A beginner’s guide to Cache synchronization strategies--转载
原文地址:http://vladmihalcea.com/2015/04/20/a-beginners-guide-to-cache-synchronization-strategies/
Introduction
A system of record is the authoritative data source when information is scattered among various data providers. When we introduce a caching solution, we automatically duplicate our data. To avoid inconsistent reads and data integrity issues, it’s very important to synchronize the database and the cache (whenever a change occurs into the system).
There are various ways to keep the cache and the underlying database in sync and this article will present some of the most common cache synchronization strategies.
Cache-aside
The application code can manually manage both the database and the cache information. The application logic inspects the cache before hitting the database and it updates the cache after any database modification.
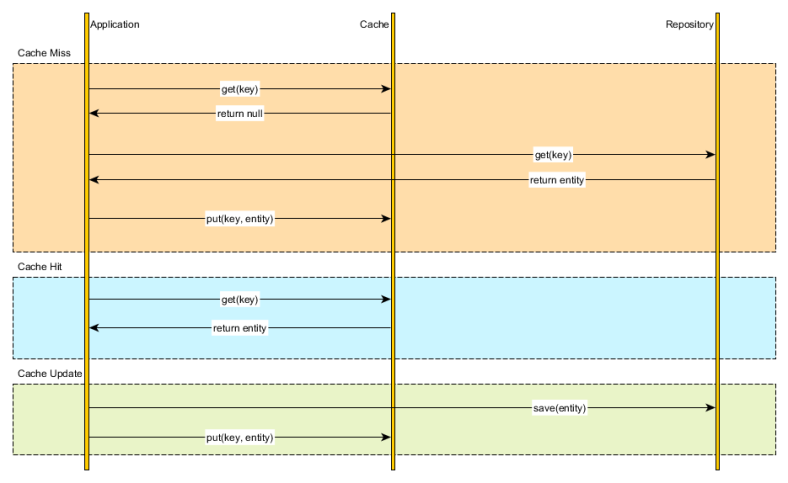
Mixing caching management and application is not very appealing, especially if we have to repeat these steps in every data retrieval method. Leveraging an Aspect-Oriented caching interceptor can mitigate the cache leaking into the application code, but it doesn’t exonerate us from making sure that both the database and the cache are properly synchronized.
Read-through
Instead of managing both the database and the cache, we can simply delegate the database synchronization to the cache provider. All data interactions is therefore done through the cache abstraction layer.
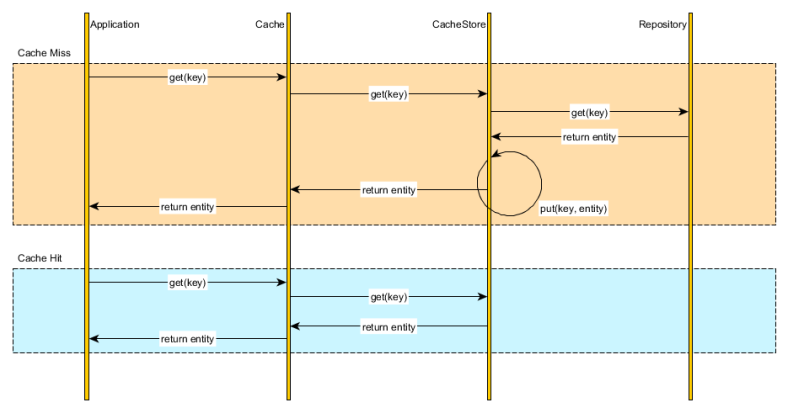
Upon fetching a cache entry, the Cache verifies the cached element availability and loads the underlying resource on our behalf. The application uses the cache as thesystem of record and the cache is able to auto-populate on demand.
Write-through
Analogous to the read-through data fetching strategy, the cache can update the underlying database every time a cache entry is changed.
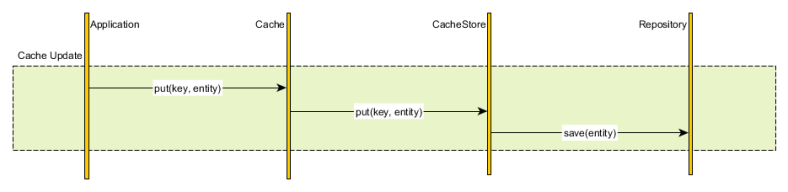
Although the database and the cache are updated synchronously, we have the liberty of choosing the transaction boundaries according to our current business requirements.
- If strong consistency is mandatory and the cache provider offers an XAResource we can then enlist the cache and the database in the same global transaction. The database and the cache are therefore updated in a single atomic unit-of-work
- If consistency can be weaken, we can update the cache and the database sequentially, without using a global transaction. Usually the cache is changed first and if the database update fails, the cache can use a compensating action to roll-back the current transaction changes
Write-behind
If strong consistency is not mandated, we can simply enqueue the cache changes and periodically flush them to the database.
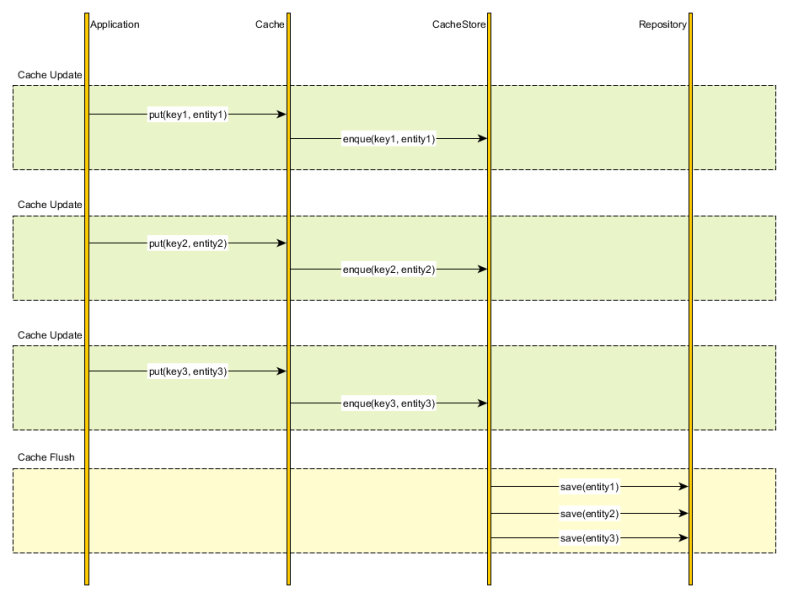
This strategy is employed by the Java PersistenceEntityManager (first-level cache), all entity state transitions being flushed towards the end of the current running transaction (or when a query is issued).
Although it breaks transaction guarantees, the write-behind caching strategy can outperform the write-through policy, because database updates can be batched and the number of DML transactions is also reduced.
A beginner’s guide to Cache synchronization strategies--转载的更多相关文章
- Photography theory: a beginner's guide(telegraph.co.uk)
By Diane Smyth, Tim Clark, Rachel Segal Hamilton and Lewis Bush 11:00AM BST 09 Jun 2014 Have you r ...
- A Beginner's Guide to Paxos
Google Drive: A Beginner's Guide to Paxos The code ideas of Paxos protocol: 1) Optimistic concurrenc ...
- Beginner's Guide to Python-新手指导
Refer English Version: http://wiki.python.org/moin/BeginnersGuide New to programming? Python is free ...
- A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks(转)
A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks Introduction Convolutional neural ...
- (转)A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks Part 2
Adit Deshpande CS Undergrad at UCLA ('19) Blog About A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolution ...
- (转)A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks
Adit Deshpande CS Undergrad at UCLA ('19) Blog About A Beginner's Guide To Understanding Convolution ...
- 新手教程之:循环网络和LSTM指南 (A Beginner’s Guide to Recurrent Networks and LSTMs)
新手教程之:循环网络和LSTM指南 (A Beginner’s Guide to Recurrent Networks and LSTMs) 本文翻译自:http://deeplearning4j.o ...
- A Beginner’s Guide to Eigenvectors, PCA, Covariance and Entropy
A Beginner’s Guide to Eigenvectors, PCA, Covariance and Entropy Content: Linear Transformations Prin ...
- A Beginner’s Guide to the OUTPUT Clause in SQL Server
原文 A Beginner’s Guide to the OUTPUT Clause in SQL Server T-SQL supports the OUTPUT clause after the ...
随机推荐
- DOM笔记(二):Node接口
所有的节点都使用Node接口来表示,可以使用很多方法去获取节点,如document.getElementsByTagName().document.getElementsByName()等均返回一个N ...
- oc_转_构造对象的方法,以及类的继承
一.构造方法 (一)构造方法的调用 完整的创建一个可用的对象:Person *p=[Person new]; New方法的内部会分别调用两个方法来完成2件事情: 1) 使用alloc方法来分配存储空间 ...
- Bmob第三方登录详解
Bmob第三方登录详解 Bmob 第三方登录 简介 本文主要介绍新浪微博,QQ,微信的登录接入以及如何配合BmobSDK中的第三方登录功能实现第三方登录. 在使用之前请先按照快速入门创建好可以调用Bm ...
- openstack 云平台API
aaarticlea/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAABVYAAAKrCAIAAACV8EEMAAAgAElEQVR4nOydeVgUaZ7n/W9299nd7n
- POJ3237-Tree (树链剖分,线段树区间更新+点更新+区间查询)
两个更新操作,一个将第i条路径权值改为w,一个是将a-b之间所有路径权值取反. 一个查询操作,求a-b之间路径中权值最大的边. 很容易想到维护一个最大最小值,取反就是把最大最小取反交换一下. 开始遇到 ...
- CodeForces 455A Boredom (DP)
Boredom 题目链接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/121334#problem/G Description Alex doesn't like b ...
- C++中#include包含头文件带 .h 和不带 .h 的区别
C++中#include包含头文件带 .h 和不带 .h 的区别? 如 #include <iostream> 和 #include <iostream.h> 包含的东西有哪些 ...
- MongoDB 快速入门--中级
索引 ensureIndex 用来创建索引,需要注意的就是一个集合最多也就64个索引 如果没加所有就是表扫表,速度很慢, 当然如果索引的键有多个,就必须考虑顺序 拓展索引 同样的也可以为内嵌文档 建立 ...
- C#中反射的使用(How to use reflect in CSharp)(2)
在上一篇里,我们叨逼了好多如何获取到程序集里的对象,但是对象有了,还不知道怎么调,OK,下面开始干这个对象: 首先,我们对上一篇的对象做了一些修改,以适应多种情况: using System; usi ...
- C# 解压RAR压缩文件
此方法适用于C盘windows文件夹中有WinRAR.exe文件 /// 解压文件(不带密码) RAR压缩程序 返回解压出来的文件数量 /// </summary> /// <par ...
