性设置
1.设置文本域的字体 <TEXTAREA STYLE="font-size:9pt;font-family:verdana;color:#333333">输入内容< ...
- java.lang.Exception: No runnable methods
java.lang.Exception: No runnable methods at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.validateInstanc ...
- 【CodeForces 697B】Barnicle
对科学计数法表示的数,输出其10进制的形式. c++来做,需要考虑这些细节: 当b==0,d==0时,只输出a. 当不需要补零的情况有两种: 一种是刚好是整数,只输出a(注意1.0e1的情况是输出1) ...
- linux定时器(crontab)实例
linux实验示例----实现每2分钟将“/etc”下面的文件打包存储到“/usr/lobal”目录下 ·Step1:编辑当前用户的crontab并保存终端输入:>crontab -u root ...
- Python字符串基础一
下一篇:Python 序列通用操作介绍 写在前面 下学期开始上计算机网络的课程,现在已经在看相关书籍,希望结合python写出一个网络爬虫程序.利用学习C++后的空余时间来看看Python并在这里总结 ...
- [bzoj1984]月下“毛景树”
Description 毛毛虫经过及时的变形,最终逃过的一劫,离开了菜妈的菜园.毛毛虫经过千山万水,历尽千辛万苦,最后来到了小小的绍兴一中的校园里.爬啊爬~爬啊爬~~毛毛虫爬到了一颗小小的" ...
- 配置服务器有错/usr/libexec/gconf-sanity-check-2的退出状态为256
问题描述: CentOS启动的时候报如下错误:“配置服务器有错/usr/libexec/gconf-sanity-check-2的退出状态为256” 问题原因: 在装hadoop的时候误删了/tmp文 ...
- 【bzoj1408】 Noi2002—Robot
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1408 (题目链接) 题意 定义了3种数,分别求这3种数的φ的和,其中φ(1)=0. Solution ...
